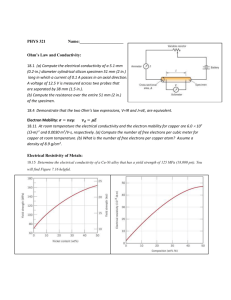
Dry type transformers Zaragoza Aluminum vs. Copper © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 1 Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity. Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity. Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour. Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour. Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 2 Historical Background: Why using Copper? Manufacturers were using Cu on HV Because there were no other option… ▪ During the 2nd World War, Copper (Cu) became scarce and manufacturers started using Aluminium (Al) as an alternative for electrical transmission and distribution. ▪ For transformers, up to the last 15 years, there were no suppliers of Al strip, small foil or wires. ▪ ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 3 There were no manufacturers for special winding machinery. Only LV windings were made in Aluminium. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity. Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity. Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour. Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour. Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 4 Next Step: Why using Aluminium? …till the option appeared due to several reasons that led the change ▪ ▪ ▪ ▪ Aluminium is the second most plentiful metallic element on Earth, so there are no problems with supply. Second lowest density. High corrosion resistance thanks to its Alumina protection. High electrical and thermal conductivity. (Higher conductivity than copper, weight for weight). ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 5 Low and non fluctuating price. Cu / Al Comparison Subscript © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 6 ▪ Preliminary reasons for winding material choice ▪ Coefficient of Expansion ▪ Electrical Conductivity ▪ Calorific Capacity ▪ Mechanical short circuit behavior Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 7 Cu / Al Comparison Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 8 Choicing Reasons Aluminum-wound transformer terminations are incompatible with copper line and load cables. Properly terminating line and load connections is more difficult for aluminum-wound transformers. Line and load connections to copper-wound transformers are more relieable than those to aluminum-wound transformers. Aluminum-wound transformers are lighter in weight than their copper-wound equivalents. Aluminum-wound transformers have higher losses because copper is a better conductor. Aluminum-wound transformers have higher hot-spot temperatures because copper is a better thermal conductor than aluminum. Copper-wound transformers can be made smaller than aluminum-wound equivalents. TRUE FALSE Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 9 Cu / Al Comparison Coefficient of Expansion for conductors and resin Hexagonal nut DIN 934 Plain Waser DIN 7349 Proper Solutions for Al terminals and Cu cable connections (Cupal Alloy) Hexagonal Bolt DIN 933 Busba r Coefficient of Aluminium Expansion ▪ Coefficient of Copper Expansion ▪ Coefficient of Resin Mix Expansion ▪ Spring Waser DIN 6796 23 16.6 34 (per ºCx10-6 at 20ºC) (per ºCx10-6 at 20ºC) (per ºCx10-6 at 20ºC) First Conclusion: Aluminium expands one third more than copper. ▪ Some says it creates problems with bolted connections. ▪ Using proper hardware (split washers) aluminium joints are equal to Copper joints. ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 10 Cu / Al Comparison Coefficient of Expansion for conductors and resin Critical point: Thermal expansion due to temperature changes, produces mechanical stresses in systems composed of different material as HV winding. ▪ Due to manufacturing process, these stresses are larger when the transformer is cooling down after casting stage. ▪ As closer are the thermal expansion coefficients lower the mechanical stresses ▪ Second Conclusion: ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 11 Tensile stress in the resin is lower with Aluminium windings. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 12 Cu / Al Comparison Electrical conductivity Aluminium has only 61% of Copper conductivity, so…higher losses??? ▪ Aluminium (Al): 36.6 106 W-¹m-¹ ▪ Copper (Cu): 59.6 106 W-¹m-¹ ▪ For two identical transformers (same winding resistance and length (amps/turns), the conductor section will be inverse to the electrical conductivity. + The section will be… RCu = LCu/SCu x Cu ;RAl = LAl /SAl x Al SAl /SCu = Cu / Al = 59.6/36.6 = 1,63 SAl = 1,63 SCu - Conclusions: ▪ ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 13 Section increasing means that result in energy losses is the same. Costwise comparison: Lower load losses are cheaper with Al windings. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour. Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour. Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 14 Cu / Al Comparison Calorific Capacity Aluminium specific heat (cAl): Copper specific heat (cCu): ▪ 0.220 cal/gºC 0.092 cal/gºC Mass of aluminium design is 0.488 times the copper one: • Calorific capacity Al = MAl x cAl ; Calorific capacity Cu = MCu x cCu • Calorific capacity Al/Calorific capacity Cu = (MAl / Mcu) x (cAl / cCu) = = 0,488 x (0,220/0,092) = 1,167 16,7% higher for Al. Conclusions: © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 15 ▪ Al windings withstand better surge and overloads currents. ▪ Better thermal behaviour to short circuits for Al windings. ▪ Longer working life for insulations materials. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 16 Cu / Al Comparison Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour ▪ Critical point: Located on Low Voltage HV windings: No short circuit forces due to stiffening by epoxy cast Into a beam simulation, considering Aluminium conductivity is 63% of Copper and from inertia moments Bending stress: = Mxt / 2I ▪ ▪ Aluminium Al = 2.34 M / t ▪ Copper Cu = 6M / t According to this, bending stress in aluminium foil is 2.54 times lower than in copper foil. Conclusion: ▪ © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 17 Aluminium foil is a very safe alternative to copper concerning mechanical stress under short circuit conditions. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 18 Cu / Al Comparison Thermal Stresses under Short Circuit Conditions ▪ Critical point: Located on Low Voltage Under short circuit conditions, the current density in LV winding rises up to several times as the inverse of impedance voltage in per unit, assumed network impedance is zero ▪ As per IEC, temperature in short circuit is calculated with the following formula: Conclusion: ▪ For the same losses the behaviour of aluminium winding is safer than copper ones, against the thermal stresses produced by a short circuit © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 19 Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 20 Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 21 ▪ Simple and safe design. ▪ Insulation distance easy to keep. ▪ Lower voltage stress. ▪ Thermal expansion of Al and resin is very similar, so thermal stresses are kept to the minimum. ▪ At equal conductivity Al design weight lighter. Very useful for transformers located inside buildings or with limited accessibility. ▪ Aluminium winding is more compact: higher bonding strength and improved short circuit behaviour. Index Historical Background: Why Using Copper? Next Step: Why Using Aluminum? Common Reasons for Winding Material Choice Cu / Al Comparison: Coefficient of Expansion for Conductors and Resin Cu / Al Comparison: Electrical Conductivity Cu / Al Comparison: Calorific Capacity Cu / Al Comparison: Mechanical Short Circuit Behaviour Cu / Al Comparison: Thermal Short Circuit Behaviour Aluminium Foil Disk Winding: Summary Conclusions © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 22 Conclusions Al windings have the following advantages This is ABB Zaragoza standard…push for it!! © ABB Group May 14, 2021 | Slide 23 ▪ Better thermal and dynamic behaviour to short circuits for Al windings ▪ Al windings withstand better surge and overloads currents ▪ Longer working life for insulations materials ▪ Stronger mechanical design ▪ Lower prices