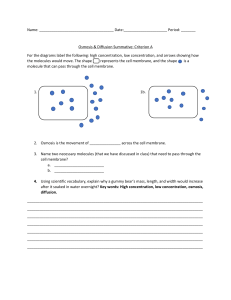
Cell Transport Learning Objectives Explain how passive transport works. Explain how active transport works. Cell Transport Cells are kind of like countries A county has a border that Separates it from other countries Control what goes in and out Cells have a border called the cell membrane It separates it from other cells Controls what goes in and comes out Cell Transport Cells need to maintain homeostasis to live Homeostasis is a state of relatively constant internal physical and chemical conditions Cells maintain homeostasis by moving molecules from one side of the membrane to the other Passive Transport In passive transport, a cell moves materials using diffusion Diffusion is the process by which molecules move from an area of high concentration to low concentration Diffusion does not require the cell to spend energy Passive Transport: Diffusion Solutes Outside Cell Cell Membrane Inside Cell Higher concentration of solute on one side of the membrane than the other Diffusion causes net movement of solute particles from the side of the membrane with the higher solute concentration to the side with the lower solute concentration. At equilibrium, particles move equally in both directions, so there is no net change. Passive Transport: Facilitated Diffusion Not all molecules can move through the cell membrane In facilitated diffusion, proteins help molecules move through the cell membrane No energy needed! Passive Transport: Osmosis aquaporin sugar water cell membrane Passive Transport: Osmosis Osmosis is the facilitated diffusion of water across the cell membrane Sometimes sugar or salt builds up on one side of the cell membrane Instead of moving the sugar or salt, the cell maintains homeostasis by moving water Osmosis Passive Transport: Osmosis In osmosis, water moves from an area of HIGH concentration to an area of LOW concentration Osmosis Vocab Solution: liquid with particles dissolved into it Solutes: particles dissolved in a liquid Passive Transport: Osmosis Osmosis Vocab Continued Isotonic: when the concentration of 2 solutions is the same Hypertonic: when comparing solutions, the solution with the HIGH concentration of solutes Hypotonic: when comparing solutions, the solution with the LOWER concentration of solutes Osmosis in Cells Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic Active Transport Active Transport takes place when a cell uses energy to move material across the cell membrane Two types of active transport Exocytosis Pushes materials out of the cell Uses protein pumps “Exo” means “out” Endocytosis Cell membrane wraps around molecule and pulls it into the cell “Endo” means “in” Active Transport Protein pumps Endocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis