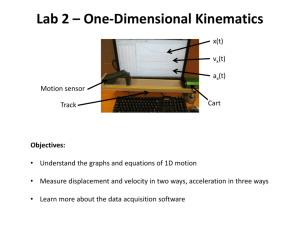
1. Any substance that has mass and takes up space is called A) matter. C) force B) energy. D) work 2. When electrical energy is converted into any other form of energy, the total amount of energy A) B) C) D) increases. decreases. remains the same. cannot be determined. 6. As a pendulum moves from the bottom of its swing to the top of its swing, the A) B) C) D) kinetic energy of the pendulum increases kinetic energy of the pendulum remains the same potential energy of the pendulum decreases potential energy of the pendulum increases 7. A car travels at 84 kilometers per hour for 7 hours. How far did it travel? A) 12 km C) 91 km B) 84 km D) 588 km 8. A cart travels a distance of 30 meters in 15 seconds. The average speed of the cart is A) 0.20 m/s C) 0.50 m/s 3. As the pendulum swings from position A to position B as shown in the diagram above, which occurs? A) The kinetic energy decrease is more than the potential energy increase. B) The kinetic energy increase is more than the potential energy decrease. C) The kinetic energy decrease is equal to the potential energy increase. D) The kinetic energy increase is equal to the potential energy decrease. 4. whether the following examples have kinetic energy, potential energy, both or neither. A stretched rubber band. A) kinetic energy C) both B) potential energy D) neither 5. Which statement best describes the energy changes that occur while a child is riding on a sled down a steep, snow-covered hill? A) Kinetic energy decreases and potential energy increases. B) Kinetic energy increases and potential energy decreases. C) Both potential energy and kinetic energy decrease. D) Both potential energy and kinetic energy increase. B) 2.0 m/s D) 5.0 m/s 9. The average speed of a plane was 500 kilometers per hour. How long did it take the plane to travel 100 kilometers? A) 0.2 hour C) 0.7 hour B) 0.5 hour D) 5 hours 10. If the force used to push a shopping cart increases, the cart's acceleration will A) decrease C) remain the same B) increase 11. A runner changing speed from 3 meters per second to 5 meters per second is an example of A) B) C) D) acceleration. velocity. changing direction. constant speed. 12. An object is uniformly accelerated from rest to a speed of 25 meters per second in 10 seconds. The acceleration of the object is A) 1.0 m/s 2 C) 1.5 m/s 2 B) 2.0 m/s 2 D) 2.5 m/s 2 13. The diagram below shows a stationary cart on a frictionless surface. Two unequal opposing forces are about to be applied to the cart. If the unequal opposing forces are applied to the cart at the same time, what will occur? A) The cart will move to the left. B) The cart will move to the right. C) The cart will alternate between moving left and right. D) The cart will remain stationary. 14. A "push or pull" best describes the term A) work C) potential energy B) momentum D) force 15. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of science. The diagram represents a person pushing a 50-kg box up a ramp. Which force will decrease if the surface of the ramp is made smoother? A) gravity C) friction B) magnetism D) electricity 16. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of science. The diagram represents a cart with a mass of 10 kilograms (kg) being pulled to the right with a force of 20 newtons (N). Identify the force between the wheels of the cart and the ground surface that opposes forward motion of the cart. 17. The force of gravitational attraction between two objects depends on the distance between the objects and their A) buoyancies C) masses B) temperatures D) shapes 20. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents a simple pendulum with a 2.0-kilogram bob and a length of 10. meters. The pendulum is released from rest at position 1 and swings without friction through position 4. 18. The gravitational force between the Moon and Earth depends on A) B) C) D) their masses, only their diameters, only their masses and how far apart they are their diameters and how far apart they are 19. Which two factors determine the gravitational attraction between two objects? A) B) C) D) time and temperature shape and orbital speed color and hardness mass and distance apart At which position does the bob have its maximum kinetic energy? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4