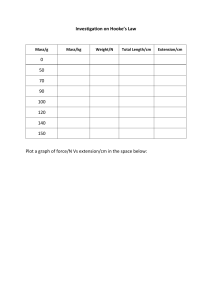
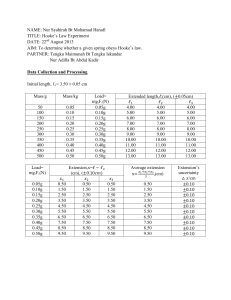
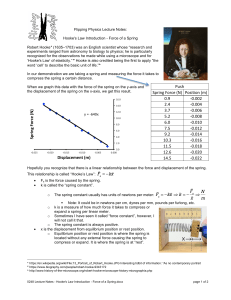
EXPERIMENT 3 HOOKE’S LAW EXPERIMENT REPORT Luvhimbi Nakisani 221788042 Department of Chemical Engineering Bachelor of Engineering technology in Chemical Engineering Engineering Physics 1 221788042@mycput.ac.za Mr S.P Noncolela 1 Aim To investigate Hooke’s law (The relation between force and stretch for a spring) and to determining the spring constant. Theory The force applied to a spring is directly proportional to the extension of the spring: 𝐹 = 𝑘𝑥 Apparatus a. Spring b. Masses c. Ruler Method a. b. c. d. The apparatus was set according to the diagram. A mass was added to the holder and the spring length was recorded. Another mass was added and recorded the new spring length. The difference of the previous spring length and the new length was calculated to calculate the extension(x) of the spring. e. The above procedure was recorded. Results and calculations Mass used (g) 0 Force (N) 0 Spring length 20 Extension (mm) 0 10 0.1 25 5 20 0.2 30 10 30 0.3 35 15 40 0.4 40 20 50 0.5 46 26 2 Force versus Extension Force versus Extension of spring 30 10 25 30 35 40 46 Strength extension 20 25 30 40 15 50 20 5 10 15 20 26 0,1 0,2 0,3 0,4 0,5 10 5 0 -5 k= 0 10 20 30 40 50 Mass 15−10 0.3−0.2 𝑘 = 50 Conclusion The spring extended each time a mass was added. This confirms Hooke’s Law which states that the extension of an elastic object (like a spring) is directly proportional to the force added. The force and extension of spring is directly proportional. 3 60