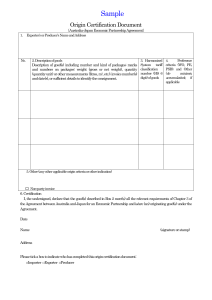
Practice MCQ-International Logistics MCQ on Letter of credit 1. Advance remittance from importer can be accepted by an exporter in India provided A. the advance does not carry interest payment. B. shipment will be made only after one year from the date of receipt of advance. C. advance does not exceed 25% of export value. D. rate of interest, if payable, does not exceed Libor plus 1%. ANSWER: D 2. A bank may refuse to accept an export bill for collection A. when the customer has sufficient limits under bill discounting facility. B. when the documents have discrepancies when compared to letter of credit requirements. C. when the documents are received from a non customer D. when the documents are received from a customer. ANSWER: C 3. If the importer refuses to accept the bill drawn on him the exporter A. should reimport the goods. B. must find an alternate buyer. C. may reimport or sell to an alternate buyer depending upon commercial expediency D. sue the importer. ANSWER: C 4. If export cargo is lost in transit, the exporter should A. claim under marine insurance. B. claim with ECGC C. seek write off of post-shipment credit. D. seek refund of customs duty. ANSWER: A 5. The red clause letter of credit is also known as A. Standby credit B. Anticipatory credit C. Automatic credit D. Back to Back credit ANSWER: B 6. The method of payment where the exporter relies on the undertaking of a bank to pay is. A. bank guarantee B. letter of credit. C. letter of comfort. D. none of the above. ANSWER: B 7. Letter of credit transactions are generally governed by the provisions of A. Uniform customs and Procedures for Documentary Credits. B. United Conference on Practices for Documentary Credits. C. Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits D. Uniform Code and Procedure for Documentary Credits. ANSWER: C 8. The beneficiary under a letter of credit is A. the bank opening the credit. B. the customer of the opening bank. C. the confirming bank. D. the exporter. ANSWER: D 9. A letter of credit is opened on behalf of A. exporter customers. B. importer customers. C. any party wishing to make payment abroad D. none of the above. ANSWER: B 10. A letter of credit is addressed to A. the beneficiary. B. the negotiating bank. C. the reimbursing bank. D. none. ANSWER: A 11. A letter of credit that provides for granting of pre-shipment finance as well as storage of goods in the name of the bank is A. a red clause letter of credit B. a standby letter of credit. C. a green clause letter of credit. D. a secured letter of credit. ANSWER: C 12. When a letter of credit does not indicate whether it is revocable or irrevocable, it is treated as A. revocable B. irrevocable C. revocable or irrevocable at the option of the beneficiary. D. revocable or irrevocable at the option of the negotiating bank. ANSWER: B 13. Payment for bills drawn under letter of credit should be made by the negotiating bank A. after the documents are approved by the issuing bank. B. immediately or on a future date depending upon the terms of credit. C. only in foreign currency. D. immediately in all cases. ANSWER: B 14. Under an acceptance letter of credit, the responsibility of the issuing bank is A. only to accept the bill B. to pay against the bill C. to accept the immediately and also to pay the amount of the bill on its due date. D. to get the acceptance of the importer on the bill. ANSWER: C 15. A confirmed letter of credit is one A. confirmed to be authentic B. confirmed by the importer to be correct. C. confirmed by the exporter that he agrees to the conditions. D. confirmed by a bank (other than the opening bank) in the exporter's country. ANSWER: D 16. Under the confirmed letter of credit the undertaking the confirming bank is A. in addition to that of the opening bank. B. in substitution of the undertaking of the opening bank. C. subject to government policies to the exporter country. D. none of the above. ANSWER: A 19. A credit which provides for reinstatement of the amount as and when bills are drawn under it is called A. reinstatement credit B. reimbursement credit C. revolving credit. D. back-to-back credit. ANSWER: C 1. Which of the following is not a basic objective of documentation in foreign trade? A. to assure that the exporter will receive the payment B. to assure that the importer will receive the goods C. to eliminate risk of non-completion D. to reduce foreign exchange risk E. none of the above 2. Which of the following is not an important document in foreign trade? A. a check for the value of goods B. a draft C. bill of lading D. a letter of credit E. none of the above 3. ______ risk is the potential exchange loss from outstanding obligations as a result of exchange-rate fluctuations. A. Trade B. Exchange C. Finance D. Noncompletion E. Transaction 4. Foreign exchange risk can be reduced by using _____. A. forward contracts B. futures contracts C. currency options D. currency denomination E. all of the above 5. Which of the following is not a condition for drafts to be negotiable? A. must be in writing, signed by the drawer B. must contain a promise to pay a certain sum if goods are received C. must contain an order to pay D. must be payable on sight or at a specified date E. must be made out to order or bearer 6. If a draft is made to bearer, payment should be made to _____. A. a bank B. drawer C. acceptor D. anyone who presents the draft E. all of the above 7. If a draft is accepted by a bank, it becomes a _____. A. valid draft B. demand draft C. usance draft D. banker's acceptance E. drawee's acceptance 8. Forms of countertrade include the following except ___. A. simple barter B. clearing arrangement C. switch trade D. counterpurchase E. mutual agreement 9. Documentary drafts require various shipping documents such as ____. A. bills of lading B. insurance certificates C. commercial invoices D. A and B E. A, B, and C 10. When IBM ships products to its subsidiary in Argentina, it will most likely use a ____ draft. A. sight B. clean C. D/P D. demand E. all of the above 11. If a carrier is instructed to deliver goods to an importer, a _____ bill of lading is used. A. straight B. order C. documentary D. on-board E. clean 12. A (n) _____ bill of lading does not guarantee that the goods have been loaded on the vessel. A. on-board B. foul C. received-for-shipment D. straight E. order 13. Which of the following is not true of a letter of credit? A. it is a document B. issued by a bank C. at the request of the exporter D. the bank agrees to honor a draft drawn on the importer E. payable in the designated currency 14. If a letter of credit can be neither cancelled nor modified without the consent of all parties, it is known as _____. A. revolving B. irrevocable C. revocable D. unconfirmed E. unclean 15. If an exporter is doubtful about an issuing bank's ability to pay, he will expect a domestic bank to join the transaction in a _____ letter of credit. A. revolving B. irrevocable C. revocable D. unconfirmed E. confirmed 16. Which of the following may be required as additional documents in a letter of credit? A. commercial invoice B. insurance document C. consular invoice D. certificate of origin E. all of the above 17. Which of the following documents should necessarily accompany a draft? A. certificate of origin B. weight list C. packing list D. inspection certificate E. none of the above 18. A commercial invoice is issued by _____. A. exporter B. exporter's bank C. importer D. importer's bank E. confirming bank 19. A document that contains a precise description of the goods is known as a _____. A. weight list B. packing list C. commercial invoice D. certificate of origin E. consular invoice 20. Which of the following is not true of a consular invoice? A. provides customs officials with all information B. facilitates easy customs clearance C. helps customs officials assess duties D. issued by the consulate of the exporting country E. it is not a title to the goods 21. Which of the following is not a form of offset agreements? A. coproduction B. licensed production C. subcontractor production D. cash in advance E. technology transfer 22. Which of the following is not a form of countertrade? A. barter B. consignment C. switch trading D. counter purchase E. compensation agreement 23. In a _____ countertrade the initial seller receives compensation in products that arise out of the original sale. A. consignment B. barter C. counterpurchase D. buy-back agreement E. switch trading 24. Buying a company's accounts receivable on a nonrecourse basis is known as _____. A. switch trading B. financing C. factoring D. funding E. free trade 25. Which of the following is not necessarily a party to a forfaiting transaction? A. exporter B. importer C. broker D. bank E. forfeiter 26. Below are five steps involved in a typical trade transaction. Which step is out of order? A. exporter agrees to ship under a letter of credit B. exporter ships the product to the importer C. importer’s bank issues the letter of credit D. exporter prepares a 60-day draft on importer in accordance with the letter of credit. E. the draft is accepted by the importer’s bank becoming a bankers’ acceptance. 27. The “three C’s” of international commerce are: A. customers B. commitment C. currency D. cultural sensitivity E. A, B, and D 28. When exporting some common pitfalls include: A. failure to use an export management company B. failure to print service, sales, and warranty messages in local languages C. chasing orders around the world instead of establishing a basis for profitable operations and orderly growth D. failure to consider licensing or joint venture agreements E. all of the above Answers 1. E 2. A 3. E 4. E 5. B 6. D 7. D 8. E 9. E 10. B 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. B 15. E 16. E 17. E 18. A 19. C 20. D 21. D 22. B 23. D 24. C 25. C 26. C 27. E 28. E 1. INCO Term commonly applied internationally does not include the following terms for type of contract a. F .O.B. b. C & F c. I.C.C. d. C.I.F 2. A document authorized by the buyer for the seller to draw on buyer’s bank, the amount stated on completion of conditions as stated in letter of credit: a. Bill of Lading b. Bill of exchange c. Export Invoice d. Marine Cargo Insurance Policy 3. In case any accident occurs, the cause in known as a. Risk b. Peril c. Damage d. None of the above 4. In Marine Insurance Policy Insurable interest must exist at the time of a. Taking policy b. At the time of claim c. Both at time of Policy & claim d. May not have insurable interest 5. Ordinary Leakage as per ICC means a. Leakage from accident Tin b. Evaporation of Liquids in atmosphere c. Leakage from defective Tin d. None of the above 6. Which of the following statements is true? Statement A: Insurer pays Rs.9,000 for total loss of a case of textiles during transit insured for Rs.10,000 but having a C.I.F. value of Rs.9,000 only. Statement B: Insurer pays Rs.2,000 in respect of a cargo insurance claim of Rs.2,000 under a marine cargo policy subject to a franchise of Rs.1,000. a. Only Statement A b. Only Statement B c. Both the Statements d. Neither of the Statements 7. Which of the following risks covered under Institute Cargo Clauses (B) are not covered under Institute Cargo Clauses (C) Statement A: Discharge of cargo at port of distress Statement B: Earthquake, volcanic eruption, lightning. a. Statement A only b. Statement B only c. Both statements d. Neither of the Statements 8. Under Institute Cargo Clauses (Air), insurance terminates on expiry of ———days after unloading of cargo from aircraft at final place of discharge. a. 60 days b. 30 days c. 7 days d. 14 days 9. Which of the following statements is true? Statement A: Cargo policy is assigned by blank endorsement, that is, mere signature of policyholder without specifying the assignee. Notice to insurer is not necessary. Statement B: Hull policies include a clause requiring that assignment shall be by specific endorsement. a. Statement A only b. Statement B only c. Both the Statements d. Neither of the Statements 10 . Which of the following statements is true under an F.O.B. contract of sale? Statement A: Seller is responsible till goods are placed on board the carrying vessel. Statement B: Buyer’s responsibility attaches once the goods are placed on board the vessel. a. Only Statement A b. Only Statement B c. Both the Statements d. Neither of the Statements ANSWER TO OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS 1. c, 2. b, 3. b, 4. b, 5. b, 6. c, 7. b, 8. a, 9. c, 10.c Incoterms MCQ 1. Incoterms cover A. trade in intangibles B. ownership and transfer rights C. contracts of carriage. D. rights and obligations of parties to contract of sales ANSWER: D 2. The incoterm providing least responsibility to seller is A. EXW. B. DDP. C. FOB D. CIF. ANSWER: A 3. The group of incoterms under which the seller's responsibility is to obtain freight paid transport Document for the main carriage is A. E terms B. C terms. C. D terms D. F terms. ANSWER: B 4. Incoterm is specific about the responsibility for marine insurance in case of A. FOB and EXW B. FOB and CIF. C. CIF and CIP. D. CPT and DDP. ANSWER: C 5. The group of terms arranged in order of increasing responsibility of exporter is. A. C,D,E and F terms. B. D,E,F and C terms. C. E,F,C and D terms. D. F,C,E and D terms. ANSWER: C 6. The price quoted by the seller for the product A. will vary depending upon the incoterm chosen. B. irrespective of the incoterm. C. will be the base price; the effect of incoterm to be added later. D. will include only cost. ANSWER: A 7. Adoption of incoterm is A. compulsory for all international contracts B. compulsory for all letter of credit transactions. C. optional for the parties to the contract. D. mandatory for transactions with Europe. ANSWER: C 8. Which of the following term cannot be used for transportation of goods by Road or Air? A. FAS. B. DDR C. EXW. D. CIR ANSWER: A Answers for following are given in the end 1. Which of the following is not a basic objective of documentation in foreign trade? A. to assure that the exporter will receive the payment B. to assure that the importer will receive the goods C. to eliminate risk of noncompletion D. to reduce foreign exchange risk E. none of the above 2. Which of the following is not an important document in foreign trade? A. a check for the value of goods B. a draft C. bill of lading D. a letter of credit E. none of the above 3. ______ risk is the potential exchange loss from outstanding obligations as a result of exchange-rate fluctuations. A. Trade B. Exchange C. Finance D. Noncompletion E. Transaction 4. Foreign exchange risk can be reduced by using _____. A. forward contracts B. futures contracts C. currency options D. currency