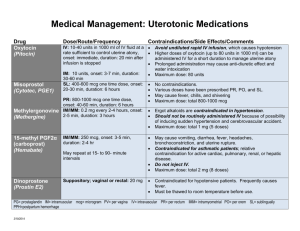
David J Hesse Clothing must be soft, washable, of the proper size, and easy to put on and take off. Parents are instructed to launder new clothing and sheets before using them to prevent skin irritation. Use of nightgowns with drawstring necks is avoided because they may lead to strangulation. Buttons must be sewn on tightly. Snaps or Velcro fasteners are safer. If the mother does not have a clothes dryer, she needs a clothes rack to dry the infant’s garments during inclement weather. Medication CARDS Student_________________________________________ Trade Names: Pitocin Action: Stimulates uterine smooth muscle, producing uterine contractions similar to those in spontaneous labor and has antidiuretic and vasopressor effects; control of postpartum hemorrhage Classification: Hormone and Oxytocic Generic Names: Oxytocin Adult Dose: Infuse 0.5-1 milliunits/min by IV; ↑ by 1-2 Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV (Used to induct labor at term) Pediatric Dose: N/A milliunits/min q 30-60 min until desired contraction patterns are established (Inducing labor) Infuse 10 units at 20-40 milliunits/min by IV Give 10 units intramuscularly after delivery of placenta (Postpartum Hemorrhage) Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor maternal BP and pulse frequently and fetal heart rate throughout administration Occasionally causes water intoxication. Monitor pt for signs and symptoms (drowsiness, listlessness, confusion, headache, anuria); notify physician or other HCP if they occur. Assess character, frequency, and duration of uterine contractions; resting uterine tone; and fetal heart rate frequently throughout administration. If contractions occur <2minutes apart and are >50-65 mm Hg on monitor, if they last 60-90 sec or longer, or if a significant change in fetal heart rate develops, stop infusion and turn patient on her left side to prevent fetal anoxia Contraindications: Hypersensitivity; Anticipated nonvaginal delivery Labs: Monitor maternal electrolytes with water retention that may result in hypochloremia and artemia Pertinent Side Effects: Coma and Seizures in mother; Intercranial hemorrhaging; Asphyxia and hypoxia in the fetus; Hypotension in mother and arrythmias in fetus; Hypochloremia, hyponatremia and water intoxication in the mother; ↑ uterine motility, painful contractions, and ↓uterine blood flow in the mother. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Magnesium Sulfate Action: Plays an important role in neurotransmission and muscular excitability. Used for replacement in deficiency states and resolution of eclampsia. Classification: Mineral and Electrolyte replacements/supplements Generic Names: Magnesium Sulfate Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV Adult Dose: Administer 4–5 g by IV infusion, concurrently with up Pediatric Dose: N/A to 5 g IM in each buttock; then 4–5 g IM q 4 hr or 4 g by IV infusion followed by 1–2 g/hr continuous infusion (not to exceed 40 g/day or 20 g/48 hr in the presence of severe renal insufficiency). Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor pulse, BP, respirations, and ECG frequently throughout administration of parenteral magnesium sulfate. Respirations should be at least 16/min before each dose. Monitor neurologic status before and throughout therapy. Institute seizure precautions. Patellar reflex (knee jerk) should be tested before each parenteral dose of magnesium sulfate. If response is absent, no additional doses should be administered until positive response is obtained. Monitor newborn for hypotension, hyporeflexia, and respiratory depression if mother has received magnesium sulfate. Monitor intake and output ratios. Urine output should be maintained at a level of at least 100 mL/4 hr. Contraindications: Hypermagnesemia; Hypocalcemia; Anuria; Heart block; Avoid using for more than 5–7 days for preterm labor (may ↑ risk of hypocalcemia and bone changes in newborn); avoid continuous use during active labor or within 2 hr of delivery due to potential for magnesium toxicity in newborn. Monitor serum magnesium