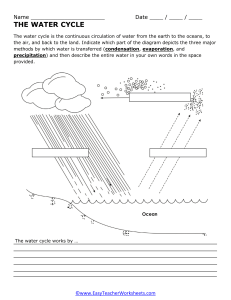
The Water Cycle Diagram: Understanding Earth's Hydrologic Cycle
advertisement

The Water Cycle Sun Atmosphere Volcanic steam Sublimation Condensation Ice, snow, and glaciers Precipitation Precipitation Evapotranspiration Deposition Precipitation Permafrost Evaporation Fog drip Planteopptak Dew Saline lakes Snowmelt runoff Surface runoff Rivers Infiltration Seepage Soil moisture Evaporation Plants and animals Springs Gr ou nd wa ter Wetlands River discharge Freshwater lakes Oceans Plant uptake Ocean currents rec har ge a nd f low U.S. Dept. of the Interior U.S. Geological Survey Howard Perlman, John Evans, USGS https://www.usgs.gov/water-science-school This diagram shows the Earth’s “Natural” water cycle, omitting the significant impacts of human influences. Groundwater storage Vents