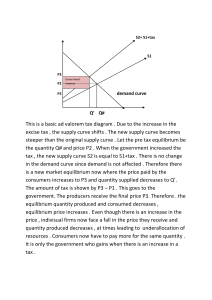
ECON 1001 AB Introduction to Economics I Dr. Ka-fu WONG Third week of tutorial sessions KKL 925, K812, KKL 106 Clifford CHAN KKL 1109 givencana@yahoo.ca Covered and to be covered Covered last week Dr. Wong finished kf002.ppt and covered up to #68 of kf003.ppt You should have at least read up to Chapter 3 Supply and Demand: An Introduction. If not, please press hard on them. We are getting to the first midterm! Start reading chapter 3 and 4 Your first midterm will cover chapter 1 – chapter 4 To be covered in the tutorial sessions this week Problems in chapter 3: #1, #3, #5, #7, #9, #11 and #13 You are advised to work on the even ones as well Problem #1, Chapter 3 State whether the following pairs of goods are complement or substitutes. (If you think a pair is ambiguous in this respect, explain why.) Tennis courts and squash courts Squash racquets and squash balls Ice cream and chocolate Cloth diapers and paper diapers Substitutes- goods that can be used / consumed interchangeably, i.e. Coca Cola and Pepsi Complements- goods that have to be used / consumed at the same time, i.e. Computer hardware and software Solution to Problem #1 (2) Tennis courts and squash courts Squash racquets and squash balls Complements- to play squash, you will need both Ice cream and chocolate Substitutes- you cannot play tennis in a squash court, and you cannot play squash in a tennis court. Two kinds of sport venue Substitutes for some people who regard them as desert Complement for some people who want to have chocolate (chips) on top of the ice cream Cloth diapers and paper diapers Substitutes- just different materials! We can use them interchangeably Problem #3, Chapter 3 Indicate how you think each of the following would shift demand in the indicated market Incomes of buyers in the market for Adirondack vacation increase Buyers in the market for pizza read a study linking hamburger consumption to heart disease Buyers in the market for CDs learn of an increase in the price of audiocassettes Buyers in the market for CDs learn of an increase in the price of CDs Demand shifts up (right)- increase in demand at any given level of price Demand shifts down (left)- decrease in demand at any given level of price Solution to problem #3 (1) Incomes of buyers in the market for Adirondack vacations increase The demand curve will shift up (right) Assume vacations are a normal good. Buyers will increase their consumption in vacations when their incomes increase. Buyers in the market for pizza read a study linking hamburger consumption to heart disease The demand curve will shift up (right) Pizza and hamburger are both junk food and can be consumed interchangeably. If a study shows proven connection between hamburger consumption and heart disease, people will consume less pizza for now. People will probably switch to consume pizza going forward. Solution to problem #3 (2) Buyers in the market for CDs learn of an increase in the price of audiocassettes. The demand will shift up (right) CDs and audiocassettes are substitutes . They both can be used to record and play music or soundtrack. If price of audiocassettes increases, people will probably switch to CDs Buyers in the market for CDs learn of an increase in the price of CDs As price of CDs goes up, people will buy less But the demand curve will not shift- why? Change in Quantity Demanded versus Change in Demand Solution to problem #3 (3) Change in Quantity Demanded Endogenous factors affecting the demand A demand graph consists of price on the Y-axis and quantity on the X-axis. Thus, price and quantity are endogenous factors Change in an endogenous factor itself (price of CDs) will only cause movement along the demand curve Change in Demand Exogenous factors affecting the demand Factors other then the endogenous factors (price and quantity) are going to shift the demand curve Price of substitutes, price of complements, increase in wealth (exogenous factors) Problem #5, Chapter 3 What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of oranges if the wage paid to orange pickers rises? Solution to problem #5 (1) Wage paid to orange pickers is actually one of the production costs of orange If now the production cost increases, suppliers will find it less profitable and so they will begin producing less orange to the market As a result, the supply of orange will decrease Is it a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied? Change in supply Increase in wage paid is an exogenous factor affecting the supply curve. It will cause the supply curve shift up (left) Supply curve shifts up (left)- decrease in supply at any given level of price Solution to problem #5 (2) Price of orange (P) S1 S0 P1 P0 D0 0 Quantity of orange (Q) Q1 Q0 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect Equilibrium price of orange increases and equilibrium quantity of orange decreases when the wage paid to orange pickers increases Problem #7, Chapter 3 What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of fish if fish oils are found to help prevent heart disease? Solution to problem #7 (1) If fish oil is found to help prevent heart disease, people will probably increase their consumption in fish so that they can be healthier As a result, the demand for fish will increase Is it a change in demand or a change of quantity demanded? Change in demand Increase in fish consumption is an exogenous factor affecting the demand curve. It will cause the demand curve shift up (right) Demand curve shifts up (right)- increase in demand at any given level of