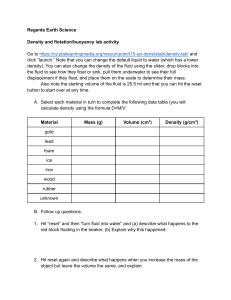
Regents Earth Science Density and flotation/buoyancy lab activity Go to https://ny.pbslearningmedia.org/resource/arct15-sci-densitylab/density-lab/ and click “launch.” Note that you can change the default liquid to water (which has a lower density). You can also change the density of the fluid using the slider, drop blocks into the fluid to see how they float or sink, pull them underwater to see their full displacement if they float, and place them on the scale to determine their mass. Also note the starting volume of the fluid is 25.5 ml and that you can hit the reset button to start over at any time. A. Select each material in turn to complete the following data table (you will calculate density using the formula D=M/V: Material Mass (g) Volume (cm3) Density (g/cm3) gold lead foam ice iron wood rubber unknown B. Follow up questions: 1. Hit “reset” and then “turn fluid into water” and (a) describe what happens to the red block floating in the beaker. (b) Explain why this happened: 2. Hit reset again and describe what happens when you increase the mass of the object but leave the volume the same, and explain: 3. Again, reset, then try the opposite - increase the volume but not the mass and explain what happens and why: 4. Under what conditions could an object's volume decrease while its mass remains the same? Explain. 5. Under what conditions could an object's volume increase while its mass remains the same? Explain. 6. Write a general statement explaining the relationship between an object’s density and its flotation: