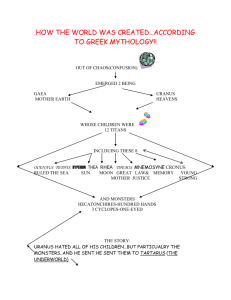
Introduction to Greek Mythology Mythology: The study of “Myths”—and myths are stories about supernatural beings in early times, which were handed down orally from one generation to another Myths attempt to explain such things as: Nature- Where did Earth come from? Heavens? Seasons? Geography? Man- Where did we come from? Gods- Where do the gods come from? The Greeks and Romans believed in polytheism… Poly=many Theism=God Polytheism=many gods Why do we study Greek Mythology? Interesting and Entertaining Shows how ancient people viewed the world and gives us an account of their history It is constantly referenced to in everyday life Some references you may have seen… The creation of the world (according to Greek Mythology) First there was Chaos Out of Chaos emerged two beings: Gaea (Mother Earth) and Uranus (Heavens) Gaea and Uranus had several children Titans Monsters Oceanus and Tethys 3 of each: Hyperion and Thea Coeus and Phoebe Hecatonchires (hundred hands Cronus and Rhea Mnemosyne Themis Crius Lapetus Cyclopes (one-eyed) Uranus hated all his children but especially the monsters… Locked the monsters in Tartarus Gaea was upset and asked the Titans to help Cronus, the youngest and strongest, overthrew is father, Uranus, and seized the rule of the Universe. Cronus took Rhea for a wife and divided the Earth among his fellow Titans Cronus and Rhea had 6 children: The Olympians Cronus feared that his children would overthrow him the way he overthrew his father… Cronus swallowed all of his children…except the last one. Rhea replaced the infant with a stone to prevent Cronus from swallowing Zeus. He grew up in hiding (Crete) When Zeus was grown he made his dad regurgitate his siblings Zeus and his siblings raged war against their father, Cronus Titanomochy , or War of the Titans Cronus VS Zeus Titans His siblings Mount Othrys Hecatonchires & Cyclopes Mount Olympus Zeus, with the use of his lightning bolt given to him by the Cyclopes, defeated Cronus and his army. Most of the Titans were confined to Tartarus. Zeus divided the world among his sibling gods… Zeus is the king of the gods, the ruler of Mount Olympus and the god of the sky and thunder. His symbols are the thunderbolt, eagle, bull, and oak. His siblings: Posiedon, Hades, Hestia, Demeter, and Hera Had many affairs and many offspring Hera Wife and older sister to Zeus Queen of Olympians Goddess of childbirth and marriage Symbols: pomegranate She took many forms, among them that of a bird. Vindictive, jealous of Zeus’s affairs Poseidon God of the sea, horses, and earthquakes One of the supreme Gods of Mount Olympus, but he spent most of his time in his watery domain. Symbols: Trident, dolphins, horses Hestia Goddess of Hearth and Home Honored at meal times She was thought of as the kindest and mildest of the kindest and mildest of the goddesses. She represented personal and communal security and happiness. Demeter Goddess of Agriculture Often shown carrying a bundle of grain Symbols: wheat, poppies, cornucopia Aphrodite Goddess of love, QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. beauty and fertility One legend states that she is the daughter of Zeus and Dione. Another legend says that she was born from seafoam She is associated with the dove Athena Goddess of wisdom and war She was the patron QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. goddess of Athens Her symbol is the owl She is the favorite daughter of Zeus Protector of the city Hades God of the underworld “King of the Dead” Symbols: Cerberus, Bident, and Cypress The Hero Many mythological stories feature Heroes Heroes have specific traits: Unusual circumstance of birth; danger or royalty Leaves family or land and lives with others An event leads to an adventure or quest Hero has special weapon only he can wield Hero has supernatural help The hero must prove himself many times while on the adventure Hero experiences atonement with his father Some heroes you may know… An Epic Poem A long narrative poem originally told (and later written) in a dignified style and presenting characters of high position engaged in a series of adventures (episodes) that are important to the history of a nation or race. Characteristics of the Epic: 1. The hero is a figure of imposing stature, of 2. 3. 4. 5. national importance, and of great historical or legendary significance The setting is vast in scope The action consists of deeds of great valor or requiring superhuman courage Supernatural forces interests themselves in the action The epic poet recounts the deeds of the heroes with objectivity Example of an epic poem: