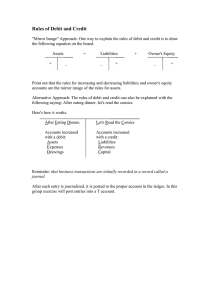
JOURNALIZING TRANSACTION, Detailed Steps in the Accounting Cycle Analyze Business Transactions. Journalize transactions in the journal. Post entries to the accounts in the ledger. Prepare unadjusted trial balance. Post-closing trial balance Journalize and post closing entries Prepare financial statements. Prepare adjusted trial balance. Journalize and post adjusting entries Analysis and Recording Business Transactions Business transaction is an economic event that causes a change in the financial position Financial Position: What the entity controls How the entity controls them (claims) Fundamental Accounting Equation ASSETS = EQUITIES ASSETS = LIABILITIES + OWNERS' EQUITY How do accounts behave? Assets = + Liabilities + + Shareholders’ Equity + So Assets increase on the left hand or debit side then they decrease on the credit side Assets + debit credit Behavior of Accounts cont… Liabilities and Owners’ Equity accounts increase on the credit side, decrease on the debit side Liabilities or Owners’ Equity Accounts debit + credit Transaction Analysis and The Duality Concept Double entry system states that every transactions affects at least two accounts. Therefore • If an asset account increases (decreases), because of duality concept there must be a corresponding: 1. increase(decrease) in a specific liability account 2. or a decrease(increase) in a another asset account 3. or an increase(decrease) in owners' equity account. What’s in a Journal Entry? Date 2. At least one debit entry Debit account, use exact account title, do not indent titles 3. At least one credit entry Credit account, use exact account title, indent titles 4. An explanation of the transaction: Check number Invoice number Accounts receivable customer name Many other elements OR details as appropriate… Remember: the accountant must leave a good audit trail so that users of accounting information can understand what occurred with each transaction 1. DR=CR Steps in Journalizing 1. 2. 3. Determine the effects of transactions on three components of the accounting equation, Determine which specific accounts are affected, and Assure that total of the increases should be equal to either increases on the other side of the equation or to decreases on the same side, or a combination there of. Rules of Debit and Credit Assets = + Dr Cr Liabilities + Dr Cr + Owners’ Equity + Dr Cr Expense Revenue + + Dr Cr Dr Cr Withdrawals/Dividends + Dr Cr Assets Give examples of an asset account: Liability Give examples of a liability account: Owner’s Equity Give examples of an owner’s equity account: Illustrations: In January of the current year, S. Moreno began a business he called “Moreno Furniture Repair Shop’ and completed the following transactions during the month: 1. On Jan 1, Moreno invested ₱300,000 to start the business. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 2. Paid ₱10,000 for the rent of the shop building Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 3. Purchased ₱80,000 of shop machinery, giving ₱30,000 cash and a promissory note in payment of the balance. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 5. Purchased ₱9,500 of shop supplies from C. Alba on credit. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 9. Collected cash on delivery of a cabinet to a customer, ₱20,000. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 13. Completed and delivered sofa bed to M. Maranan ₱13,000 on credit. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 15. Paid wages of the shop helpers, ₱15,000 Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 15. Paid the delivery services rendered by C. Rana Trucking, ₱8,000. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 18. Paid the account due to C. Alba, ₱9,500. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 20. Took ₱1,000 worth of shop supplies for use in his carport. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 23. Received ₱5,000 from M. Maranan in partial payment of his account. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 25. Withdrew ₱5,000 for personal expenses. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 28. Collected ₱5,000 on the delivery of small chairs. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 30. Paid ₱8,000 for the delivery service on the second half of the month. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 30. Paid the wages of the shop helpers, ₱15,000. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit 30. Paid the light and power bill, ₱3,500. Event Assets No 1 Total Liabilities Owners’ Equity GENERAL JOURNAL Page 1 Date Account Title and Description Acct.No. Debit Credit Accounting Cycle-Revisited Analyze and record the transactions Close the accounts and prepare trial balance Post the transactions and prepare trial balance Prepare the financial statements Adjust the accounts and prepare trial balance THE END THANK YOU