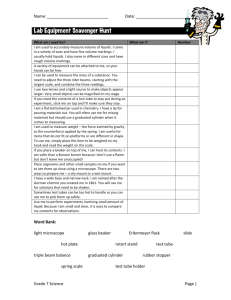
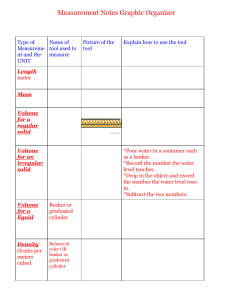
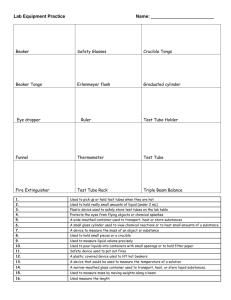
Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Lab Equipment Rotation Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 In this activity, students will be rotating around a classroom to complete different tasks using science lab equipment. Some of the tasks include making observations, taking measurements, finding volume and mass using tools such as the microscope, hand lens, hot plate, graduated cylinder, beakers, test tubes, triple beam balance, and thermometer. There is a lab sheet included as well as 10 station cards. This activity is super interactive and engaging for students! PREVIEW PREVIEW Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Time frame: 45-90 minutes " " Materials needed: Microscope, Slides, Pond Water, Hand Lens, Hot Plate, Graduated Cylinder, Beakers, Test Tubes, Test Tube Rack, Meter Stick, Triple Beam Balance, Thermometer and Spring Scale." " Group Size: 2 students but can be done individually. Groups any bigger would not give students ample opportunity to be working with materials and equipment.! " Students will be rotating around the room to complete activity at each station. I have made the activities short enough to be complete in 3-4 minutes. This should give you enough time to have students get through all the station that have been provided for you. You can make any modifications to the stations that you see fit. " " I have also made the directions so that it can fit with whatever you have in your classroom. I do not name anything specific other than the equipment needed and water." " Here is a list of materials needed by station:" " MICROSCOPE: microscope, prepared slide (plant or animal)" HAND LENS: hand lens, object to make observations such as leaf or insect or specimen" HOT PLATE: hot plate, safety gloves, beaker, food coloring, sugar, spoon or stirrer, water" GRADUATED CYLINDER: graduated cylinder, water, small object small enough to fit in the opening (ex. small rock)" BEAKERS: beaker, water, food coloring, salt, spoon or stirrer." TEST TUBES: 3 test tubes, 3 small beakers with water colored red, yellow and blue, test tube rack" METER STICK: meter stick, items to be measured (ex. books, cereal box…), toy car, piece of tape" TRIPLE BEAM BALANCE: triple beam balance, assortment of items to be measured" THERMOMETER: thermometer, beaker filled with ice water, beaker with warm water." " Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 " Microscope What To Do:! 1. Place prepared slide on the microscope stage." 2. Focus using low power." 3. Switch to high power." 4. Draw what you see on your lab sheet." 5. Answer the following question on your lab sheet." 1. What is the lowest magnification of the microscope?" 2. What is the highest magnification of the microscope?" 3. Can measurements be made using the microscope? Microscope Use 1. 2. 3. 4. Plug microscope in and turn it on." Make sure lens in on low power and stage is all the way down." Place slide on stage." Focus on low power first, then increase power by changing to a different lens. " 5. Use fine focus for details." 6. When done, put lens back on lowest power and move stage down. " 7. Unplug microscope and wrap cord around base." Safety Precautions • Carry the microscope with two hands so that it does not hit tables or chairs. " • Do not touch the lenses. " • Do not use direct sunlight as the light source — eye damage will result." • Be cautious when handling glass slides and cover-slips" • Always clean slides and microscope when finished." • Store microscope on lowest position." • Cover microscope with dust cover and return to storage. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Hand Lens What To Do:! 1. Using the hand lens provided, make observations. " 2. Make sure to hold the lens near your eye and record what you see on the lab sheet." 3. Answer the following questions and record on the lab sheet." 1. Is there a unit of measurement that is used with the hand lens?" 2. Are hand lenses better for making qualitative (what you see) or quantitative (number related) observations? " Hand Lens Use 1. Hold lens close to one eye, by the handle. " 2. Shut the other eye and bring the object toward the lens until it comes into focus. Safety Precautions • Lens will become scratched if they touch objects. " • Be careful not to hurt a live specimen with the lens." • Keep the lens clean for later use. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Hot Plate What To Do:! 1. Place beaker on a flat surface." 2. Fill beaker with 100 ml of water." 3. Add 2 drops of food coloring." 4. Add 2 teaspoons full of sugar to the water." 5. Place the beaker on the hot plate." 6. Stir the mixture until all of the salt is dissolved." 7. Make observations and record on the lab sheet." 8. Answer the following questions and record on the lab sheet." 1. What do you think the hot plate did to the mixture?" 2. What is the unit of measurement? " Hot Plate Use 1. One method is to suspend glassware slightly above the surface of the plate with no direct contact. Safety Precautions • Use goggles and an apron when using a hot plate." • Use a hot plate with a smooth, clean surface." • Hot plates appear exactly the same whether hot or at room temperature. Always assume they are hot and act accordingly." • Keep the electrical cord of a hot plate away from water and heating surface." • The cord of the hot plate should be checked periodically for frays and faults. Any hot plate with faulty wiring should not be used. It should be repaired or replaced immediately. