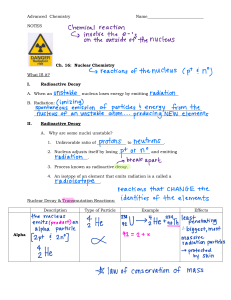
CHAPTER 8: RADIOACTIVITY TEACHER MARNI BINTI YUSUF SMK SULTAN BADLISHAH 8.1 – DISCOVERY OF RADIOACTIVITY History of radioactivity In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X-ray. In 1896, discovered Radioactivity. Found rays emitted from the nucleus of uranium can blacken a photographic plate even in the dark. In the end of 1897, Successfully detected radioactive beams through ionization power rather than through photographic effects. By April 1902, Successfully extracted 2 radioactive elements from uranium ore namely polonium and radium. In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered X-ray. Marie dan Pierre Curie In the end of 1897, Successfully detected radioactive beams through ionization power rather than through photographic effects. By April 1902, Successfully extracted 2 radioactive elements from uranium ore namely polonium and radium. Polonium Antoine Henri Becquerel, In 1896, discovered Radioactivity. Found rays emitted from the nucleus of uranium can blacken a photographic plate even in the dark. Radioactive Substances Radioactivity: is a random and spontaneous decay process of an unstable nucleus by emitting radioactive radiation Radioactive Decay Radioactive decay is a process where an unstable nucleus emits radioactive radiation until the nucleus become more stable. Radioactive decay is a random and spontaneous process without being affect by physical factor such as pressure, temperature, chemical changes and force. Radioactive Decay Unstable nucleus for 1 radioisotope Atom New Nucleus that is more smaller and stable Gamma Ray Alpha Particles/ Radiation (ά) Positive charged Same as Helium nucleus Negative charged No charge/ neutral Same as electron electromagnetic waves + energy A-nombor jisim/RAM Z-Atomic Number + Energy + energy + energy PRACTICE : + energy + energy + energy + energy A-nombor jisim/RAM Z-Atomic Number + energy + energy PRACTICE : + energy + energy A-nombor jisim/RAM Z-Atomic Number PRACTICE : Decay of cobalt -60* Decay of Radon - 222 Radon gas decays into solid polonium through emitting an alpha particle Units of radioactivity Units of radioactivity Curie (Ci) rate of unstable nuclei decay 1 Ci = 3.7 X 1010 decay/s Becquerel (Bq) 1 decay per second 1 Bq = 1 decay/s Relationship between Becquerel and Curie 1 Ci = 37000000000 Bq 1 Bq = 2.7027027027027 x 10-11 Ci Example: convert 15 Bq to Ci: 15 Bq = 15 × 2.7027027027027 x 10-11 Ci = 4.054054054054 x 10-10 Ci Half-life of Radioactive Decay • Half-life T½, is the time taken for the number of undecayed nuclei to be reduced to half of its original number (value). Masa yang diambil untuk suatu bahan radioisotop mereput menjadi separuh daripada jisim asalnya disebut setengah hayat (half-live). Half-life of Radioactive Decay For safety, the half life for radioactive substances must be short. Decay Curve Half-life of Radioactive Decay Nuclei decay of radioactive element with half-life of 5 days Example 1 Example 2 Example 3 Formative Practice 8.1 Summative Practice 8 Page 252 (No 1 & 4) Summative Practice 8 Page 252 (No 1 & 4) Module 155-156 Module 155-156