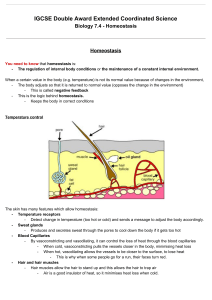
IGCSE Double Award Extended Coordinated Science Biology 7.4 - Homeostasis Homeostasis You need to know that homeostasis is: - The regulation of internal body conditions or the maintenance of a constant internal environment. When a certain value in the body (e.g. temperature) is not its normal value because of changes in the environment, - The body adjusts so that it is returned to normal value (opposes the change in the environment) - This is called negative feedback - This is the logic behind homeostasis. - Keeps the body in correct conditions Temperature control The skin has many features which allow homeostasis: - Temperature receptors - Detect change in temperature (too hot or cold) and sends a message to adjust the body accordingly. - Sweat glands - Produces and secretes sweat through the pores to cool down the body if it gets too hot - Blood Capillaries - By vasoconstricting and vasodilating, it can control the loss of heat through the blood capillaries - When cold, vasoconstricting pulls the vessels closer in the body, minimising heat loss - When hot, vasodilating allows the vessels to be closer to the surface, to lose heat - This is why when some people go for a run, their faces turn red. - Hair and hair muscles - Hair muscles allow the hair to stand up and this allows the hair to trap air - Air is a good insulator of heat, so it minimises heat loss when cold. Blood glucose level control The pancreas produces two hormones which allow the liver to change blood glucose levels - Insulin - tells the liver to decrease blood glucose level by converting glucose into glycogen - Glucagon - tells the liver to increase blood glucose level by breaking down glycogen With negative feedback, - When blood glucose level is too high, the pancreas produces insulin - To decrease the blood glucose level - When blood glucose level is too low, the pancreas produces glucagon - To increase the blood glucose level This allows the blood glucose level to be at the right level. The syllabus says you should be able to, (SO check if you can): - Define homeostasis as the maintenance of a constant internal environment. - Identify, on a diagram of the skin: hairs, sweat glands, temperature receptors, blood vessels and fatty tissue. - Describe the maintenance of a constant body temperature in humans in terms of insulation and the role of temperature receptors in the skin, sweating, shivering, vasodilation and vasoconstriction of arterioles supplying skin-surface capillaries and the coordinating role of the brain. - Explain the concept of control by negative feedback. - Describe the control of the glucose content of the blood by the liver, and by insulin and glucagon from the pancreas.