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Graduated Cylinder What To Do:! 1. Measure and fill graduated cylinder with 100ml of water." 2. Visually verify that there are 100ml of water." 3. Place the small object that has been provided for you into the graduated cylinder." 4. Again, visually take a measurement of the water in the graduated cylinder." 5. Record information on lab sheet." 6. Answer questions and record on lab sheet:" 1. What happened to the level of the water after you put the object in the graduated cylinder? Why?" 2. What are you measuring by doing this? " Graduated Cylinder Use Safety Precautions 1. Place the cylinder of a flat surface." 2. Look at the cylinder from the side at eye level. The top of the liquid should be at eye level. The via of the surface of the liquid will be curved. This curved surface is a called the meniscus." 3. Read the graduated cylinder at the bottom of the meniscus." • When filing the graduated cylinder, make sure you are not directly over the opening at the top. " • Keep yourself at eye level to the cylinder to avoid risks to the eyes." Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Beakers What To Do:! 1. Place beaker on a flat surface." 2. Fill beaker with 100 ml of water." 3. Add 2 drops of food coloring." 4. Add 2 teaspoons full of salt to the water." 5. Stir the mixture until all of the salt is dissolved." 6. Make observations and record on the lab sheet." 7. Answer the following questions and record on the lab sheet." 1. What is the maximum measurement of the beaker that you chose? Why did you choose this beaker?" 2. What is the unit of measurement? " Beaker Use 1. Choose a beaker with an appropriate measurement." 2. Make sure that the beaker that you will be using is clean and free of any materials." 3. Place the beaker on a flat surface." 4. Fill the container with the specified amount of material." 5. When done, dispose of the material inside of the beaker." 6. Rinse and dry the beaker for later use. Safety Precautions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Always use the beaker on a flat surface so that it does not fall and break." Avoid splashing the liquid that your are pouring into the beaker." Stir the liquid with a spoon or stirrer." If using flame or heat, do not fill the beaker more than 1/3." Always using safety tongs when handling a hot beaker." Pour liquid using the spout around the top of the beaker. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Test Tubes What To Do:! 1. Place three test tube on rack." 2. Measure 10 ml of yellow liquid into the first test tube." 3. Measure 20 ml of red liquid into the second test tube" 4. Measure 15 ml of blue liquid into the third test tube." 5. Measure 10 of red liquid into the FIRST test tube." 6. Measure 20 ml of blue liquid into the SECOND test tube." 7. Measure 15 ml of yellow liquid into the THIRD test tube." 8. Record all the information on your lab sheet." 9. Answer the following questions and record on your lab sheet:" 1. How do you know the exact measurement of the liquid?" 2. What is the unit of measurement? " Test Tube Use 1. Place test tube in rack." 2. Measure liquid that will go into the test tube, then fill from the top." 3. When done using the test tube, dispose of the materials properly." 4. Rinse out test tube and clean with test tube brush. Safety Precautions • If you need to smell the contents of the test tube, waft the fumes toward your nose. Never put your nose directly over the test tube. Contents could be hazardous!" • If using test tube to heat something, make sure your are using a test tube clamp and pointing the opening of the test tube away from yourself or any other people." • When heating, make small circular motions, never hold the test tube still." • Do not heat test tube too much, it could break from the heat. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Meter Stick What To Do:! 1. Take the meter stick and measure the length and width of the items that are in front of you. Record that information on the lab sheet." 2. Mark a starting point and with the toy car push it gently. Let it keep going until it comes to a stop. Measure the distance that the car traveled. Record that on the lab sheet." 3. Answer the following question, then record you answers on the lab sheet." 1. What do the numbers on the meter stick mean?" 2. What do the little lines in between the numbers mean? " Meter Stick Use Safety Precautions 1. Line up the meter stick with the object that is being measured." 2. Remember to start at the line which indicated 0 if there is one, if not then line up with the end of the meter stick." 3. Know what the unit of measurement is for the meter stick." 4. Get an exact measurement, then record your information. • Do not swing the meter stick." • Do not touch other people with the meter stick." • Try not to put too much weight on the meter stick unless it is supported. The meter stick might break. Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Triple Beam Balance What To Do:! 