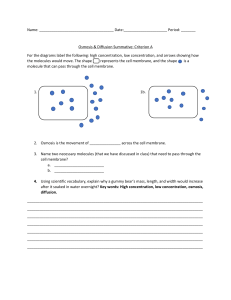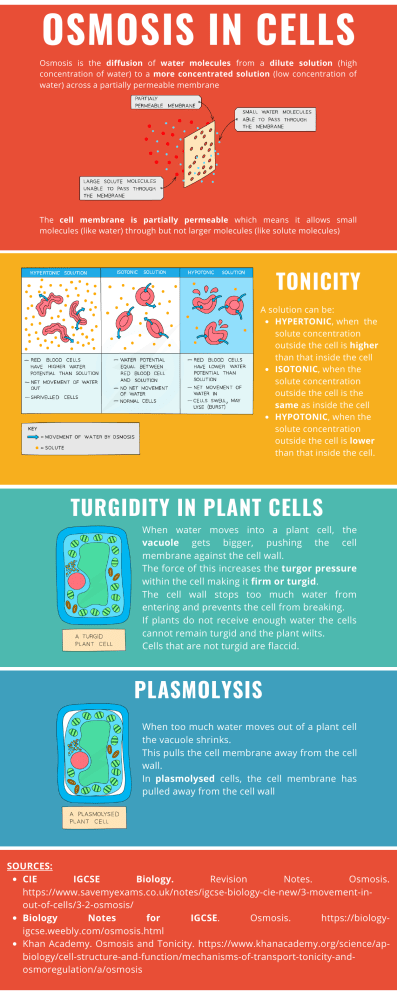
OSMOSIS IN CELLS Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules from a dilute solution (high concentration of water) to a more concentrated solution (low concentration of water) across a partially permeable membrane The cell membrane is partially permeable which means it allows small molecules (like water) through but not larger molecules (like solute molecules) TONICITY A solution can be: HYPERTONIC, when the solute concentration outside the cell is higher than that inside the cell ISOTONIC, when the solute concentration outside the cell is the same as inside the cell HYPOTONIC, when the solute concentration outside the cell is lower than that inside the cell. TURGIDITY IN PLANT CELLS When water moves into a plant cell, the vacuole gets bigger, pushing the cell membrane against the cell wall. The force of this increases the turgor pressure within the cell making it firm or turgid. The cell wall stops too much water from entering and prevents the cell from breaking. If plants do not receive enough water the cells cannot remain turgid and the plant wilts. Cells that are not turgid are flaccid. PLASMOLYSIS When too much water moves out of a plant cell the vacuole shrinks. This pulls the cell membrane away from the cell wall. In plasmolysed cells, the cell membrane has pulled away from the cell wall SOURCES: CONTACT: HELLO@REALLYGREATSITE.COM CIE IGCSE Biology. Revision Notes. Osmosis. https://www.savemyexams.co.uk/notes/igcse-biology-cie-new/3-movement-inout-of-cells/3-2-osmosis/ Biology Notes for IGCSE. Osmosis. https://biologyigcse.weebly.com/osmosis.html Khan Academy. Osmosis and Tonicity. https://www.khanacademy.org/science/apbiology/cell-structure-and-function/mechanisms-of-transport-tonicity-andosmoregulation/a/osmosis