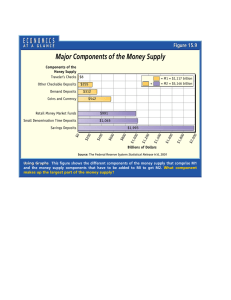
Workshop 9 Money and Monetary Policy 1. Which of the following are wholesale and which are retail? (a) Large-scale deposits made by firms at negotiated rates of interest. ................ retail / wholesale (b) Loans made by high street banks at published rates of interest. ..................... retail / wholesale (c) Deposits in savings accounts in high street banks. .......................................... retail / wholesale (d) Deposits in savings accounts in building societies .......................................... retail / wholesale (e) Large-scale loans to industry syndicated through several banks. ................... retail / wholesale 2. Rank the following assets of a commercial banks in order of decreasing liquidity. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Money at call and short notice Operational balances with the Bank of England Cash Personal loans Sale and repurchase agreements (repos) Mortgages Government bonds (of from one to five years to maturity) High liquidity ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... ......................................................... Low liquidity Money and Monetary Policy Workshop 9 3. Consider the items in the following table, selected from a Bank A’s balance sheet. A range of sterling assets and liabilities of Bank A Notes and coin £m 2 Sight deposits in Bank A 100 Time deposits in Bank A 110 Investments in the public sector 30 Certificates of deposit in Bank A 40 Advances to UK private sector 170 Bills of exchange 20 Loans from other financial institutions 30 Operational balances with the Banks of England 1 Sale and repurchase agreements with Bank of England (repos) 20 Market loans (to other financial institutions) 77 (a) Use these figures to compile a balance sheet of Bank A. Arrange the assets in descending order of liquidity. Liabilities £m Assets Total liabilities £m Total assets (b) What is the cash ratio (counting operational balances as equivalent of cash)? ................................. (c) What is the total of liquid assets ........................................................................................................ (d) What is the liquidity ratio? ................................................................................................................. 2 Money and Monetary Policy Workshop 9 4. Assuming that banks choose to maintain a liquidity ratio of 20 per cent and assuming that new cash deposits of £100m are made in the banking system: (a) Complete the following table which shows how credit is created. £m Banks receive £m 100 Second round deposits rise by ____ Third round deposits rise by ____ Fourth round deposits rise by ____ Fifth round deposits rise by ____ Hold 20 Lend 80 Hold ___ Lend ___ Hold ___ Lend ___ Hold ___ Lend ___ Hold ___ Lend ___ Total deposits after five rounds (b) How much credit will have been created after five rounds? ........................................................ (c) To what level will total deposits eventually increase? ................................................................. (d) Define the bank multiplier ............................................................................................................ (e) What is the bank multiplier in this case? ...................................................................................... (f) How is it related to the liquidity ratio? ......................................................................................... 3 Money and Monetary Policy Workshop 9 5. (a) If banks operate a 25 per cent liquidity ratio, by how much will credit expand if new deposits of £100 million are made by the customers of banks. .............................................................. (b) Show the combined balance sheet (of additional liabilities and assets) for all banks (i) at the beginning, and (ii) at the end of this process. (i) Initial effect LIABILITIES Initial new deposits Total initial new liabilities £m ASSETS £m …… Initial additional liquid assets …… Initial additional credit …… …… Total initial new assets …… .…. (ii) Eventual effect LIABILITIES Eventual new deposits £m ASSETS …… Eventual additional liquid assets …… Eventual additional credit …… Total eventual additional liabilities …… Total eventual additional assets 6. £m …… .…. An increase in the money supply will affect the level of economic activity in the country through a sequence of events. In each of the following, delete the wrong words. 1. The rise in the money supply will lead to a rise / fall in the rate of interest. 2 (a) The rise / fall in the rate of interest will lead to a rise / fall in investment and other forms of borrowing. 2.(b) The rise / fall in the rate of interest will lead to a rise / fall in the rate of exchange.. 3. The rise / fall in the exchange rate will lead to a rise / fall in exports and a rise / fall in imports. 4. The rise / fall in investment and the rise / fall in exports and rise / fall in imports will lead to a multiplied rise / fall in national income and a possible rise / fall in prices. 4