levels and renal function periodically throughout administration of parenteral magnesium sulfate Pertinent Side Effects: drowsiness; ↓ respiratory rate; arrhythmias, bradycardia, hypotension; diarrhea; muscle weakness; flushing, sweating; & hypothermia. Labs: Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Cervidil Action: Produces contractions similar to those occurring during labor at term by stimulating the myometrium; also Initiates softening, effacement, and dilation of the cervix and can be used to stimulate GI smooth muscle. Classification: Prostaglandin Generic Names: Dinoprostone Adult Dose: 10 mg vag insert; Cervical Ripening Vag (Adults, Cervical): Endocervical gel—0.5 mg; if response is unfavorable, may repeat in 6 hr (not to exceed 1.5 mg/24 hr). Vaginal insert—one 10-mg insert. Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: Vaginal Pediatric Dose: N/A Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor temperature, pulse, and BP periodically throughout therapy. Dinoprostone-induced fever (elevation >1.1°C or 2°F) usually occurs within 15–45 min after insertion of suppository. This returns to normal 2–6 hr after discontinuation or removal of suppository from vagina. Auscultate breath sounds. Wheezing and sensation of chest tightness may indicate hypersensitivity reaction. Assess for nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea in patients receiving suppository. Vomiting and diarrhea occur frequently. Patient should be premedicated with antiemetic and antidiarrheal. Monitor amount and type of vaginal discharge. Notify health care professional immediately if symptoms of hemorrhage (increased bleeding, hypotension, pallor, tachycardia) occur. (cervical ripening) Monitor uterine activity, fetal status, and dilation and effacement of cervix continuously throughout therapy. Assess for hypertonus, sustained uterine contractility, and fetal distress. Insert should be removed at the onset of active labor. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to prostaglandins; The gel/insert should be avoid situations of prolonged uterine contractions. This includes: 1)Previous cesarean section or uterine surgery; 2)Cephalopelvic disproportion; 3) Traumatic delivery or difficult labor; 4) Multiparity (≥6 term pregnancies); 5)Hyperactive/ hypertonic uterus; 6. Fetal distress (if delivery is not imminent); 7. Unexplained vaginal bleeding; 8. Placenta previa; 9. Vasa previa; 10. Active herpes genitalis; 11. Obstetric emergency requiring surgical intervention; 12. Situations in which vaginal delivery is contraindicated; 13. Presence of acute pelvic inflammatory disease or ruptured membranes; 14. Concurrent oxytocic therapy (must wait for 30 min after removing insert before using oxytocin). Labs: N/A Pertinent Side Effects: uterine contractile abnormalities, warm feeling in vagina; back pain; amniotic fluid embolism, fever; headache, drowsiness, syncope; coughing, dyspnea, wheezing; hypotension, hypertension; diarrhea, nausea, vomiting; UTERINE RUPTURE, urinary tract infection, uterine hyperstimulation, vaginal/uterine pain; allergic reactions including ANAPHYLAXIS, chills, fever. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Bricanyl Action: Produces bronchodilation. By inhibiting the release of mediators of immediate hypersensitivity reactions from mast cells. Relatively selective for beta2 (pulmonary)-adrenergic receptor sites, with less effect on beta1 (cardiac)-adrenergic receptors; May be used in management of preterm labor (tocolytic) Classification: Bronchodilator; Adrenergic Generic Names: Turbutaline Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV Adult Dose: 2.5–5 mg 3 times daily, given q 6 hr (not to exceed 15 Pediatric Dose: (Children >15 yr): 2.5–5 mg 3 times daily, given q 6 hr (not to exceed 15 mg/24 hr). PO mg/24) 250 mcg; may repeat in 15–30 min (not to exceed 500 mcg/4 hr). Subq 2.5–10 mcg/min infusion; ↑ by 5 mcg/min q 10 min until contractions stop (not to exceed 30 mcg/min). After contractions have stopped for 30 min, ↓ infusion rate to lowest effective amount and maintain for 4–8 hr (unlabeled). IV (Tocolysis) (Children 12–15 yr): 2.5 mg 3 times daily (given q 6 hr) (not to exceed 7.5 mg/24 hr). PO (Children <12 yr): 0.05 mg/kg 3 times daily; may ↑ gradually (not to exceed 0.15 mg/kg 3–4 times daily or 5 mg/24 hr). (Children ≥12 yr): 250 mcg; may repeat in 15–30 min (not to exceed 500 mcg/4 hr). (Children <12 yr): 0.005–0.01 mg/kg; may repeat in 15–20 min. Subq Nursing Interventions/Considerations: For bronchodilator: Assess lung sounds, respiratory pattern, pulse, and BP before administration and during peak of medication. Note amount, color, and character of sputum produced, and notify health care professional of abnormal findings. Monitor pulmonary function tests before initiating therapy and periodically throughout therapy to determine effectiveness of medication. For preterm labor: Monitor maternal pulse and BP, frequency and duration of contractions, and fetal heart rate. Notify health care professional if contractions persist or increase in frequency or duration or if symptoms of maternal or fetal distress occur. Maternal side effects include tachycardia, palpitations, tremor, anxiety, and headache. Assess maternal respiratory status for symptoms of pulmonary edema (increased rate, dyspnea, rales/crackles, frothy sputum). Monitor mother and neonate for symptoms of hypoglycemia (anxiety; chills; cold sweats; confusion; cool, pale skin; difficulty in concentration; drowsiness; excessive hunger; headache; irritability; nausea; nervousness; rapid pulse; shakiness; unusual tiredness; or weakness) and mother for hypokalemia (weakness, fatigue, U wave on ECG, arrhythmias). Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to adrenergic amines. Labs: Monitor maternal serum glucose and electrolytes. May cause hypokalemia and hypoglycemia. Monitor neonate’s serum glucose, because hypoglycemia may also occur in neonates Pertinent Side Effects: nervousness, restlessness, tremor, headache, insomnia; pulmonary edema; angina, arrhythmias, hypertension, myocardial ischemia, tachycardia; nausea, vomiting; hyperglycemia; hypokalemia. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Cytotec Action: decreasing gastric acid secretion (antisecretory effect) and increasing the production of protective mucus (cytoprotective effect). Causes uterine contractions. Prevention of gastric ulceration from NSAIDs Classification: antiulcer agent; cytoprotective agent; prostaglandin Generic Names: misoprostol Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: Vaginal Adult Dose: PO Antiulcer—200 mcg 4 times daily with or after Pediatric Dose: N/A meals and at bedtime, or 400 mcg twice daily, with the last dose at bedtime. If intolerance occurs, dose may be ↓ to 100 mcg 4 times daily. Termination of pregnancy—400 mcg single dose 2 days after mifepristone if abortion has not occurred. Intravaginally; 25 mcg (1/4 of 100–mcg tablet); may repeat q 3–6 hr, if needed. Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Assess patient routinely for epigastric or abdominal pain and for frank or occult blood in the stool, emesis, or gastric aspirate. Assess women of childbearing age for pregnancy. Misoprostol is usually begun on 2nd or 3rd day of menstrual period following a negative pregnancy test result. Termination of pregnancy: Monitor uterine cramping and bleeding during therapy. Cervical Ripening: Assess dilation of cervix periodically during therapy. Hypersensitivity to prostaglandins; OB: Should not be used to prevent NSAID-induced gastric injury due to potential for fetal harm or death; Lactation: May cause severe diarrhea in the nursing infant. Contraindications: Labs: N/A Pertinent Side Effects: headache; abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, nausea, vomiting; miscarriage, menstrual disorders. