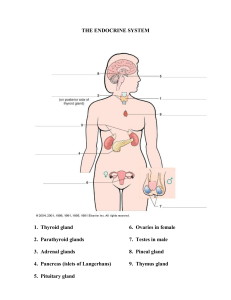
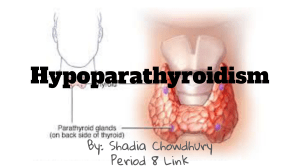
PARATHYROID GLAND DISORDERS Prepared by: Dr. PA Maroma Parathyroid Gland Disorder Parathyroid Gland ⚫ Produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) or parathormone which regulates calcium and phosphorous balance ⚫ Hyperparathyroidism Hypercalcemia ⚫ Hypoparathyroidism Hypocalcemia Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hyperparathyroidism ⚫ characterized by excessive secretion of the PTH ⚫ Causes: ⚫ parathyroid adenoma ⚫ congenital hyperparathyroidism ⚫ multiple endocrine neoplasia ⚫ Secondary hyperparathyroidism can occur due to ⚫ rickets (softening of the bone) ⚫ vitamin D deficiency ⚫ chronic renal failure Pathophysiology PTH Bone resorption Ca++ in the blood Ca++ reabsorption in Kidney & absorption in GI hypophosphatemia renal stone formation, osteoporosis pancreatitis and peptic ulcer Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hyperparathyroidism: Assessment ⚫ CNS ⚫ psychomotor and personality disturbances, loss of memory, depression, psychosis, stupor and coma ⚫ GI ⚫ abdominal pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia and constipation ⚫ Neuromuscular ⚫ fatigue, marked muscle weakness and atrophy Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hyperparathyroidism: Assessment ⚫ Renal ⚫ nephrolithiasis, renal insufficiency ⚫ Skeletal ⚫ chronic lower back pain, fractures, bone tenderness and joint pain Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hyperparathyroidism: Assessment Diagnostic test: ⚫ Increased serum calcium, with decreased level of phosphate ⚫ X-rays will show diffuse demineralization of bones, bone cysts, erosions ⚫ Increased alkaline phosphatase levels Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hyperparathyroidism: Medical Management ⚫ Surgery to remove the adenoma ⚫ Increased fluids to force diuresis ⚫ Dietary restrictions of calcium ⚫ Medications: ⚫ Furosemide and ethacrynic acid, oral calcitonin, oral potassium phosphate Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism ⚫ deficiency of PTH, that leads to hypocalcemia and produces neuromuscular symptoms ranging from paresthesia to tetany ⚫ Causes: ⚫ congenital absence, autoimmune disease ⚫ removal of the parathyroid glands ⚫ post-thyroidectomy ⚫ massive thyroid radiation therapy Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism: Assessment ⚫ Manifestations of HYPOCALCEMIA ⚫ positive Chvostek’s and Trosseau’s ⚫ tetany, paresthesia ⚫ neuromuscular irritability, DTR ⚫ psychosis ⚫ dysphagia, abdominal pain ⚫ arrhythmias ⚫ cataracts ⚫ hair loss, brittle nails, dry skin ⚫ weakened tooth enamel Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism: Assessment ⚫ Diagnostic Test ⚫ PTH calcium ⚫ serum phosphate ⚫ X-ray reveals increased bone density ⚫ ECG- prolonged QT intervals and QRS complex and ST segment changes ⚫ serum Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism ⚫ Medical Management ⚫ Therapy includes vitamin D supplements, and supplemental calcium ⚫ Life-threatening hypocalcemia is managed by IV calcium gluconate to raise calcium levels. ⚫ Sedatives and anti-convulsants are used to prevent seizures Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism ⚫ Nursing Interventions ⚫ Maintain a patent IV line & keep calcium gluconate 10% solution available ⚫ Administer prescribed sedatives, anticonvulsants & calcium gluconate (slow IV) ⚫ Institute seizure precaution Parathyroid Gland Disorder Hypoparathyroidism ⚫ Nursing Interventions ⚫ Keep a tracheostomy set and endotracheal tube available ⚫ Watch