denomination E. all of the above 5. Which of the following is not a condition for drafts to be negotiable? A. must be in writing, signed by the drawer B. must contain a promise to pay a certain sum if goods are received C. must contain an order to pay D. must be payable on sight or at a specified date E. must be made out to order or bearer 6. If a draft is made to bearer, payment should be made to _____. A. a bank B. drawer C. acceptor D. anyone who presents the draft E. all of the above 7. If a draft is accepted by a bank, it becomes a _____. A. valid draft B. demand draft C. usance draft D. banker's acceptance E. drawee's acceptance 8. Forms of countertrade include the following except ___. A. simple barter B. clearing arrangement C. switch trade D. counterpurchase E. mutual agreement 9. Documentary drafts require various shipping documents such as ____. A. bills of lading B. insurance certificates C. commercial invoices D. A and B E. A, B, and C 10. When IBM ships products to its subsidiary in Argentina, it will most likely use a ____ draft. A. sight B. clean C. D/P D. demand E. all of the above 11. If a carrier is instructed to deliver goods to an importer, a _____ bill of lading is used. A. straight B. order C. documentary D. on-board E. clean 12. A(n) _____ bill of lading does not guarantee that the goods have been loaded on the vessel. A. on-board B. foul C. received-for-shipment D. straight E. order 13. Which of the following is not true of a letter of credit? A. it is a document B. issued by a bank C. at the request of the exporter D. the bank agrees to honor a draft drawn on the importer E. payable in the designated currency 14. If a letter of credit can be neither cancelled nor modified without the consent of all parties, it is known as _____. A. revolving B. irrevocable C. revocable D. unconfirmed E. unclean 15. If an exporter is doubtful about an issuing bank's ability to pay, he will expect a domestic bank to join the transaction in a _____ letter of credit. A. revolving B. irrevocable C. revocable D. unconfirmed E. confirmed 16. Which of the following may be required as additional documents in a letter of credit? A. commercial invoice B. insurance document C. consular invoice D. certificate of origin E. all of the above 17. Which of the following documents should necessarily accompany a draft? A. certificate of origin B. weight list C. packing list D. inspection certificate E. none of the above 18. A commercial invoice is issued by _____. A. exporter B. exporter's bank C. importer D. importer's bank E. confirming bank 19. A document that contains a precise description of the goods is known as a _____. A. weight list B. packing list C. commercial invoice D. certificate of origin E. consular invoice 20. Which of the following is not true of a consular invoice? A. provides customs officials with all information B. facilitates easy customs clearance C. helps customs officials assess duties D. issued by the consulate of the exporting country E. it is not a title to the goods 21. Which of the following is not a form of offset agreements? A. coproduction B. licensed production C. subcontractor production D. cash in advance E. technology transfer 22. Which of the following is not a form of countertrade? A. barter B. consignment C. switch trading D. counterpurchase E. compensation agreement 23. In a _____ countertrade the initial seller receives compensation in products that arise out of the original sale. A. consignment B. barter C. counterpurchase D. buy-back agreement E. switch trading 24. Buying a company's accounts receivable on a nonrecourse basis is known as _____. A. switch trading B. financing C. factoring D. funding E. free trade 25. Which of the following is not necessarily a party to a forfaiting transaction? A. exporter B. importer C. broker D. bank E. forfaiter 26. Below are five steps involved in a typical trade transaction. Which step is out of order: A. exporter agrees to ship under a letter of credit B. exporter ships the product to the importer C. importer’s bank issues the letter of credit D. exporter prepares a 60-day draft on importer in accordance with the letter of credit. E. the draft is accepted by the importer’s bank becoming a bankers’ acceptance. 27. The “three C’s” of international commerce are: A. customers B. commitment C. currency D. cultural sensitivity E. A, B, and D 28. When exporting some common pitfalls include: A. failure to use an export management company B. failure to print service, sales, and warranty messages in local languages C. chasing orders around the world instead of establishing a basis for profitable operations and orderly growth D. failure to consider licensing or joint venture agreements E. all of the above Answers Multiple Choice Questions 1. E 2. A 3. E 4. E 5. B 6. D 7. D 8. E 9. E 10. B 11. A 12. C 13. C 14. B 15. E 16. E 17. E 18. A 19. C 20. D 21. D 22. B 23. D 24. C 25. C 26. C 27. E 28. E