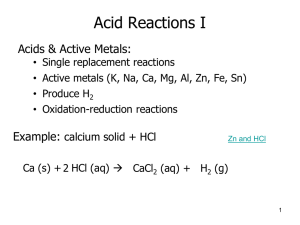
Acid Base Practice Questions 1) Write equations for the dissociation of the following compounds in aqueous solution. Identify the acid base conjugate pairs in each case (use appropriate arrows for strong and weak species) a. CH3COOH + H2O <-> CH3COO- + H3O+ b. CH3NH2 + H2O <-> CH3NH3+ + OH+ c. NH3 + H2O <-> NH4 + OH d. HNO3 + H2O <-> NO3- + H3O+ 2) Define the term amphiprotic. Write appropriate equations to show the amphiprotic nature of water. Can accept or donate a proton + a. NH3 (acting as an acid) + H2O <-> NH4 + OH + b. HNO3 + H2O <-> NO3 + H3O (acting as a base) 3) Calculate the pH of the following solutions a. [H+] = 2.5 x 10-5 mol/L b. [OH-] = 1.8 x 10-4 mol/L c. 0.006 M NaOH 4.6 10.25 11.77 4) Compare the [H+] in solutions with the pH of 3 and 5 (pH 3 has 100x higher [H+]) + 5) Calculate the concentration of H and OH ions in 0.005 M solution of NaOH. a. [OH-] = 0.005 b. [H+] = 2.0 x 10 -12 6) Calculate the pH of a 0.0004 M solution of Ba(OH)2 10.9 7) Describe how you would experimentally distinguish a strong base and a strong acid. a. Test pH b. React with a metal 8) Consider the reaction: 2NH3 + H2SO4 (NH4)2SO4. a. What volume of 2.0 M ammonia is needed to neutralize 50 mL of a 0.5 M sulfuric acid? 25mL b. Is the ammonium sulphate an acidic, basic or a neutral salt? Acidic 9) What are indicators? What factors must be considered when selecting an indicator for a titration? a. Substances that change colour over a specific pH range (called endpoint of indicator) b. The pH at equivalence for titration must fall within the endpoint of indicator 10) Calculate the pH of (pH of a weak acid) a. 0.005 M solution of ethanoic acid b. 0.003 M solution of ammonia 11) Calculate the a. pKa for acetic acid (Ka: 1.76 x 10-5) b. pKb for NH3 (Kb = 1.8 x 10-5) 12) How are Ka, pKa and Kb and pKb related? (Ka = 1.76 x 10-5) (Kb = 1.8 x 10-5) 3.52 10.4 4.75 4.74 (higher Ka, lower pKa) (higher Kb, lower pKb) 13) What are buffers? a. Substances that resist change in pH when small amounts of a strong base/acid is added to them 14) What are the main components of an acidic buffer, a basic buffer? Give examples. a. Acidic buffer: weak acid and a salt containing its conjugate base b. Basic Buffer: weak base and a salt containing its conjugate acid 15) Briefly describe how an acidic buffer works when a. An acid is added to it i. The conjugate base reacts with the added acid. Equilibrium shifts to the left b. A base is added to it i. The acid reacts with the added base. Equilibrium shifts to the right 16) Calculate the pH of a buffer containing 0.005M CH3COOH and 0.0045 M CH3COO-. 4.8 17) Consider the pH curve shown below a) What does a pH or titration curve show? pH of analyte vs Volume of Titrant b) What is the analyte? Titrant? Analyte: unknown, Titrant: Standard c) How can you identify if the analyte is an acid or a base? Weak or strong? By looking at the initial pH of the analyte d) How can you find the pH at equivalence? (mid-point of the vertical line)