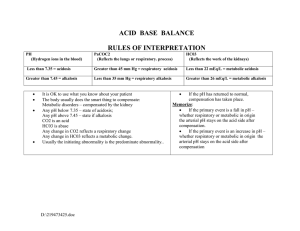
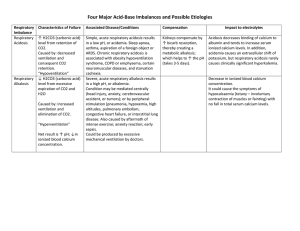
1. A nurse reviews the arterial blood gas results of a client and notes the following: pH 7.21, Pco2 of 60, and HCO3- of 24. The nurse analyzes these results as indicating which condition? A. Normal B. Respiratory acidosis uncompensation C. Metabolic acidosis, partial compensation D. Respiratory acidosis, complete compensation Answer: B Answer: D is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m 2. A nurse reviews the arterial blood gas results of a client and notes the following: pH 7.45, PaCO2 50, HCO3- 30 nurse analyzes these results as indicating which condition? A. Respiratory Acidosis, Partially Compensated B. Respiratory Alkalosis, Fully Compensated C. Metabolic Alkalosis, Partially Compensated D. Metabolic Alkalosis, Fully Compensated 3. A nurse reviews the arterial blood gas results of a client and notes the following: pH 7.6, PaCO2 53, HCO3- 38 nurse analyzes these results as indicating which condition? A. Metabolic Alkalosis, Fully Compensated B. Respiratory Alkalosis, Fully Compensated C. Metabolic Alkalosis, Partially Compensated D. Respiratory Acidosis, Partially Compensated Answer: C 4. A young man with chronic asthma has a PaCO2 of 48 mmHg, a pH of 7.31, and a normal HCO3 blood gas value. The nurse interprets this as which of the following? A. Metabolic acidosis B. Respiratory alkalosis C. Respiratory acidosis D. Metabolic alkalosis Th Answer: C sh 5. A 54 old patient has COPD and was brought into the ED. After measurement of arterial blood gas, they showed pH 7.31, PaCO2 68, HCO3 28, and PaO2 60 mm Hg. The nurse would interpret which of the following? A. Respiratory Acidosis, Partially Compensated B. Respiratory Acidosis, uncompensated C. Metabolic Alkalosis, Fully Compensated D. Metabolic Acidosis, partially compensated Answer: B This study source was downloaded by 100000767548566 from CourseHero.com on 07-11-2021 10:08:37 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/60793662/ABG-notesdocx/ is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Arterial blood gases (ABGs) are an important to monitor the acid-base balance of patients. They may help make a diagnosis, indicate the severity of a condition and help to assess treatment. ABGs provide the following information: oxygenation, adequacy of ventilation, and acid-base levels. As blood passes through your lungs, oxygen moves into the blood while carbon dioxide moves out of the blood into the lungs. Blood for an ABG test is taken from an artery. An ABG measures: Partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2). This is pressure of oxygen dissolved in the blood and how well oxygen is able to move from the airspace of the lungs into the blood. Partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2). This measures the pressure of carbon dioxide dissolved in the blood and how well carbon dioxide is able to move out of the body. pH. The pH measures hydrogen ions (H+) in blood. The pH range is 7.35 and 7.45. A pH of less than 7.0 is acid and a pH greater than 7.0 is basic (alkaline). Blood is slightly basic. Bicarbonate (HCO3). Bicarbonate is a chemical (buffer) that keeps the pH of blood from becoming too acidic or too basic. Oxygen saturation (O2Sat) values. O2 content measures the amount of oxygen in the blood. Oxygen saturation measures how much of the hemoglobin in the red blood cell is carrying oxygen (O2). Normal values for ABGs: pH 7.35-7.45 PaCO2 35-45 HCO3 22-26 Respiratory Acidosis- cause of CO2 build up in lungs. To compensate for this the kidney starts to conserve bicarbonate to increase the blood’s pH back to normal. Cause: “ DEPRESS” sh Th Drug: opioids, sedative and poison can cause respiratory depression. (Hypoventilation). Disease of neuromuscular system (guillain-barre, myasthenia gravis. Edema (pulmonary) extra fluid in the lung causes impaired gas exchange Pneumona-excessive mucous production affect gas exchange. Respiratory center of brain damaged (brain injury, stroke) Emboli- blocks the pulmonary artery or branch of the lungs causes carbon dioxide to increase. Spasms of bronchial tubes (asthma) bronchioles constrict and you have decreased gas exchange Sac elasticity of alveolar sac are damaged and this restricts air flow in and out of the lungs and this increases carbon dioxide (Emphysema & COPD) Sign and symptoms: