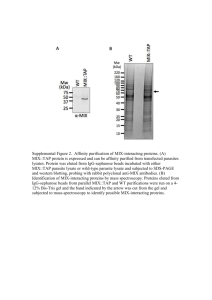
SECTION A 1. C 2. A 3. B 4. C 5. C 6. D 7. A 8. C 9. C 10. B 11. D 12. A 13. C 14. D SECTION B 1. Predicted size of protein = number of amino acids 0.11kDa = 1130 3 amino acids 0.11kDa = 41.43 kDa 41 kDa 2. Four phases of bacterial growth curve. (i) Lag phase (ii) Log/exponential growth phase (iii) Stationary phase (iv) Death/Decline phase Figure 1: Diagram representing bacterial growth curve. 3. (a) When the cell density is 0,6-0,8 the bacteria are usually in the exponential growth phase and at this point the entire cell is wired for growth. (b) Addition of IPTG helps to bind to any repressors in the operator region of lac operon. When this happens, RNA polymerase finds its way to synthesize RNA molecules which later be translated to protein. This process only occurs in the presence of sugar. Without IPTG, repressors stick to the operator region and inhibit RNA polymerase to start synthesizing RNA molecule, as a result, no protein is produced or the process can occur slowly. 4. (a) Components Coomassie Brilliant blue Function It is used as a common analytical dye in SDSPAGE. sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) It is used to denature proteins. Glycerol It is used to add density to the sample. β-mercaptoethanol It is used to break all the disulfide bonds. (b) What do you need to do to in order to analyse the gel? • The gel must be stained using a staining buffer. Components of the staining buffers (i) Coomassie Brilliant blue (ii) Ethanol (iii) Destilled water (c) Discontinuous gel electrophoresis consists of staking and resolving gel with different concentration gradient of polyacrylamide. As a result, proteins separate better as they migrate through different gradient producing high separation resolution of different proteins. 5. Affinity chromatography is a separation method based on a specific binding interaction between an immobilized ligand (Nickel beads) and its binding partner (His-Tagged protein). In this technique, the stationary of this chromatogram is made up of beads that has high binding affinity to the histidine tagged proteins. As a result, proteins with the tag binds to the beads and the remaining molecules with no tag stays unbound. Furthermore, the use of imidazole enables to elute the protein of interest since it has higher binding affinity as compared to the histidine tag in protein of interest. (i) Binding: A sample of different proteins can be used in order to purify only protein of interest. However, only his-tagged protein will bind to the nickel beads since it has high binding affinity. The rest will not bind to the beads as indicated by figure 2 (i). (ii) Wash To remove the unbound molecules or proteins, the washing step is applied. The washing buffer used to wash unbound molecules consists of low concentration of imidazole. The protein of interest will remain bound to the beads since it has high binding affinity through the tag as indicated by figure 2 (ii). (iii) Elute In order to elute the protein of interest, high concentration of imidazole is used as elution buffer to remove the bound proteins since high concentration of imidazole have more binding affinity to the beads than his tagged protein. As a result, protein of interest in then eluted as indicated by figure 2 (iii). (i) Bind (ii) Wash (iii) Elute Figure 2: Diagram representing Nickel affinity chromatography. 6. Marker Gel Dimer (82 kDa) Figure 3: Diagram representing a formation of dimer