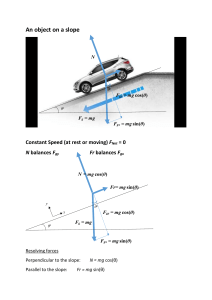
Lesson 3 Forces in Two Dimensions Focus Question How can you analyze forces on a train as it climbs a hill? New Vocabulary equilibrant Review Vocabulary equilibrium: the condition in which the net force on an object is zero. Equilibrium Revisited • Recall that when the net force on an object is zero, the object is in equilibrium. • Three forces are acting on a ring and the individual vectors are shown below. • The sum of these forces is zero, and the object is in equilibrium. Equilibrium Revisited • A force that puts an object in equilibrium is called an equilibrant. • To find the equilibrant, first find the resultant of the forces being exerted on the object. • The equilibrant has the same magnitude as the resultant force, but it is in the opposite direction. Inclined Planes • To determine net force when motion is not horizontal or vertical, choose your coordinate system carefully. • In the example below, the girl’s acceleration is parallel to the incline, and therefore one axis — the x-axis — should be in that direction. Inclined Planes Use with Example Problem 5. Problem Jeff, who weighs 640.0 N, sits on the slope of a hill that descends at an angle of 35.0° from horizontal. What are the components of his weight parallel and perpendicular to the surface of the hill? Response KNOWN Fg = 640.0 N θ = 35.0° UNKNOWN +y +x 35.0° Fgy Fgx Fg Fgx = ? Fgy = ? SOLVE FOR THE UNKNOWN • Use trigonometry to find the components of weight. SKETCH AND ANALYZE THE PROBLEM Fgx 640.0 Nsin 35.0 367 N • Choose axes such that +y is downward Fgy 640.0 Ncos 35.0 524 N and normal to the slope, and +x is down the slope. • Draw a vector diagram and indicate the EVALUATE THE ANSWER • Force is in newtons, so the units are correct. components of Fg. • The components of Fg are smaller than Fg itself, as • List the knowns and unknowns. expected. Ff KNOWN Inclined Planes μ = 0.18 θ = 30.0° Use with Example Problem 6. UNKNOWN Problem ax = ? FN Fgy Fg Fgx 30.0° A child slides from rest at the top of a playground slide. If the slide is inclined SOLVE FOR THE UNKNOWN at 30.0° and the coefficient of kinetic • Use Newton’s second law to write equations for motion in friction between the slide and the child’s the x- and y-directions. pants is 0.18, what is the child’s max Fgx Ff may Fgy FN 0 acceleration? max mg sin FN FN Fgy mg cos Response • Combine the two equations and solve for the acceleration. SKETCH AND ANALYZE THE PROBLEM • Choose axes such that +y is upward ax g sin μg cos and normal to the slope, and +x is 9.8 N/kgsin 30.0 0.189.8 N/kgcos 30.0 down the slope. • Draw a vector diagram and indicate 3.4 m/s2 the components of Fg. EVALUATE THE ANSWER • List the knowns and unknowns. • Force is in newtons, so the units are correct. • The acceleration is less than g, which was expected. Quiz 1. When an object is at equilibrium, which is always true? A The object is not moving. B The object is accelerating at a constant rate. C The net force on the object is zero. D The object is oscillating. CORRECT Quiz 2. Which is the term for a force that puts an object in equilibrium? A normal force C equilibrant CORRECT B static friction force D resultant force Quiz 3. The equilibrant force has ______ magnitude compared to the resultant force, and it is in the _______ direction. A a greater / same B the same / opposite C the same / same D a smaller / opposite CORRECT