Altered level of consciousness Confusion This study source was downloaded by 100000767548566 from CourseHero.com on 07-11-2021 10:08:37 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/60793662/ABG-notesdocx/ Personality Changes LOC Progressively decreases Hypotension Bradypnea Dysrhythmias Pulse Elevated Nursing interventions: oxygen therapy, encourage deep breath and coughing, maintain patent airway, bronchodilation, mucolytic, place in semi-flowers, monitor heart rate and rhythm, administer IV solution such as LR. Respiratory alkalosis (Hyperventilation ) To compensate for this the kidneys, start to excrete bicarbonate to decrease the blood’s pH back to normal. is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Cause: TACHYPENA Temperature increase due to increased metabolic needs of the body which causes the respiratory center to try to compensate by making the respiratory rate increase. Aspirin toxicity: too much aspirin in the body leads to hyperventilation Controlled ventilation mechanical ventilation Hyperventilation expelling too much carbon dioxide hYsteria (anxiety) leads to rapid breathing and expelling of carbon dioxide. Pain…rapid breathing blowing off too much carbon dioxide. Pneumonia Neurological injuries from a head injury or Embolism or Edema in the lungs Asthma due to hyperventilation Sign and symptoms: Syncope Vertigo Seizures Coma Th Nursing Interventions: oxygen therapy, breathing techniques, anxiety reduction, closely watch patients on mechanical ventilation to ensure breaths are not hyperventilating the patient, provide safety and seizure precautious. Assess level or awareness. sh Metabolic Acidosis is a metabolic problem due to the buildup of acid in the body fluids which affects the bicarbonate. This is from increased acid production, decreased acid excretion and loss of too much bicarb. To compensate, the repiatory system will cause the body to start to hyperventilate by increase breathing. (Kussmauls) The body is trying to expel CO2, to help increase the pH. Cause: This study source was downloaded by 100000767548566 from CourseHero.com on 07-11-2021 10:08:37 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/60793662/ABG-notesdocx/ DKA Shock Diarrhea Impaire kidney function Lactic acidosis Excessive intake of acid (aspirin) is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Sign and Symptoms Weakness Altered level of Consciousness Tachypnea Kussmal respirations Abdominal discomfort N/V Dysrhythmias Hypotension Coma Nursing Interventions Assess electrolyte levels Watch neruo status Dialysis may be needed if patient is renal failure Give insulin if DKA Administer antidiarrheal Provide rehydration If bicarbonate low, administer sodium bicarbonate Metabolic Alkalosis: a metabolic problem caused by the excessive loss of acids or increased amount of bicarb produced in the body that leads to an alkalotic state in the body. sh Th Cause: “ALKALI” Aldosterone production excessive (hyperaldosteronism) activates renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Loop diuretics (Lasix) or thiazide therapy: causes the kidneys to waste hydrogen ions and chloride through the urine which in turn increases the bicarb. alKali ingestion of food (baking soda, milk, antacids) increases bicarb level in the blood Anticoagulant “citrate” used as a storage agent in blood and during continuous forms of renal replacement therapy Loss of fluids – cause by vomiting and GI suctioning. Increased sodium bicarb administration (trying to correct metabolic acidosis) Sign and symptoms: Altered Level of Consciousness Nausea Vomiting Diarrhea This study source was downloaded by 100000767548566 from CourseHero.com on 07-11-2021 10:08:37 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/60793662/ABG-notesdocx/ Bradypnea Seizures Coma sh Th is ar stu ed d vi y re aC s o ou urc rs e eH w er as o. co m Nursing Intervention: Based on cause, if vomiting give antiemetic, stop diuretic Monitor electrolyte status Doctor may order diamox (Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors): a diuretic which reduces the reabsorption of bicarb Watch ABGs and signs of respiratory distress This study source was downloaded by 100000767548566 from CourseHero.com on 07-11-2021 10:08:37 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/60793662/ABG-notesdocx/ Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)