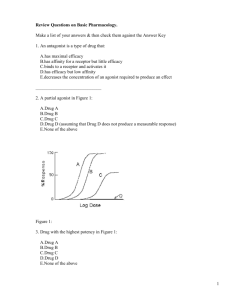
Functional Protein receptors: Fluoxetine on serotonin tpt Penicillin on transpeptidase in bacterial cell wall synthesis Antacids Al/Mg hydroxide Nucleic acid receptors: Actinomycin D on DNA Streptomycin on RNA Bulk laxatives agar/methyl cellulose Osmotic diuretics mannitol D binds R Receptor theory Not all drugs need receptors Receptor: any component of a biological system that interacts with a drug, leading to the drug effect Agonist Interacts w/ receptor elicits direct response Antagonist interacts with receptor no direct response affinity (Kd) Principles of Drug Action DR complex efficacy chemical antagonism potency (EC50) dose required to procduce a given degree of response slide 13, 14, 15 efficacy affinity measure of biological effectiveness of DR complex P(drug molecule interacts with its receptor to form DR complex) lower EC50 = higher potency slide 12 slide 10 Effector (activated by DR complex) Response = elicited because receptor occupied - more DR complex, more response chemical antagonism (drug level) physiological antagonism pharmacological antagonism (receptor level) antagonist binds to R, prevents active drug from binding -C or NC antagonism no pharmacological efficacy but may have clinical efficacy (therapeutic)