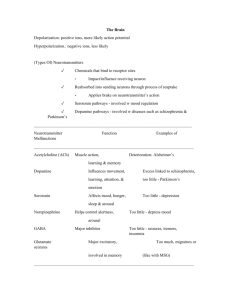
NURS 3125 Test 2 Study Guide All previously assigned readings and PowerPoint material is subject to be on Test 2. This is a general guide and not all encompassing Psychiatric Mental Health Assessment / Risk Assessment Components of the nursing assessment and patient/family history Components of a Bio-Psycho-SocialAssessment ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Identifying Data Chief Complaint History of Present Illness Psychiatric History Medical History Family Psychiatric History Primary focus on immediate family (grandparents, parents, sibling, children) -Psych Diagnoses (When? By whom?) -Treatment -Hospitalizations (Why? When? Where? How long?) -Medications (Name, Dose, Indication, Tolerated, Effective, Length of tx?) -Individual therapy (When? How long? Effective/skills learned?) -Substance Use -Suicide Ideation -Suicide Attempt (lethality, medical intervention?, did they go to someone or did someone find them?) -Self Injurious behavior (hx cutting, burning, picking) ▪ Family Medical History -Conditions (Thyroid, Cardiovascular, Cancer, Metabolic syndrome, etc…) -Treatments ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Social/Developmental History Work History Legal History (civilian and military) Habits (substance use, ETOH, caffeine, supplements, tobacco) Mental Status Exam Assessment (risk assessment, case formulation, multi-axial dx) Initial Treatment Plan Components of the MSE ▪ Appearance. Is clothing clean, put on appropriately, are they healthy, hair, color or texture, color of clothes. Fidgety, depressed and not keeping eye contact, posture, are they slumped? Bizarre look? Unusual facial features? Do they look their age? Older or young? ▪ Behavior. Are they being cooperative? Rude, twitching? Seductive, defensive, Guarded, Hostile, Agitated, Combativeness, Rigid, Gait, Adlity ▪ Thought Content What is the person actually thinking about? Disturbances= Delusions, hallucinations, illusions, ideas of reference, obsessions, homicidal ideations, suicidal ideations ▪ Thought Process Linear logical & goal directed, tangential (inability to get to the point of the story), flight of ideas (thoughts move abruptly from idea to idea; often expressed through rapid, pressured speech), circumstantiality (over inclusion of trivial or ▪ Speech (Quality, Quantity, Rate) Speaking slow or fast, Pressured (through teeth) Yellowing // Quantity: Talkative, unspontaneous, Normally responsive to cues? // Rate: Rapid, slow, hesitant, Stuttered Quality: Monotone, Loud, Whispered, Slurred, Mumbled ▪ Mood (subjective): depressed, despairing, irritable, anxious, angry, expensive, euphoric, empty, guilty, hopeless. Labile or reactive (shifting between mood extremes: depressed to angry?) ▪ Affect: Objective; defined by pts facial expression, range of expressive behavior Described as: Normal, constricted (range and intensity of expression is reduced; happy but not able to smile often), blunted (emotional expression is further reduced: emotion but not visible: poker face), flat, expensive Inappropriate//incongruent: killed pet and were happy ▪ Perception: hallucinations and illusions irrelevant details that impede the sense of getting to the point), clang associations (thoughts associated by the sound of words rather than meaning; right sight light might), looseness of associations (breakdown in both the logical connection between idea and the overall sense of goal-directedness. Words make sense but not together) perseveration (repeating the same word or idea back to you), echolalia (parrot-like repetition of the words spoken by another), neologisms (new words that an individual invents that are meaning less to others), word salad (group of words that are put together in a random fashion), blocking (abrupt interruption in train of thought before a thought or idea is finished) ▪ Sensorium and Cognition Level of alertness/consciousness; orientation; memory; capacity for abstract thought; intelligence ▪ Impulsivity Is pt capable of controlling sexual, aggressive and other impulses? Is pt aware of socially appropriate behavior ▪ Judgment and Insight Capacity of pts ability to make decision of best interest ▪ Reliability Insight is a pts degree of awareness and understanding about being ill 6 levels of insight … Includes an estimate of pts truthfullness Components of a risk assessment Screening = low sensitivity levels compared to assessment tools Suicide Risk Factors (acute = modifiable) *intent; for secondary gain (attention-cry for help) vs. meant to die? Active self-mutilation: have they practiced attempt? Chronic (often static) middle age Caucasian men Chronic medical problems (COPD) Mitigating risk factors: Married Denies si, no previous history Absence of alcohol No weapon Willingness to engage in treatment Develop crisis response plan Risk factors vs protective factors Suicidal desire and ideation (SDI) Reasons for living Wish to die Frequency of ideation Wish not to live Passive attempt Resolved plans and preparation (RPP) …. “an attempt” SAFE-T & CAMS = framework to determine overall SI level of risk Risks: Mild= none Moderate= any symptom or indicator Severe= 2 or more Extreme= severe symptoms Nursing process: Assessment Diagnosis Risk for SI Outcomes identified Implementation Depression / Bipolar / Mood Disorders Types of mood disorders: