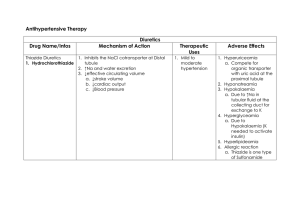
ANTI HYPERTENSIVE DRUGS 1.Alpha blocker Types Drugs Non-selective Phenoxybenza mine (LA) Selective MOA Phentolamine (SA) Doxazosine (LA) Prazosin (SA) • A1 / a2 adrenoblockers will block aR in BV • Red SM contract • Vasodilation • Red VR , increase blood flow • Red BP Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic Not used in chronic essentials hypertension (dt a2R block) Only used sometime as phaeochromocytoma used in chronic essentials hypertension ADRs • Orthostatic hypotension [phenomenon of first dose ; sudden BP drop & dev of orthostatic collapse after first dose ] *remind the PT not to stand up quickly • Reflex tachycardia (less in a1 selective) • Drowsiness , weakness • Urinary incontinence • Nasal congestion Clinical uses / Add Ons 1. Hypertension • + diuretics (dec Na & H2O retention • +propranolol [B blocker] (a1 blocker has favor effects on lipid met, combine with B blocker red the effects) 2. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (red prostatic and urethral sm tone & provide sympa relief to PT with early hyperthrophy) 3. Phaeochromocytoma 2.Beta blocker Types Drugs Cardio nonselectives (B1& B2 blocker) Propranolol MOA ▪ ▪ Block existing sympa tone Greater effects if sympa tone high Heart – dec HP, CO & pacemaker activity BV- dec peripheral resistance dt red renin release , dec AT II , vasodilation , low BP Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic Prototypes of nonsel comp antagonist at B1 & B2 R PKs ▪ Oral ▪ High lipid solubility (can cross BBB go to CNS ; leads to drowsiness ) ▪ 2/3 inactivated via first pass met ▪ Large interindividual variation ADRs Effects ▪ Common: dizziness. fatigue, depression ▪ Chronic use in hypertension: Increase VLDL & LDL (bad lipid profile) ▪ Use with caution in diabetics masks signs of hypoglycemia (tachycardia) that are important "clues" to diabetic patient ▪ Contraindicated in most asthmatics and COPD: broncho-constriction due to B2 blockage ▪ Sudden withdrawal syndrome (B receptor synthesis is increased by B blocker use. Example of receptor up-regulation) ➢ rebound hypertension, anginal attack & possibly MI if drug suddenly withdrawn after chronic therapy Contra: ➢ acute treatment heart failure ➢ 2nd and 3rd degree heart block ➢ Cardiogenic shock Drug interaction ➢ Other hypotensive meds (guanethidine , methyldopa ) Cause sudden drop in BP ➢ Other cardiodepressive agents (Ca channel blockers, lidocaine) Worsen effects leads to HF ➢ Insulin & oral hypoglycemic D Prolong hpgc and masks sign Clinical uses / Add Ons Types Drugs Cardio b1 selective blocker Metoprolol (lipid soluble) Atenolol (water soluble) Esmolol MOA Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic Very rapid onset & short duration of action B blocker with partial agonist activity Pindolol ISA – exerting low level agonist activity at the B- adrenergic R while simulatneouslt acting as R site antagonist aB blocker Labetolol Comp block B1 R in myocardium and a1 R in vascular SM →vasodilation→ dec systhemic arterial BP and vascular resistance →no red in HR, CO ,SV ( a & b combines block activity No reflex tachycardia Better lipid profile ADRs Effects Clinical uses / Add Ons Safer for asthma and (Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) COPD patients Hypertension Hypertension Stable angina Use as IV infusion for peri-operative tachycardia and hypertension Cause little or no • Sinus bradycardia resting HR • Sick sinus syndrome depression but • Raynaud like block increased rate symptoms dt exercise • Chronic obstructive lung disease Same with non• Preg induced selective B1&B2 hypertension • Hypertensive emergencies (IV) • Pheochromocytoma (tumor at adrenal medulla→cause high NorE and NorA) 3.Centrally acting antihypertensive drugs Types Drugs MOA 1st gen- a2 agonist Clonidine a-Methyldopa • Methyldopa is structural Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic • analog of DOPA • Alpha-methyldopa is • converted to methyl norepinephrine • It will act as agonist to alpha 2 adrenoreceptor(Gi Receptor) in medulla • It will inhibit release of noradrenaline and norepinephrine • Causing decrease in peripheral sympathetic outflow • It will cause vasodilation • Lead to reduction in TPR • Thus lowering the blood pressure 2nd gen – imidazoline receptor I2 agonist Moxonidine ADRs Imidazoline I2 R found in medulla oblongata Cause decc in SNS activity and dec BP • • • Higher affinity to Imidazoline I2 R than a2 R Effects Edema (vasodilate→fluid retention Sedation (increase effects of sedative hypnotic D , acts on CNS) Orthostatic (postural) hypotension Bradycardia (increase vagal stimulation of SA Node + sympa withdrawal) Cry mouth WARNING Rebound hypertension may be severe if clonidine stop suddenly • Clinical uses / Add Ons Major therapeutic indications • Chronic outPT managemen t of hypertensio n • Amethyldopa uses during pregnancy Treat mild moderate hypertension 4.Diuretics Drugs First line drugs Thiazides (hydrochlorothiazides, chlorthalidone) MOA Pharmacodynamic ADRs & Pharmacokinetic • Low dose safe • K+ loss (min by using low dose , and effective in diet and combination with K+preventing sparing diuretic, triamterene) hypertensive complications • Hyperuricemia (bad for gout) • Dyslipedimia (increase LDL & VLDL → atherosclerosis) • Dyperglycemia (glucose intolerance , bad for diabetes) Clinical uses / Add Ons • Monotherapy of mild hypertension • Multidrugs therapy in severe cases • Low dose minimize side effect (K loss) • Can be use with symphatolytics , ACEi , CCB 5. Ca2+ channel blockers (CCB) Types Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic Dihydropyridin Nifedipine (SA) MOA Predominant actions on es •Antagonist Ca2+ block L- Arterioles type channels (found in h and bv) •Dec freq of opening in respond to depolarization •Calcium cannot enter Amlodipine SM artery / cardiac M (LA) •No contraction of muscle Phenylalkylam ines Drugs MOA Verapamil Predominant actions on heart Diltiazem • Reflex tachycardia • Increase sympa activity • Ankle edema • Headache In btwn Arterioles & heart Effects Cardiac Minimal effects on Ca2+ entry to heart muscle Vascular Relaxation of arterioles more than vein→ red afterload not preload →vasodilation →red TPR →red BP→reflex tachycardia Reduce entry of Ca2+ by blocked the channel leads to • red pacemaker activity→ red HR • red atrium conduction to vent • red contraction → red SV (Same ) Lesser effect on arterioles & more depression to heart • Ankle edema • Headache • Constipitation Contra : • Sinus bradycardia • AV conduction defects Contraindication : Severe cardiac failure benzothiazepi nes ADRs (Same) Clinical uses / Add Ons • Red BP • Hypertensive emergencies • Prinzmetal’s angina (Cause by vasospasm of coronary A) • Hypertension • Angina pectoris 6. RAS Inhibitor Types Drugs MOA ADRs DRI Aliskiren • block cleavage of AT to AT1 (inhibit active enzyme site of renin) • dec BP • Limitation of uses renin inhibitiors ( block – feedback by AT II on renin synthesis) ACEi Enalapril (LA) • Enalapril is an angiotensin converting enzymes inhibitors (ACEi) Captopril (SA) • Enalapril will bind and inhibit ACE • So there will no production of angiotensin II • Angiotensin II is the most potent vasoconstrictor • Dry-nonproductive cough 25% (effect on bradykinin metabolism) • Angioedema • Acute renal failure • Hyperkalemia (especially if PT take K sparing diuretic) Contraindication / indication Clinical uses / Add Ons contraindications -pregnancy Fetal hypotension Fetal renal failure Fetal malformation or death • Treat HPT • CHF (prvt progressive LV remodelling) • Renal insuff. (diminish proteinuria & stabilize renal fx • So the blood vessel will vasodilate • Thus TPR and VR will decrease • Reduce in VR will cause decrease in CO • Thus the blood pressure will decrease ARBs Losartan • • • • Block AT1 R directly Cause vasodilation Red secrete vasopressin (ADH) Red prod & secret. of aldosterone • No dry cough (no effect on bradykinin metab) • Rare ADR ➢ angioneurotic edema (less than ACEi) ➢ hyperkalemia • • angioedema pregnancy • HPT • CHF • Renal insufficiency 7. VASODILATORS Types Drugs Hydralazine Minoxidil Na nitroprusside MOA Nitrix Oxide donator • cause fall intracell Ca2+ • red IP3, limit Ca release from SR of smooth muscle • less SM contraction • BV vasodilate • Increase NO Potassium channel opener • activates ATP modulated K+channel • cause K+ efflux in smooth muscle • hyperpolarisation n muscle relax • vasodilation • red BP Nitrix Oxide donator • • • • • nitrovasodilator Release NO thus activate guanylylcyclase increase Cgmp vasodilation Pharmacodynamic & Pharmacokinetic • directly acting arteriolar vasodilator • decrease TPR • less postural hypotension • no action on coronary arteries • Well absorbed from GIT • Longer action • rapidly & constantly acting vasodilator • arteriolar & venous dilation PKs • IV • Rapid onset ~ 30 secs • Shorter action ADRs ➢ extension of pharmacological effect of drugs • Flushing • reflex tachy • Na retention Clinical uses / Add Ons • • not a 1st line drug in HPT Usually given in low dose with other drug ➢ immunological reaction • systemic lupus erythematous (in young female) • Hypertrichosis (promote hair growth) • salt & water retention • reflex tachy • HPT • Alopecia (baldness)- topical application • reflex tachycardia • • • cyanide poisoning (high dose, long, • chronic usage →cyanide accumulation) • • hypotension Arrythmia HPT emergency to improve CO in CHF, in HPT patient induce controlled hypotension during anaesthesia