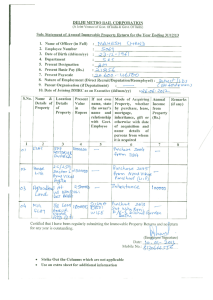
FEATURES ECONOMIC SYSTEMS MARKET ECONOMY COMMAND ECONOMY MIXED ECONOMY Ownership of property : Private ownership Government ownership Private + Public (govt.) ownership Motive or objective: Profit maximization Collective welfare social Allocative mechanism: Price mechanism ( demand and supply) Freedom of choice Rationing mechanism (central planning & quota’s ) No freedom of choice Yes No Private Sector Profit maximsation Public Sector Collective Welfare Private Sector Price mechanism Public sector Rationing mechanism Private Sector yes Public sector no Private Sector yes Public sector no Govt. limit its role to the provision of necessary goods & services & regulate private sector for social welfare.. Private Sector yes Public sector no Private sector High quality Public sector Poor quality usually Private Sector Quick response Public sector Slow response Freedom of choice: (In Production & Consumption) Competition: Role of government: (In allocation of resources i.e.) Variety of goods & services: Quality of goods & services: Response to changes in demand: Consumer sovereignty Efficiency: Producing most desirables goods (allocative efficiency) with least cost methods(productive efficiency) Shortages & surpluses: (Shortage = Demand > Supply) (Surplus = > Supply > Demand) Merit goods: e.g. Healthcare, education etc Public goods: .e.g. street light national defense Demerit goods: e.g. alcohol, drugs, cigarettes etc. Distribution of income & Wealth: Useless duplication of goods & services: Negative externalities: (e.g. Noise , pollution , Congestion, etc) Necessities & luxury goods: Private Monopolies: Existence in real world: Other terms: Minimum role of govt. in economic affairs. Only limited to maintain law & order in the country. All economic & noneconomic affairs are in the hands of govt. Yes No High quality Quick response to changes in consumers preferences. *efficient allocation of resources usually because of existence of profit motive *Sometime inefficient .e.g. private Monopolies. Price mechanism clears markets and there are no shortages & surpluses. Poor quality usually slow or no response. Inefficient allocation of resources because of absence of profit motive. Inefficiency of private sector is minimized by govt. policies. Central planning is unable to guess exact quantities demanded , Shortages & surpluses are present. Private sector No shortages & surpluses Public sector Shortages & surpluses are present. *private sector underprovision *Missing markets of merit goods will be supplied by govt. provision. Underproduction & under consumption. non-marketable and therefore missing Socially optimum overproduction & over consumption. Less or no demerit goods unequal distribution Even distribution Yes provides public goods from central finance. No More than socially optimum level Less necessities & more luxury goods Socially optimum develop and exploit consumers by setting high prices No private monopolies are there in command economy. No pure market economy No pure command economy Free economy, Capitalism, free market economy, laissez faire. Communism, socialism, planned economy, centrally planned economy. more necessities & less luxury goods Public sector provides public goods. govt. discourage consumption & production will be by high taxation and legal actions. Progressive taxation and welfare payments to poor will reduce the disparity between rich & poor. may be in private sector but not in public sector. Govt. will regulate the emissions of negative externalities by taxes and legal actions Public sector will provide necessities to even those who can’t pay. Govt. regulates private monopolies and protects consumer’s from exploitation. All economies are mixed but proportion of private & public sector vary from country to country.