price Solution to problem #7 (2) Price of fish (P) S0 P1 P0 D1 D0 0 Quantity of fish (Q) Q0 Q1 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect Both the equilibrium price and quantity of fish increase when fish is found healthy Problem #9, Chapter 3 Use supply and demand analysis to explain why hotel room rental rates near your campus during parents’ weekend and graduation weekend might differ from rates charged during the rest of the year. Solution to problem #9 (1) As many parents visit the campus and participate in their children’s activities during parents’ weekend and graduation weekend, there will be a higher demand for hotel rooms near the campus than other periods in the year The demand for hotel rooms near the campus during the weekends during the special weekends will increase Is it a change in demand or a change in quantity demanded? Change in demand Increase in demand for hotel rooms during the time is an exogenous factor affecting the demand curve. It will cause the demand curve shift up (right) Demand curve shifts up (right)- increase in demand at any given level of price Solution to problem #9 (2) Price of hotel rooms (P) S0 P1 P0 D1 D0 0 Quantity of hotel rooms (Q) Q0 Q1 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect Both the equilibrium price and quantity of hotel rooms increase when it is a special weekend for parents Problem #11, Chapter 3 Suppose the current issue of the New York Times reports an outbreak of mad cow disease in Nebraska, as well as the discovery of a new breed of chicken that gains more weight than existing breeds that consume the same amount of food. How will these developments affect the equilibrium price and quantity of chickens sold in the United States? Solution to problem #11 (1) Beef and chicken are substitutes If there is an outbreak of mad cow disease, people will generally switch from consuming beef to consuming chicken As a result, the demand for chicken will increase Is it a change in demand or a change in quantity demanded? Change in demand Increase in demand for chicken is an exogenous factor affecting the demand curve. It will cause the demand curve shift up (right) Demand curve shifts up (right)- increase in demand at any given level of price Solution to problem #11 (2) If there is a discovery of a new breed of chicken that gains more weight than existing breeds that consume the same amount of food, it will be more profitable for chicken suppliers As a result, the supply of chicken will increase Is it a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied? Change in supply Increase in supply of chicken is an exogenous factor affecting the supply curve. It will cause the supply curve shift down (right) Supply curve shifts down (right)- increase in supply at any given level of price Solution to problem #11 (3) Price of chicken (P) S0 S1 P1 P0 D1 D0 0 Q0 Quantity of chicken (Q) Q1 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect IF THE INCREASE OF DEMAND IS GREATER THAN THE INCREASE IN SUPPLY, both the equilibrium price and quantity of chicken increase Solution to problem #11 (4) Price of chicken (P) S0 S1 P0 P1 D1 D0 0 Q0 Quantity of chicken (Q) Q1 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect IF THE INCREASE OF DEMAND IS LESS THAN THE INCREASE IN SUPPLY, the equilibrium price will decrease and the equilibrium quantity will increase Solution to problem #11 (5) To summarize, the equilibrium quantity of chicken will definitely increase The equilibrium price of chicken, however, is ambiguous It depends on the relative change in demand and change in supply Problem #13, Chapter 3 What will happen to the equilibrium price and quantity of apples if apples are discovered to help prevent colds and a fungus kills 10 percent of existing apple trees? Solution to problem #13 (1) If apples are discovered to help prevent colds, people will probably increase their consumption in apples so that they can be healthier As a result, the demand for apples will increase Is it a change in demand or a change in quantity demanded? Change in demand Increase in demand for apples is an exogenous factor affecting the demand curve. It will cause the demand curve shift up (right) Demand curve shifts up (right)- increase in demand at any given level of price Solution to problem #13 (2) If a fungus kills 10% of existing apple trees, there will be a decrease in supply of apples As a result, the supply of apples will decrease Is it a change in supply or a change in quantity supplied? Change in supply Decrease in supply for apples is an exogenous factor affecting the supply curve. It will cause the supply curve shift up (left) Supply curve shifts up (left)- decrease in supply at any given level of price Solution to problem #13 (3) Price of apples (P) S1 S0 P1 P0 D1 D0 0 Quantity of apples (Q) Q0 Q1 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect IF THE INCREASE OF DEMAND IS GREATER THAN THE DECREASE IN SUPPLY, both the equilibrium price and quantity of apples increase Solution to problem #13 (4) Price of apples (P) S1 S0 P1 P0 0 D1 D0 Quantity of apples (Q) Q1 Q0 Equilibrium is achieved where a demand curve and a supply curve intersect IF THE INCREASE OF DEMAND IS LESS THAN THE DECREASE IN SUPPLY, the equilibrium price will increase and the equilibrium quantity will decrease Solution to problem #13 (5) To summarize, the equilibrium price of apples will definitely increase The equilibrium quantity of apples, however, is ambiguous It depends on the relative change in demand and change in supply The end Thanks for coming! See you next week!