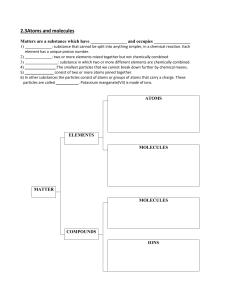
Properties of Matter - Pressure - Density Please remember to mark attendance on Teachworks during the lesson. Student Notes need to be sent 24-48 hours from the lesson. email frontdesk@c3coaching.com.au after lesson to notify them that lesson notes are completed so that they can be checked - David learns Visually , examples and diagrams, Properties of Matter Review definitions of atoms; molecules; compounds and mixtures o The standard model of matter is that everything in the universe is found to be made from a few basic building blocks called fundamental particles, governed by four fundamental forces. o ATOMS: an atom is made of positively charged proton and and neutrally charged neutron which makes up a nucleus, which is orbited by negatively charged electron. Majority of mass of an atom lies in the nucleus o Molecules: are a group of atoms chemically bonded to each other (which o o can be considered a 'direct connection', if you will). The molecule can consist of atoms of the same element, or atoms of different elements. Compounds A pure substance made from atoms of different elements chemically bonded together. All compounds are molecules. But not all molecules are compounds Mixtures are impure substance made of two or more substances not chemically bonded. o Describe molecules and their properties of attraction and repulsion o Molecules are atoms bonded together chemically. (eg. H2O) o Dipole-dipole attraction and repulsion occur Dipole -dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule. Polar molecules align so that the positive end of one molecule interacts with the negative end of another molecule. Intermolecular forces are attraction and repulsion of positive and negative charges Unlike covalent bonds between atoms within a molecule (intramolecular bonding), dipole-dipole interactions create attractions between molecules of a substance ( intermolecular attractions). positive hydrogen atom in H2O attracts negative oxygen atoms in H2O. Explain the kinetic theory of matter with reference to solids, liquids and gases o The kinetic theory of matter says that all matter consists of many, very small particles which are constantly moving or in a continual state of motion. The amount of movement of particles is determined by their energy and their intermolecular attractions with other particles. The particles might be atoms or molecules o Three important theories of kinetic theory: 1. Matter is composed of small particles (atoms, molecules, and ions). 2. The space the molecules occupy (volume) depends on the space between the molecules and not the space the molecules occupy themselves. 3. The molecules are in constant motion. This motion is different for each of the three states of matter. They are colliding with each other and the walls of their container. Temperature: Temperature is the term used to explain how hot or cold an object is. Temperature is the average kinetic energy of particles in the substance. Water molecules at 0º C. lave lower kinetic energy than water at 100º C Discuss the ideal gas laws: Pressure law: relationship between pressure and temperature of a gas o Temperature in Kelvin, NOT degree Celsius. o Pressure directly proportional to temperature given that the volume of gas is kept constant (P ∝ T) o o o Formula: When temperature increase, kinetic energy increase, air molecules collide with the wall of container at higher speed , and more frequently. As a result, the pressure of the gas will increase within a CLOSED container (constant volume) o Charles’ law o Boyle’s law: relationship between pressure and volume of gas o Formula: o Pressure is inversely related to Volume, this means when P, Vol . When P Vol o Combined gas law o Calculate different variables based on the ideal gas law equations o Describe the following properties of matter: Diffusion o Surface tension o Adhesion and cohesion o Capillarity Links: https://www.le.ac.uk/se/centres/sci/selfstudy/particle01.html#:~:text=The%20kinetic%20theory%20of %20matter,their%20relationship%20to%20other%20particles. – kinetic theory of matter Pressure law: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K0V1Lcy2AnE Boyle’s law: https://www.pharmacology2000.com/physics/Chemistry_Physics/gas_law_problems1.htm Density Define density o Apply the formula for density to calculate [for example] mass given volume and density. o Describe how the density of solids, liquids and gases can be measured. o Define Relative Density [specific gravity] and state that it has no units. o State that relative density can be greater, less than or equal to 1. o Describe how density is affected by: The compression or expansion of an object o Change of volume due to change of temperature o Apply knowledge of density to deduce how the loading of cold fuel affects the relative density, the weight of full tanks and the available range Pressure Define pressure and state the unit used for the measurement of pressure Calculate pressure given mass and surface area Describe pressure within a liquid and explain why pressure increases with depth State Pascal’s principle i.e. that pressure acts equally in all directions and acts on equal areas with equal force Apply Pascal’s principle to explain the operation of simple hydraulic machines Describe the operation of car brakes in terms of hydraulic principles Explain how hydraulic machines can be used as force multipliers Describe pressure within the earth’s atmosphere Explain why the pressure of the atmosphere is not normally noticeable to humans and why it puts no stress on to un-pressurized aircraft Describe the pressure difference that exists between the inside and the outside of a pressurized aircraft and why this must be limited Describe the following devices for measuring pressure: Bourdon tube U-tube manometer Mercury barometer Aneroid barometer Describe some of the implications of unusually low or high pressure: In aviation In space