Human Nutrition Worksheet: Diet, Digestion, and Absorption
advertisement

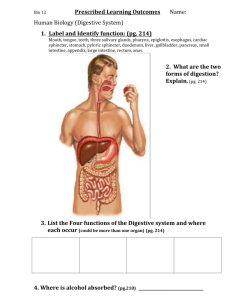
Worksheet for Topic7 human nutrition Name: 7.1 Diet Balanced diet: a diet which contains all groups of nutrients in the correct amounts and proportions. 糖类 营养种类 Nutrient 蛋白质 Seven types of nutrients 脂肪 维生素 矿物质 水 纤维素 Function Specific vitamin and mineral requirements Vitamin/mineral Function Sources Effect of deficiency Vitamin C Vitamin D Calcium Iron Malnutrition (营养不良) is caused by not eating a balanced diet . Malnutrition Types Cause Effects Starvation Coronary heart disease Constipation Obesity Protein Energy Malnutrition Type Marasmus Kwashiorkor Cause 7.2 The alimentary canal (消化道) The Stages of Food Breakdown Ingestion 摄入 Mechanical digestion: Digestion Absorption Assimilation Egestion Chemical digestion: Structure Function 口腔 唾液腺 食道 胃 小肠 大肠 胰腺 肝脏 胆囊 7.3 Teeth and mechanical digestion Mechanical digestion is the breakdown of food into smaller pieces without chemical change to the food molecules Name of teeth Function Dental decay Gum disease(牙龈病) Tooth decay(龋齿,蛀牙) Caused by bacteria Caused by bacteria 1.Bacteria in mouth together with substances 1.If sugar is left in the mouth after from saliva form a sticky film over your teeth eating, bacteria in plaque will feed on it called plaque 2.Plaque is soft and easy to remove at first, however if it hardens and forms tartar, it cannot be removed by brushing 2.They use it in respiration and turn it into Acids 3.Tartar around the edges of teeth and gums can 3.The acids gradually dissolve the enamel allow bacteria to work their way into roots, coating causing gum disease and loss of teeth the dentine of the teeth, working its way into 4.Dentine is softer than enamel and so dissolves more easily and quickly 5. This is tooth decay and if not dealt with, can cause painful infections and loss of teeth Tips for dental health: 1. 2. 3. 7.4 Enzyme and chemical digestion Chemical digestion is to break down large, insoluble molecules (carbohydrates, proteins and lipids) into small, soluble molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream Food Starch Lipid Enzyme Product Pepsin Trypsin Protein Role of bile: 1. It is alkaline (碱性的) to neutralize (中和) the hydrochloric acid which comes from the stomach. 2. It breaks down large drops of fat into smaller ones. This is known as emulsification with area. lipid digestion by (乳化). It helps increasing surface 7.5 Absorption Absorption is the movement of digested food molecules from the digestive system into the blood (glucose and amino acids) and lymph (fatty acids and glycerol). Water is absorbed in both the small intestine happens in the small and the colon, but most absorption of water also intestine Adaptations of small intestine for absorption Adaptation Long Folds of lining villi microvilli Function 7.6 Diarrhoea(腹泻) causes and treatment 1. Bacteria (Vibrio Cholerae 霍乱弧菌) attach to the wall of the small intestine, they produce a toxin (毒素). 2. The toxin stimulates the cells lining the intestine to release chloride into the lumen of the intestine 3. The chloride potential there ions from inside the cells ions accumulate in the lumen of the small intestine and lower the water 4. Once the water potential is lower than that of the cells lining the intestine, water starts to move out of the cells into the intestine (by osmosis) 5. Large quantities of water are lost from the body in watery faeces 6. The blood contains too little chloride ions and water 7. Severe diarrhoea can cause the loss of significant amounts of water causing the tissues and organs to stop working properly 8. Treatment: oral rehydration therapy dissolved) and ions from the body, (drink water with small amount of sugar and ions