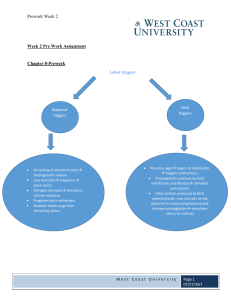
Introduction to Electronic Fetal Monitoring Looking for oxygenation when looking at the fetal monitor Metabolic acidemia and hypoxia Maternal pathway to oxygenation of the fetus (asthma, preeclampsia, HTN) Disruption can be maternal, disruption at the umbilical cord, at the placenta, or at the fetus Toconometer- Band measuring contractions at the top of the fundus Fetal monitoring occurs lower on the abdomen, allows continuous monitoring for FHR (fetal heart rate). If heart tones are found on the fundus, baby is probably breech. Primary Objective 1.To provide information about fetal oxygenation and prevent fetal injury from impaired oxygenation 2.To detect fetal heart rate changes before they are prolonged and profound Leopold’s Maneuvers: Determining the position of the fetus to assist with monitor placement - If you feel some squishy up high, probably buttocks, if it’s hard, probably head - Check side to side, find fetal back and place monitor there Fetal Strip: - Time between big boxes is 1 minute, small boxes are 10 seconds - Fetal heart rate in upper pane, uterine contractions in lower pane Contractions: Measure from the start of one contraction to the start of the next for frequency, count from beginning of one contraction to the end of same contraction for duration. - More than 5 uterine contractions in 10 minutes (averaged over 30 minutes), or 2 uterine contractions lasting more than 120 seconds in duration is called tachysystole and requires nurse intervention. (Too many contractions, can be caused by Pitocin Fetal Monitor Interpretation: - Baseline FHR - FHR variability (think oxygenation) - Are HR accelerations present? (if you have accel, you have oxygenation) - Are decelerations present? If yes, which variety - Determine FHR category - Intervention necessary Normal Values: - 110-160 FHR What is variability? - Absent= no changes= not good= metabolic acidemia or hypoxia - Minimal 0-5 beats of change (less than ½ box) = acuity depending on situation - Moderate 6-25 beats of change (more than ½ box to 2 ½ boxes)= we have fetal oxygenation - Marked= greater than 25 beats of change (more than 2 ½ boxes) Accelerations: 15 beats above baseline for at least 15 seconds, usually accompanied by fetal movement (called 15 x 15’s), younger babies may only be 10 x 10’s Decelerations: - Variable= below baseline 15 beats, abrupt descent of FHR, may occur with contraction or independently= related to cord compression - Early= Occurs with a contraction, will mirror contraction (starts at same time and ends at same time) Late= Starts after the contraction has started (usually after the peak of the contraction) = uterine placental insufficiency Prolonged= below baseline for more than 2 minutes but less than 10 min= metabolic acidemia or hypoxia, baby needs to be delivered Epidural= can cause hypotension, and decreased perfusion, but can cause late decelerations. Usually, fluid is given prior to getting an epidural to try and prevent the hypotension and late deceleration. Sinusoidal FHR pattern= baby has metabolic acidemia, fetal hemorrhage or anemia, abnormal neural tube. Strip looks like equal triangles up and down, like a uniformed v-fib Deceleration/Cause V=Variable—C= Cord compression E=Early—H= Head compression A= Acceleration—O= Okay or oxygen L= Late—P= Placental Insufficiency Category 1 – GoodBaseline range 110-160Baseline variability - moderateLate or variable decelerations – absentEarly decelerations – present or absentAccelerations – present or absent (baby is okay, no metabolic acidemia or hypoxia) - NICHD Terminology: Normal baseline FHR, moderate variability, and lack of concerning decelerations- Continue monitoring. Category 2 – Caution *Baseline range – may have tachycardia or bradycardia without absent variability*Baseline variability – minimal or absent without recurrent decelerations or marked.