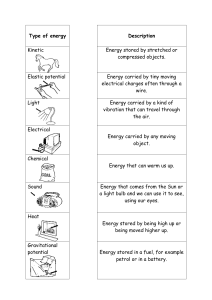
ENERGY & POWER CHAPTER 7 WORK, ENERGY & POWER Work, W is defined as the product of force, F and displacement, s in the direction of the force that is W=Fs The S.I unit for work is Joule SEVERAL ACTIVITIES IN THE DAILY LIFE CALCULATING WORK DONE ENERGY & POWER Energy is defined as the ability to do work. The S.I unit for energy is Joule When a force of 1N is used to move an object over a distance of 1m in the direction of force, 1J of energy is used Power, P is defined as the rate of doing work, W The S.I unit for power is watt, W When 1 Joule of work is done in 1 second(s), power of 1 watt(W) is used that is 1W= 1 Js-1 EXAMPLE OF CALCULATION OF POWER IN DAILY LIFE EXERCISE POTENTIAL ENERGY & KINETIC ENERGY GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY Gravitational potential energy is the work done to lift an object to a height, h from the earth’s surface RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN WORK AND GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY Elastic potential energy is the work done to compress or stretch an elastic material over a displacement of x from the position of equilibrium RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN WORK AND ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY A spring is stretched x m with a force of F N, so the value of force acting of the spring changes from 0 to F N KINETIC ENERGY Kinetic Energy is the energy possessed by a moving object PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY The Principle of Conservation of Energy state that energy cannot be created or destroyed but only be converted form one form to another form OSCILLATING SYSTEM OBEY THE PRINCIPLE OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY TRANSFORMATION OF KINETIC ENERGY & POTENTIAL ENERGY IN A CLOSED SYSTEM In a closed system, the Transformation of kinetic Energy & Potential Energy obey the Principle of Conservation Energy Total potential energy & kinetic energy is constant EXERCISE