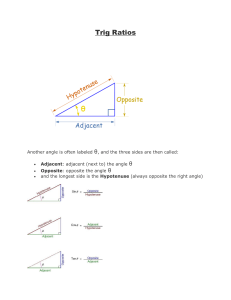
Trigonometry brochure Canayel Agdan 9-Helium TRIGONOMETRY Trigonometry comes from the ancient greek word: Trigon, meaning :triangle, and Metron, meaning: Measure. So Trigonometry is the study involving triangles.There are three sides of a rightangled triangle with respect to any of its acute angles are known as the trigonometric ratios of that particular angle. The three sides of the right triangle are: Hypotenuse which is the longest side, adjacent which is the side next to the angle opposite which is the opposite side to the angle THERE ARE 3 BASIC TRIGOMETRIC RATIO WICH IS THE SINE 0 =OPPOSITE/HYPOTENUSE/SO H, COSINE 0= ADJACENT/HYPOTENUSE/CA H, AND TANGENT 0= OPPOSITE/ADJACENT /TOA THERE ARE 3 OTHER TRIGONOMIC RATIO CALLED THE RECIPROCAL TRIGONOMETRIC RATIO WHICH IS, COSECANT 0= HYPOTENUSE/OPPOSITE/CH A, SECANT 0= HYPOTENUSE/ADJACENT/SH A, AND COTANJENT= ADJACENT/OPPOSITE/CAO TIGONOMETRIC RATIOS OF SPECIAL ANGLES in trigonometry 30°, 45°, 60° are called as special angles and they always lie in the first quadrant. This is the table of the trigonometric ratios of special angles. Computing the numerical value of trigonometric ratios using ANGLE OF ELEVVATION AND ANGLE OF DEPRESSION special angles Example: ANGLE OF ELEVATION The angle of elevation is an angle that is formed between the horizontal line and the line of sight basically the angle of elevation is the line above the line of sight ANGLE OF DEPRESSION The angle of depression is the the angle of depression is the angle between the horizontal line basically it is the angle of depression is the line below the liine of sight