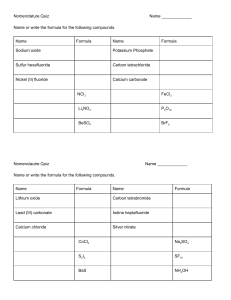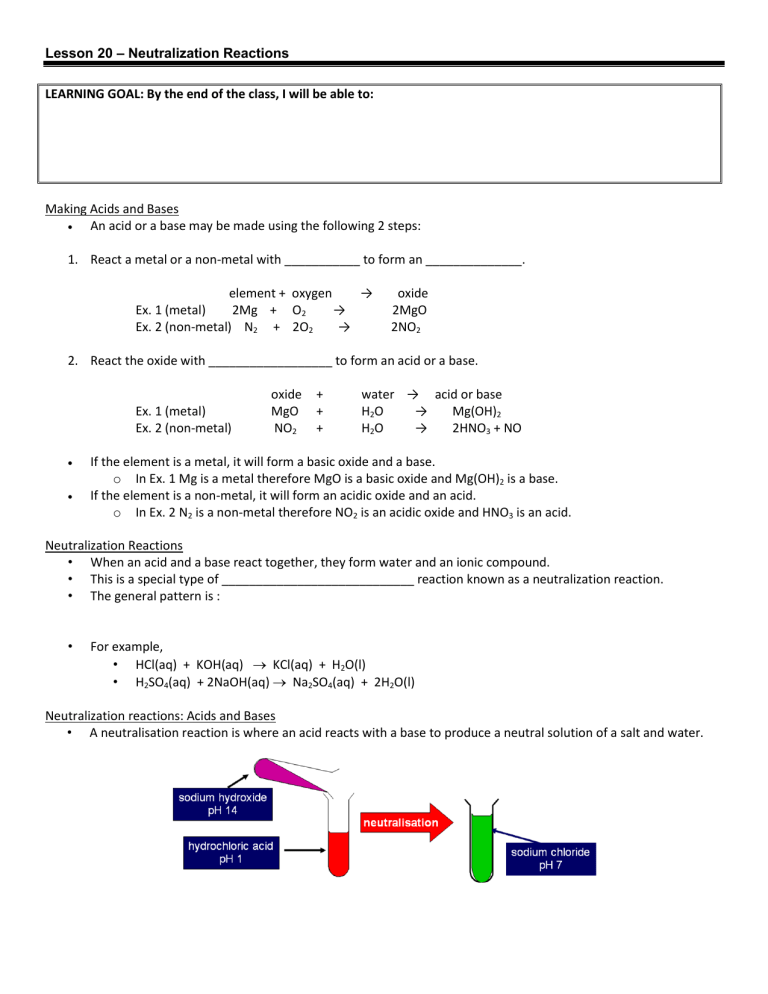
Lesson 20 – Neutralization Reactions LEARNING GOAL: By the end of the class, I will be able to: Making Acids and Bases An acid or a base may be made using the following 2 steps: 1. React a metal or a non-metal with ___________ to form an ______________. element + oxygen → Ex. 1 (metal) 2Mg + O2 → Ex. 2 (non-metal) N2 + 2O2 → oxide 2MgO 2NO2 2. React the oxide with __________________ to form an acid or a base. Ex. 1 (metal) Ex. 2 (non-metal) oxide MgO NO2 + + + water → acid or base H2O → Mg(OH)2 H2O → 2HNO3 + NO If the element is a metal, it will form a basic oxide and a base. o In Ex. 1 Mg is a metal therefore MgO is a basic oxide and Mg(OH)2 is a base. If the element is a non-metal, it will form an acidic oxide and an acid. o In Ex. 2 N2 is a non-metal therefore NO2 is an acidic oxide and HNO3 is an acid. Neutralization Reactions • When an acid and a base react together, they form water and an ionic compound. • This is a special type of ____________________________ reaction known as a neutralization reaction. • The general pattern is : • For example, • HCl(aq) + KOH(aq) KCl(aq) + H2O(l) • H2SO4(aq) + 2NaOH(aq) Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l) Neutralization reactions: Acids and Bases • A neutralisation reaction is where an acid reacts with a base to produce a neutral solution of a salt and water. Neutralization reactions: hydroxides • Each OH- ion reacts with one H+ ion. Neutralization reactions: carbonates • Each carbonate ion provides one oxygen to join with two H+ ions. At the same time carbon dioxide is released. Neutralization Equations 1. Complete the word equation 2. Replace the words with the correct formula 3. Check that it balances (same number of each type of atom each side). Eg. Potassium hydroxide + hydrochloric acid Applications of Neutralization Reactions • treating chemical spills • using antacids to provide relief of heartburn by neutralizing stomach acid • restoring lakes affected by acid precipitation Neutralization - Indigestion • If we have too much acid in our stomachs, we get indigestion. • Acid can move up out of our stomach creating a burning feeling in the chest. • We neutralize the excess acid by taking a tablet containing a base. • This is usually a carbonate or an oxide. • Strong soluble bases (like sodium hydroxide) would create too alkaline a solution and cannot be used. Neutralisation - Stings • One way to treat a an acidic bee sting is to dab on a base: bicarbonate of soda more properly known as sodium hydrogen carbonate. • One way to treat a basic wasp’s sting is with an acid : vinegar - ethanoic acid. Neutralisation – Soil pH • Plants remove compounds from the soil in a way that tends to leave the soil acidic. • Many plants won’t grow well in acid soil and so farmers have to regularly check the pH and adjust it by adding a base. • Calcium carbonate or calcium hydroxide are cheap and so are often used for this purpose. Homework Page 281, #1-9 Neutralization Worksheets