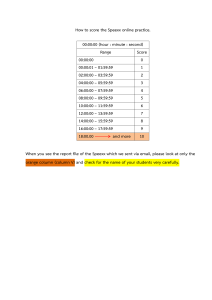
Score: 4. 100/100 Points 100 % Award: 12.50 out of 12.50 points You received credit for this question in a previous attempt Exercise 1-14 Cost Classification [LO1-2, LO1-3, LO1-4, LO1-5] Wollogong Group Ltd. of New South Wales, Australia, acquired its factory building 10 years ago. For several years, the company has rented out a small annex attached to the rear of the building for $30,000 per year. The renter’s lease will expire soon, and rather than renewing the lease, the company has decided to use the annex to manufacture a new product. Direct materials cost for the new product will total $80 per unit. To have a place to store its finished goods, the company will rent a small warehouse for $500 per month. In addition, the company must rent equipment for $4,000 per month to produce the new product. Direct laborers will be hired and paid $60 per unit to manufacture the new product. As in prior years, the space in the annex will continue to be depreciated at $8,000 per year. The annual advertising cost for the new product will be $50,000. A supervisor will be hired and paid $3,500 per month to oversee production. Electricity for operating machines will be $1.20 per unit. The cost of shipping the new product to customers will be $9 per unit. To provide funds to purchase materials, meet payrolls, and so forth, the company will have to liquidate some temporary investments. These investments are presently yielding a return of $3,000 per year. Required: Using the table shown below, describe each of the costs associated with the new product decision in four ways. In terms of cost classifications for predicting cost behavior (column 2), indicate whether the cost is fixed or variable. With respect to cost classifications for manufacturers (column 3), if the item is a manufacturing cost, indicate whether it is direct materials, direct labor, or manufacturing overhead. If it is a nonmanufacturing cost, then select “none” as your answer. With respect to cost classifications for preparing financial statements (column 4), indicate whether the item is a product cost or period cost. Finally, in terms of cost classifications for decision making (column 5), identify any items that are sunk costs or opportunity costs. If you identify an item as an opportunity cost, then select “none” as your answer in columns 2-4. Cost Classifications for: Name of the Cost Predicting Cost Behavior Preparing Financial Statements Manufacturers Decision Making Rental revenue forgone, $30,000 per year None None None Opportunity cost Direct materials cost, $80 per unit Variable Direct materials Product None Rental cost of warehouse, $500 per month Fixed None Period None Rental cost of equipment, $4,000 per month Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product None Direct labor cost, $60 per unit Variable Direct labor Product None Depreciation of the annex space, $8,000 per year Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product Sunk cost Advertising cost, $50,000 per year Fixed None Period None Supervisor's salary, $3,500 per month Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product None Electricity for machines, $1.20 per unit Variable Manufacturing overhead Product None Shipping cost, $9 per unit Variable None Period None Return earned on investments, $3,000 per year None None None Opportunity cost Garrison 16e Rechecks 2017-09-18 rev: 01_19_2019_QC_CS-154146 References Matching Learning Objective: 01-02 Identify and give examples of each of the three basic manufacturing cost categories. Exercise 1-14 Cost Classification [LO1-2, LO13, LO1-4, LO1-5] Learning Objective: 01-03 Understand cost classifications used to prepare financial statements: product costs and period costs. Difficulty: 1 Easy Learning Objective: 01-04 Understand cost classifications used to predict cost behavior: variable costs, fixed costs, and mixed costs. Learning Objective: 01-05 Understand cost classifications used in making decisions: differential costs, sunk costs, and opportunity costs. Exercise 1-14 Cost Classification [LO1-2, LO1-3, LO1-4, LO1-5] Wollogong Group Ltd. of New South Wales, Australia, acquired its factory building 10 years ago. For several years, the company has rented out a small annex attached to the rear of the building for $30,000 per year. The renter’s lease will expire soon, and rather than renewing the lease, the company has decided to use the annex to manufacture a new product. Direct materials cost for the new product will total $80 per unit. To have a place to store its finished goods, the company will rent a small warehouse for $500 per month. In addition, the company must rent equipment for $4,000 per month to produce the new product. Direct laborers will be hired and paid $60 per unit to manufacture the new product. As in prior years, the space in the annex will continue to be depreciated at $8,000 per year. The annual advertising cost for the new product will be $50,000. A supervisor will be hired and paid $3,500 per month to oversee production. Electricity for operating machines will be $1.20 per unit. The cost of shipping the new product to customers will be $9 per unit. To provide funds to purchase materials, meet payrolls, and so forth, the company will have to liquidate some temporary investments. These investments are presently yielding a return of $3,000 per year. Required: Using the table shown below, describe each of the costs associated with the new product decision in four ways. In terms of cost classifications for predicting cost behavior (column 2), indicate whether the cost is fixed or variable. With respect to cost classifications for manufacturers (column 3), if the item is a manufacturing cost, indicate whether it is direct materials, direct labor, or manufacturing overhead. If it is a nonmanufacturing cost, then select “none” as your answer. With respect to cost classifications for preparing financial statements (column 4), indicate whether the item is a product cost or period cost. Finally, in terms of cost classifications for decision making (column 5), identify any items that are sunk costs or opportunity costs. If you identify an item as an opportunity cost, then select “none” as your answer in columns 2-4. Cost Classifications for: Name of the Cost Predicting Cost Behavior Manufacturers Preparing Financial Statements Decision Making Rental revenue forgone, $30,000 per year None None None Opportunity cost Direct materials cost, $80 per unit Variable Direct materials Product None Rental cost of warehouse, $500 per month Fixed None Period None Rental cost of equipment, $4,000 per month Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product None Direct labor cost, $60 per unit Variable Direct labor Product None Depreciation of the annex space, $8,000 per year Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product Sunk cost Advertising cost, $50,000 per year Fixed None Period None Supervisor's salary, $3,500 per month Fixed Manufacturing overhead Product None Electricity for machines, $1.20 per unit Variable Manufacturing overhead Product None Shipping cost, $9 per unit Variable None Period None Return earned on investments, $3,000 per year None None None Opportunity cost Garrison 16e Rechecks 2017-09-18 rev: 01_19_2019_QC_CS-154146 Explanation: No further explanation details are available for this problem.