*Late or variable decelerations – recurrent variable with minimal or moderate variability, Prolonged >2min but <10 min, recurrent late with moderate variability*Early decelerations – present or absent*Accelerations – present or absent (baby could be okay, but also could be heading towards metabolic acidemia or hypoxia) - NICHD Terminology: FHR patterns that are concerning enough to warrant increased frequency in monitoring, but that respond to interventions provided- General measures; consider discontinuing oxytocin; consider potential need to expedite delivery if abnormalities persist or worsen. Category 3 – Intervention neededBaseline range – 110-160, bradycardia or tachycardiaBaseline variability –AbsentLate or variable decelerations – recurrent variable or recurrent late (Impending or current metabolic acidemia or hypoxia, needs immediate delivery within 30 min) - NICHD Terminology: Absent baseline FHR variability with recurrent late or variable decelerations and/or bradycardia or with a sinusoidal patter- General measures; discontinue oxytocin; expedite delivery by operative vaginal or cesarean delivery. Uterine Resuscitation: (position change, IV fluids, O2, Pitocin) - IV Fluid Bolus (lactated Ringer’s 500 mL rapidly with pressure bag) - Maternal position change (left lateral, right lateral, hands and knees, hips open with the use of peanut ball, high Fowler’s). - Apply O2 10 L via non-rebreather facemask - Turn Pitocin off. Fetal tachycardia main cause is MATERNAL FEVER Laboring: First stage of labor: begins with onset of regular uterine contractions, ends with full cervical effacement and dilation - Latent phase: up to 3cm of dilation - Active phase: 4-7 cm of dilation - Transition phase: 8-10cm of dilation •Maternal status (vital signs, pain, prenatal record review) - Vaginal examination (cervical dilation, effacement, membrane status, fetal descent and presentation) - Rupture of membranes - Uterine contractions - Leopold’s maneuvers Typical signs of 2nd stage: Contraction frequency, duration, intensity, Maternal vital signs, Fetal response to labor via FHR, Amniotic fluid with rupture of membranes, Coping status of woman and partner. - Infant is born Begins with full cervical dilation (10 cm) Complete effacement (100%) Ends with baby’s birth Upper limits for duration of second stage - Two phases: o o o Latent: relatively calm with passive descent Descent: active pushing and urges to bear down S/S of impending birth Third stage: Placental separation and expulsion, Firmly contracting fundus, Change in shape of uterus, Sudden gush of dark blood from introitus, Apparent lengthening of umbilical cord, Vaginal fullness Blood loss for deliveries: 500mL vaginal, 1000mL C-section Ideal presentation: Occiput, anterior. If it is occiput posterior, baby is coming out sunny side up Fourth stage: Assessment - Vital signs, fundus, perineal area, comfort level, lochia, bladder status - Interventions - Support and information - Fundal checks; perineal care and hygiene - Bladder status and voiding - Comfort measures - Parent–newborn attachment - Breastfeeding support - Teaching Jeopardy Baby’s first vaccine is Hep B Most common cause of maternal hemorrhage is uterine atony Most common cause of fetal tachycardia is maternal fetus Saturated perineal pad 3 hrs after birth- massage the fundus Variable fetal decelerations caused by cord compression 2 reasons for a postpartum Pt to have bladder distention: urethral trauma, epidural interfering with sensation to void Why does mag sulfate admin during labor poses a risk for PPH? Works on smooth muscle, so uterus relaxes and bleeding can occur Newborn stomach only holds 5-7mL Best reason for recommending formula over breastfeeding is if the mother has a medical condition or is taking drugs that can pass through the breast milk The presence of adequate urine output indicates adequate tissue perfusion Why is Vit K given? B/C gut is sterile and they don’t have the bacteria to be able to synthesize vitamin K for the first week of life Claiming, synchronicity, Mastitis can be avoided by massaging the ducts and frequent breast feeding, also making sure baby is latched over the whole areola and not just the nipple