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: RhoGam Action: Prevent production of anti-Rho(D) antibodies in Rho(D)-negative patients who were exposed to Rho(D)-positive blood. Increase platelet counts in patients with ITP. Prevention of antibody response and hemolytic disease of the newborn (erythroblastosis fetalis) in future pregnancies of women who have conceived a Rho(D)-positive fetus. Prevention of Rho(D) sensitization following transfusion accident. Decreased bleeding in patients with ITP. Classification: vaccines/immunizing agents; immune globulins Generic Names: Rho(D) Immune Globulin Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV Adult Dose: Rho(D) Immune Globulin (for IM use only) Following Delivery IM (Adults): HyperRHO S/D Full Dose, RhoGAM—1 vial standard dose (300 mcg) within 72 hr of delivery. Before Delivery IM (Adults): HyperRHO S/D Full Dose, RhoGAM—1 vial standard dose (300 mcg) at 26–28 wk. Termination of Pregnancy (<13 wk Gestation) IM (Adults): HyperRHO S/D Mini-Dose, MICRhoGAM—1 vial of microdose (50 mcg) within 72 hr. Termination of Pregnancy (>13 wk Gestation) IM (Adults): RhoGAM—1 vial standard dose (300 mcg) within 72 hr. Large Fetal-Maternal Hemorrhage (>15 mL) IM (Adults): RhoGAM—20 mcg/mL of Rho(D)-positive fetal RBCs. Transfusion Accident IM (Adults): HyperRHO S/D Full Dose, RhoGAM—(Volume of Rh-positive blood administered × Hct of donor blood)/15 = number of vials of standard dose (300 mcg) preparation (round to next whole number of vials). Rho(D) Immune Globulin IV (for IM or IV Use) Following Delivery IM, IV (Adults): WinRho SDF—600 IU (120 mcg) within 72 hr of delivery. Rhophylac—1500 IU (300 mcg) within 72 hr of delivery. Prior to Delivery: Pediatric Dose: IV (Children): WinRho SDF, Rhophylac—50 mcg (250 IU)/kg initially (if Hgb <10 g/dL, ↓ dose to 25–40 mcg [125–200 IU]/kg); further dosing/frequency determined by clinical response (range 25–60 mcg [125–300 IU]/kg). Each dose may be given as a single dose or in 2 divided doses on separate days Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company IM, IV (Adults): WinRho SDF, Rhophylac—1500 IU (300 mcg) at 28 wk; if initiated earlier in pregnancy, repeat q 12 wk. Following Amniocentesis or Chorionic Villus Sampling IM, IV (Adults): WinRho SDF (before 34 wk gestation)—1500 IU (300 mcg) immediately; repeat q 12 wk during pregnancy. Rhophylac—1500 IU (300 mcg) within 72 hr of procedure. Termination of Pregnancy, Amniocentesis, or Any Other Manipulation IM, IV (Adults): WinRho SDF—600 IU (120 mcg) within 72 hr after event. Large Fetal-Maternal Hemorrhage/Transfusion Accident IM : WinRho SDF—6000 IU (1200 mcg) q 12 hr until total dose is given (total dose determined by amount of blood loss/hemorrhage). IV (Adults): 3000 IU (600 mcg) q 8 hr until total dose is given (total dose determined by amount of blood loss/hemorrhage). Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura IV (Adults and Children): WinRho SDF, Rhophylac—50 mcg (250 IU)/kg initially (if Hgb <10 g/dL, ↓ dose to 25–40 mcg [125–200 IU]/kg); further dosing/frequency determined by clinical response (range 25– 60 mcg [125–300 IU]/kg). Each dose may be given as a single dose or in 2 divided doses on separate days Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Assess vital signs periodically during therapy in patients receiving IV Rho(D) immune globulin. ITP: Monitor patient for signs and symptoms of intravascular hemolysis (IVH) (back pain, shaking chills, fever, hemoglobinuria), anemia, and renal insufficiency. If transfusions are required, use Rho(D)-negative packed red blood cells to prevent exacerbation of IVH Contraindications: Prior hypersensitivity reaction to human immune globulin; Rho(D)- or Du-positive patients. Labs: Pregnancy: Type and crossmatch of mother and newborn’s cord blood must be performed to determine need for medication. Mother must be Rho(D)-negative and Du- negative. Infant must be Rho(D)-positive. If there is doubt regarding infant’s blood type or if father is Rho(D)-positive, medication should be given. An infant born to a woman treated with Rho(D) immune globulin antepartum may have a weakly positive direct Coombs’ test result on cord or infant blood. ITP: Monitor platelet counts, RBC counts, hemoglobin, and reticulocyte levels to determine effectiveness of therapy. Pregnancy: Type and crossmatch of mother and newborn’s cord blood must be performed to determine need for medication. Mother must be