depression, alterations in emotions-mania/depression or both. Depressive Disorder Bipolar Disorder (BP 1 more severe: mania/depression/psychosis;hallucinations/illusions) 2: major depressive w hypomania symptoms Seasonal Affective Disorder Post Partum Depression If one episode 50% chance of another, 2 episodes 70% chance, 3 episodes 90% (about environment, genetics) Sadness vs Depression Sadness: Depression: Expected human emotion Never normal Response to life Might happen suddenly Intermittent Continuous Insight Insight variable Little or no functional impairment Functional impairment CBT (Cognitive behavioral therapy) Drugs Counseling Group Therapy Phototherapy (seasonal affective disorder) Electroconvulsive Therapy: used when medications aren’t working or side effects intolerable: takes about 30 min inpatient setting, post recovery.. check ABC’s – maybe some amnesia as side affect Ketamine Therapy: formally an anesthesia, formally club drugs, date rape drug bc hallucinations: infuse through IV for about 6 times. Works in in an hour or two. Medications and group counseling is key treatment CBT: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy: get patient to change thinking pattern Focus on staying in the HERE & NOW: problem solving, coping mechanisms, role play Effective w major depressive order, anxiety, bipolar Once a day to wk but have to stick w it: highly effective Nursing interventions Antidepressants and Mood Stabilizers Alleviate symptoms associate w moderate to severe depression Ellevate/restore mood Prevent recurrence of depression Prevent the swing into mania for bipolar patients Effective with Bipolar, anxiety, alcoholism, schizophrenia, chronic pain/migraine ECT: When is it used for treatment? Pre and Post Care Used when pharm options don’t work: Application of electrodes to head to deliver electrical impulse to brain- causes seizure. Shock stimulates brain chemistry to correct imbalance of depression 6-15 treatments to be effective Schizophrenia / Psychotic Disorders Positive vs negative symptoms Hallucinations vs delusions Types of hallucinations Types of delusional thinking Diagnostic screenings Nursing interventions Types of psychosocial treatment Antipsychotic medications Medications for Depression / Bipolar / Mood Disorders / Schizophrenia / Psychotic Disorders (Do not need to know dosages) Class or type SSRIs: serotonin 2nd Gen ***Increase concentration of norepinephrine, serotonin, and/or dopamine in the body by blocking the reuptake of these neurotransmitters SNRIs: serotonin and norepinephrine 2nd Gen Buproprion 2nd Gen Tricyclic 1st Gen MAOIs 1st Gen Don’t eat tyramine containing foods Prozac (fluoxetine) Paxil (paroxetine) Zoloft (sertraline) Celexa (citalopram) Luvox (fluvoxamine) Lexapro (escitalopram) Trintellix (vortioxetine) Viibryd (vilazodone) Desvenlafaxine (Pristiq, Khedezla) Duloxetine (Cymbalta, Irenka) Ievomilnacipran (Fetzima) Milnacipran (Savella) Venlafaxine (Effexor XR): fewer sexual side effects but hypertension Increase concentration of norepinephrine, serotonin Amitriptyline (pain management, fibromyalgia, migraines) Amoxapine Desipramine (Norpramin) Doxepin (Silinor) (used for insomnia) Imipramine (Tofranil) Maprotiline Nortriptyline (Pamelor) Protriptyline (Vivactil) Trimipramine (Surmontil) Inhibit monoamine oxidase enzymes that inactivate norepinephrine, serotonin and/or dopamine in the body Isocarboxazid (Marplan) Phenelzine (Nardil) Selegiline (Emsam) Tranylcypromine (Parnate) No alcohol because causes psychotic symptoms Sexual dysfunction and weight gain Serotonin syndrome ANXIETY (speaking in front of ppl, or going into the store because too many people) Not effective after taking for longer then 5 days because PRN Really sedates pts, interacts with those listed above. Can aggravate symptoms in schizophrenia and psychotic episodes in older patients. Potential for cardiac dysrhythmias! LETHAL IN OVERDOSE. Huge drug interactions w SSRIs due to serotonin syndrome. Should not be taken with amphetamines and cough meds, decongestants. Insomnia is most common side effect. Most dangerous is hypertensive crisis. Have to take BP prior to administering. Symptoms of Hypertensive Crisis: increased blood pressure, fever sweating, chin to chest = pain Given to pts w no insurance bc cheaper but deadly when taken w street drugs Avoid using MAOI within 2 weeks of adverse agent (SNRI,SSRI,TCA), and 5 weeks of Prozac therapy (takes awhile to get out of symptom) Can be lethal 6-10 times daily dose: use gastric lavage if w/in an hour or hemodialysis if longer Understand Mechanism of Action, which neurotransmitter they work on Not fully understood how they work: start slow and go slow. Takes time to reregulate how the brain works o Why one class would be used before another Mental illnesses they treat Know off label use of some medications used in psychiatry Contraindications Responsibilities of the nurse in administering psychopharmaceuticals Important patient education ie: diet, labs, mixing meds, black box warnings Side effects o Signs and symptoms Mild and Severe side effects – which drugs cause specific side effects o Priority nursing actions o Labs/tests All have sedation and weight gain as a side effect, sexual dysfunction as a side effect. If pt taking heparin or coumadin check Pt, PTT, Inr. Antidepresants can cause hyponatremia in the elderly