out for cardiac arrhythmias and decreased cardiac output ⚫ Encourage to take high calcium and low phosphate diet early in the disease process ⚫ Creams and lotions can be used to sooth dry skin Quick Review Quick Review Anti-diuretic hormones (ADH) ⚫ Enhance re-absorption of H2O in the kidneys ⚫ Used in Diabetes Insipidus (DI) ⚫ Desmopressin ⚫ Pitressin and Lypressin intranasally IM ⚫ SIDE-effects ⚫Flushing and headache ⚫Water intoxication Quick Review Thyroid hormones ⚫ Levothyroxine (Synthroid) and Liothyroxine (Cytomel) ⚫ Used to replace hormonal deficit in HYPOTHYROIDSM ⚫ Side-effects ⚫Nausea and Vomiting ⚫Signs of metabolism (tachycardia, hypertension, etc..) Quick Review Thyroid hormones: Nursing Responsibility ⚫ Monitor weight, VS ⚫ Instruct client to take daily medication the same time each morning WITHOUT FOOD ⚫ Advise to report palpitation, tachycardia, and chest pain ⚫ Instruct to avoid foods that inhibit thyroid secretions like cabbage, spinach and radishes Quick Review ANTI-THYROID medications ⚫ Inhibit the synthesis of thyroid hormones ⚫ Methimazole (Tapazole) ⚫ PTU (Prophylthiouracil) ⚫ Iodine solution (SSKI) and Lugol’s solution ⚫ Side-effects ⚫ N/V ⚫ Diarrhea ⚫ AGRANULOCYTOSIS (WBC) ⚫ Most important to monitor Quick Review ANTI-THYROID medications Nursing responsibilities ⚫Monitor VS, T3 and T4, weight ⚫Take medications WITH MEALS to avoid gastric upset ⚫Instruct to report SORE THROAT or unexplained FEVER ⚫Monitor for signs of hypothyroidism. Instruct not to stop medication abruptly Quick Review ANTI-THYROID medications Lugol’s Solution ⚫ Used to decrease the vascularity of the thyroid ⚫ Diminishes T3 and T4 production ⚫ Given per orem, can be diluted with juice ⚫ Use straw Quick Review ⚫ Steroids ⚫ Used to replace the steroids in the body if there is deficiency ⚫ Cortisol, cortisone, betamethasone, and hydrocortisone Side-effects ⚫HYPERglycemia ⚫Increased susceptibility to infection ⚫Hypokalemia ⚫Edema Quick Review Steroids ⚫ Used to replace the steroids in the body if there is deficiency ⚫ Cortisol, Cortisone, Betamethasone & Hydrocortisone Side-effects ⚫ HYPERglycemia ⚫ Increased susceptibility to infection ⚫ Hypokalemia ⚫ Edema ⚫ If high doses: osteoporosis, growth retardation, peptic ulcer, hypertension, cataract, mood changes, hirsutism, and fragile skin Quick Review Steroids: Nursing responsibilities ⚫ Monitor VS, electrolytes, glucose ⚫ Monitor I&O, weight, edema ⚫ Protect patient from infection ⚫ Handle patient gently ⚫ Instruct to take meds WITH MEALS to prevent gastric ulcer formation ⚫ Caution the patient NOT to abruptly stop the drug ⚫ Drug is tapered to allow the adrenal gland to secrete endogenous hormones Quick Review: Hypothyroidism ⚫ Hyposecretion of thyroid hormones ⚫ Common causes: ⚫ Iodine deficiency, Hashimoto’s disease ⚫ Manifestations: ⚫ related to hypo-metabolic state: ⚫ constipation ⚫ weight gain ⚫ cold intolerance ⚫ poor appetite ⚫ mental slowness Quick Review: Hypothyroidism ⚫ Nursing Management: ⚫ Provide warm environment ⚫ LOW calorie diet ⚫ HIGH fiber diet ⚫ Avoid sedatives ⚫ Medications: Hormone replacement Quick Review: Hyperthyroidism ⚫ Hyper-secretion ⚫ Common ⚫ Grave’s of thyroid hormones cause: disease, Toxic goiter ⚫ Manifestations: ⚫ related to hyper-metabolic state: ⚫ diarrhea ⚫ weight loss ⚫ heat intolerance ⚫ hypertension Quick Review: Hyperthyroidism ⚫ Nursing Management: ⚫ Adequate rest and sleep ⚫ Cool environment ⚫ HIGH calorie foods ⚫ Eye care ⚫ Drugs: anti-thyroid: PTU and methimazole, propranolol ⚫ Care of patients after thyroidectomy Nursing Assessment ⚫ Thyroid disturbances