Rho(D)-negative and Du-negative. Infant must be Rho(D)-positive. If there is doubt regarding infant’s blood type or if father is Rho(D)-positive, medication should be given. An infant born to a woman treated with Rho(D) immune globulin antepartum may have a weakly positive direct Coombs’ test result on cord or infant blood. ITP: Monitor platelet counts, RBC counts, hemoglobin, and reticulocyte levels to determine effectiveness of therapy Pertinent side effects: dizziness, headache; hypertension, hypotension; rash; diarrhea, nausea, vomiting; acute renal failure; ITP—Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Intravascular Hemolysis, anemia; arthralgia, myalgia. Local: pain at injection site; fever. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: MMR, M-M-R II Action: induces antibody formation against the Measles, Mumps, and Rubella viruses Classification: Vaccine Generic Names: Measles, Mumps, Bubella Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: Adult Dose: N/A Pediatric Dose: 0.5 mL Subq at 12-15 mo and at 4-6 yr Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Assess for latex allergies, monitor previous vaccine history and for hypersensitivity reactions Contraindications: Anaphylactic reaction after a previous dose or to vaccine component (includes eggs, neomycin, or gelatin); severe immunosuppression; pregnancy Labs: N/A Pertinent Side Effects: Arthralgia, encephalitis, fever, pain at injection site Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Methergine Action: Directly stimulates uterine and vascular smooth muscle and Uterine contraction. Classification: oxytocic; ergot alkaloid Generic Names: Methylergonovine Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV Adult Dose: PO (Adults): 200–400 mcg (0.2–0.4 mg) q 6–12 hr Pediatric Dose: N/A for 2–7 days. IM, IV (Adults): 200 mcg (0.2 mg) q 2–4 hr for up to 5 doses Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor BP, heart rate, and uterine response frequently during medication administration. Notify health care professional promptly if uterine relaxation becomes prolonged or if character of vaginal bleeding changes. Assess for signs of ergotism (cold, numb fingers and toes, chest pain, nausea, vomiting, headache, muscle pain, weakness). Contraindications: Hypersensitivity; OB: Should not be used to induce labor; Lactation: Do not breast feed during treatment and for 12 hours after the last dose; Concurrent use of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors Labs: If no response to methylergonovine, calcium levels may need to be assessed. Effectiveness of medication is ↓ with hypocalcemia. May cause ↓ serum prolactin levels Pertinent Side Effects: Stroke, dizziness, headache; tinnitus; dyspnea; Hypertension, arrhythmias, AV block, chest pain, palpitations; nausea, vomiting; cramps; diaphoresis; paresthesia; allergic reactions. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Mephyton Action: Required for hepatic synthesis of blood coagulation factors II (prothrombin), VII, IX, and X; Prevention of bleeding due to hypoprothrombinemia Classification: antidotes, vitamins; fat-soluble vitamins Generic Names: Phytonadione Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: IV Adult Dose: Treatment of Hypoprothrombinemia due to Vitamin Pediatric Dose: Treatment of Hypoprothrombinemia due to Vitamin K Deficiency (from factors other than Subcut, IV (Adults): 10 mg. PO (Adults): 2.5–25 mg/day. P1029 Subcut, IV (Children >1 mo): 1–2 mg single dose. PO (Children >1 mo): 2.5–5 mg/day. K Deficiency (from factors other than warfarin) Vitamin K Deficiency (Supratherapeutic INR) Secondary to Warfarin PO (Adults): INR ≥5 and <9 (no significant bleeding)—Hold warfarin and give 1–2.5 mg vitamin K; if more rapid reversal required, given ≤5 mg vitamin K; INR >9 (no significant bleeding)— Hold warfarin and give 2.5–5 mg vitamin K. IV (Adults): Elevated INR with serious or life-threatening bleeding—10 mg slow infusion. P1029 Prevention of Hypoprothrombinemia during Total Parenteral Nutrition warfarin) Prevention of Hypoprothrombinemia during Total Parenteral Nutrition IV (Children): 2–5 mg once weekly. Prevention of Hemorrhagic Disease of Newborn IM (Neonates): 0.5–1 mg, within 1 hr of birth, may repeat in 6–8 hr if needed. May be repeated in 2–3 wk if mother received previous anticonvulsant/anticoagulant/anti-infective/antitubercular therapy. 