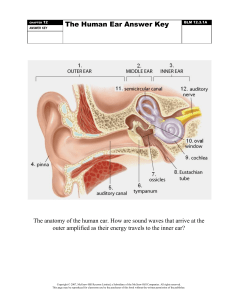
Chapter 15 Ears, Nose, Mouth and Throat ● Air conduction- transmission of sound through the tympanic membrane ● Auricle- also known as the pinna, the outer portion of the ear ● Bone conduction- conduction of sound through the bones of the skull to the cochlea and auditory nerve ● Cerumen-yellow brown wax that lines the canal of the ear (RED OR GREEN ABNORMAL) ● Cochlea- a spiraling chamber that contains the receptors for hearing. Portion of the inner ear, also responsible for equilibrium ● Cold sore- also known as a fever blister, a lesion or blister on the lip ● Eustachian tube- auditory tube that connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx. Helps to equalize air pressure on both sides of the tympanic membrane ● Fever blister- see cold sore ● Helix- the external large rim of the auricle ● Lobule- earlobe ● Mastoiditis- refers to the inflammation or infection of the mastoid bone Can be caused by middle ear infection or throat infection. Difficult to treat. Spreads to the brain. (or can) ● Nasal polyps- smooth, pale, benign growths found in many patients with chronic allergies ● Ossicles- bones of the middle ear (malleus, incus, stapes) ● Otitis externa- infection of the outer ear that causes redness and swelling of the auricle and ear canal and scanty drainage (swimmer’s ear) ● Otitis media- infection of the middle ear (red bulging eardrum, fever, hearing loss) ● Palate- anterior portion of the roof of the mouth ● Paranasal sinuses- mucus-lined, air-filled cavities that surround the nasal cavity and perform the air-processing functions of filtration, moistening, and warming ● Pinna- see Helix ● Tragus- stiff projection that protects the anterior meatus of the auditory canal (if painful when pressed, ABNORMAL) ● Tympanic membrane- thin translucent membrane is pearly gray in color and lies obliquely in the canal. It separates the external and middle ear ● Uvula- fleshy pendulum that hangs from the edge of the soft palate in the back of the mouth. Focused questions, review pages 270-273. Remember to ask questions like “do you work in a noisy environment? Do you wear hearing protection or get hearing tests?” “Any change in your hearing? Describe your hearing” -CSF can be determined through the presence of glucose. This is an abnormal clear drainage of the ear suspicious of head injury -Hearing loss in 1 ear only can be suggestive of a ruptured ear drum. - Tophi: small white nodules on the helix or antihelix that contain uric acid crystals and are a sign of GOUT - Remember how to check for a perforated septum and that it could indicate a drug problem -Know the difference between rhinitis and sinusitis -Remember her story about tonsil stones. (BLECH)