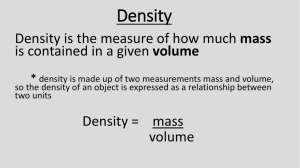Density PP
advertisement

Learning Target: Be able to explain how an object’s density is related to its mass and volume both mathematically (quantitatively) and in words (qualitatively). Learning Outcome: Complete “Density Lab” An object’s density is related to the amount of matter or “stuff” (mass) contained in a corresponding unit of volume. Density is a physical property of matter. It is an Intensive property meaning density of a material does not change depending on the amount measured (see first slide). Density is a ratio (mass/volume) with SI dimensions [kg]/[m3] For our class, we will mostly use units of g/cm3 Substance ρ [kg]/m3 Air 0.0013* Ice 0.917 Water 1.00 (Sometimes used as Reference) Aluminum (Al) 2.70 Iron (Fe) 7.86 Gold (Au) 19.3 *at 0o C and 1 atm Pressure In general, density decreases as a substance moves from solidliquidgas Do you notice any exceptions above? Density is related to buoyancy because objects less dense than another (i.e. water) will float. To calculate a relative density, just divide the substance you are analyzing by a reference: pH2O= 1.00kg/m3 pIce= .917kg/m3 .917/1.00 = .917 If the substance is less than the reference (ratio is < 1) it will float.