1–5 mg may be given IM to mother 12–24 hr before delivery. Treatment of Hemorrhagic Disease of Newborn IM, Subcut (Neonates): 1–2 mg/day. IV (Adults): 5–10 mg once weekly. Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor for flank and occult bleeding (guaiac stools, Hematest urine, and emesis). Monitor pulse and BP frequently; notify health care professional immediately if symptoms of internal bleeding or hypovolemic shock develop. Inform all personnel of patient’s bleeding tendency to prevent further trauma. Apply pressure to all venipuncture sites for at least 5 min; avoid unnecessary IM injections. Pedi: Monitor for side effects and adverse reactions. Children may be especially sensitive to the effects and side effects of vitamin K. Neonates, especially premature neonates, may be more sensitive than older children. Contraindications: Hypersensitivity; Hypersensitivity or intolerance to benzyl alcohol Labs: Monitor prothrombin time (PT) prior to and throughout vitamin K therapy to determine response to and need for further therapy. Pertinent Side Effects: gastric upset, unusual taste; flushing, rash, urticaria; hemolytic anemia; erythema, pain at injection site, swelling; allergic reactions, hyperbilirubinemia (large doses in very premature infants), kernicterus Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: HepB, Engerix-B, Recombivax HB Action: induces antibody formation against the Hepatitis B virus Classification: Vaccination Generic Names: Hepatitis B Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: Adult Dose: 1 mL IM, given at 0, 1 and 6 months Pediatric Dose: 1 mL IM, given at 0, 1 and 6 months Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Assess for latex allergies, monitor previous vaccine history and for hypersensitivity reactions Contraindications: Anaphylactic reaction after a previous dose or to vaccine component Labs: N/A Pertinent Side Effects: Injection site reaction Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company Trade Names: Eyemycin, Action: bacteriostatic or bactericidal, depending on susceptibility and concentration; binds to 50S ribosomal subunit, inhibiting protein synthesis (macrolide) Classification: Antibacterials, Ophthalmic Generic Names: Erythromycin (Eye Ointment) Routes: of Administration: PO_____ SQ_____IM_____Topical_____ Other: Adult Dose: Pediatric Dose: ½-in. strip 2–6 times daily. Children: ½-in. strip 2–6 times daily. Infants: Prophylaxis of ophthalmia neonatorum—½-in. strip in each eye as a (single dose) Nursing Interventions/Considerations: Monitor and report signs of superinfection (black, furry overgrowth on the tongue; vaginal itching or discharge; loose or foul-smelling stools); Teach about application of eye ointment Contraindications: Hypersensitivity; Hypersensitivity or intolerance to crossmatching; Concurrent use of pimozide, ergotamine, dihydroergotamine, procainamide, quinidine, dofetilide, amiodarone, or sotalol; Long QT syndrome; Hypokalemia; Hypomagnesemia; Heart rate <50 bpm; Known alcohol intolerance (most topicals); Tartrazine sensitivity (some products contain tartrazine—FDC yellow dye #5); Products containing benzyl alcohol should be avoided in neonates Labs: no routine tests recommended Pertinent Side Effects: eye irritation; seizures (rare); ototoxicity; Torsade de Pointes, Ventricular arrhythmias, QT interval prolongation; Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhea (CDAD), nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, hepatitis, infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis, pancreatitis (rare); interstitial nephritis; rash; phlebitis at IV site; allergic reactions, superinfection. Vallerand, A. H., Sanoski, C. A., & Deglin, J. H. (2017). Davis's drug guide for nurses (16th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: F.A. Davis Company