1. Set the balance to zero by moving the weights for all three beams to zero." 2. Place first object on pan and measure the mass. Record on lab sheet. Remove from pan." 3. Place second object on pan and measure the mass. Record on lab sheet. Remove from pan." 4. Place third object on pan and measure the mass. Record on lab sheet. Remove from pan." 5. Answer the following question and record on lab sheet." 1. What is difference between the three balances?" 2. What is the unit of measurement? " Triple Beam Balance Use 1. Move all of the riders as far as they will go to the left. The pointer should now be in line with the zero marking. If not, move the adjustment know very slowly until the loiter is in line with the zero marking." 2. Place an object on the pan. The pointer will swing up. Move the riders, starting with the back beam, until the pointer returns to the zero mark." 3. Total the masses indicated by each rider to find the mass of the object." 4. Move the riders to the left again and remove the object. Safety Precautions • Never place a powder or liquid directly on the pan." • Powders should be placed on weighing paper and liquids should be in a container." • Place all objects on the pan gently." • The adjustment know is used to zero the balance." Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Thermometer What To Do:! 1. Discuss with your partner, which end of the thermometer should go into the beakers." 2. Using the thermometer, take a measurement of the liquid that is inside of beaker 1. Record that information on your lab sheet." 3. Using the thermometer, take a measurement of the liquid that is inside of beaker 2. Record that information on your lab sheet." 4. Answer the following questions, then record the answer:" 1. What is the thermometer measuring?" 2. What is the unit of measurement in a science classroom?" 3. What unit of measurement do we usually use? Thermometer Use 1. Place the bulb end of the thermometer into the object with an unknown temperature." 2. Wait several minutes for the thermometer to adjust to the temperature of the object." 3. Without removing the thermometer from the object, note the number nearest the top of the column of liquid in the thermometer." 4. Safety Precautions Never use a thermometer as a stirring device." Never swing or shake down a thermometer." Never use an open flame on a thermometer bulb." Use extreme care when inserting or removing a thermometer from a rubber stopper." • Don’t place thermometers where they are likely to roll or be knocked off a table. All thermometers should have anti-roll devices." • Make sure you choose a thermometer with an appropriate temperature range. Overheating a thermometer can cause breakage of its reservoir. • • • • Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Spring Scale What To Do:! 1. Record the three items that you will be measuring on the lab sheet." 2. Take each item and attach it to the spring scale and measure the amount of force for each. Record on the lab sheet." 3. Answer the following questions, then record the answer on the lab sheet." 1. What is the spring scale measuring?" 2. What is the unit of measurement? " " " Spring Scale Use Safety Precautions 1. Adjust the measurement on the spring scale to 0." 2. With one hand, hold the spring scale up." 3. Bring the object that you are measuring up to the hook of the spring scale" 4. Make sure that it is secured to the spring scale." 5. Let go and read the scale" 6. Record your information. • Do not try to measure any object that is too heavy." • Take care with the hook end of the spring scale, keep away from eyes." • Place the scale down when done using. " " Created by CurlyQueScience, 2014 Thanks for downloading this Curly Que Science product! I really hope that you will find it useful, and am so excited that you decided to use this activity in your classroom. Below you will find a general outline of the activity:! In this activity, students will be rotating around a classroom to complete different tasks using science lab equipment. Some of the tasks include making observations, taking measurements, finding volume and mass using tools such as the microscope, hand lens, hot plate, graduated cylinder, beakers, test tubes, triple beam balance, and thermometer. There is a lab sheet included as well as 10 station cards. This activity is super interactive and engaging for students! " Curly Que Science " This activity can be used as a whole group, small group and/or individual activity." " Please check out other products in my store." Digestive System Structure and Function Foldable" Label the Digestive System" Excretory System Sort, Fold, Diagram and Clipart" Human Body Task Cards" Photosynthesis Bundle" Heat Transfer (Conduction, Convection and Radiation) Bundle" and many others to come!" " **All pictures, graphics, and artwork in our lessons are either purchased legally for use or are created by Curly Que Science**" Copyright Notice: The original purchaser of this document is granted permission to reproduce the pages in needed quantities for the purchaser’s classroom only. Minor editing is allowed; the document remains under copyright even when edited. Duplication for other classes or by other teachers or for use in wide distribution as within a school district or on the internet in any for is strictly forbidden." " Yellow Frame (1st page): Clip Art by Delightful Daily Deals© -