Naming Ionic & Covalent Compounds: Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

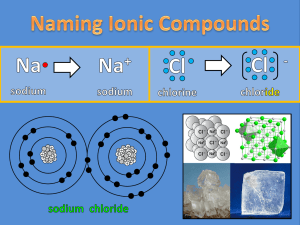
Naming Ionic Compounds Chemical reactions occur when atoms gain, lose, or share electrons. Metals Nonmetals gain / accept electrons. Nonmetals _____________ This gives them a ____ charge. anions Negative ions are called ___________. lose / donate Metals ________________ electrons. _ This gives them a ____ + charge. cations Positive ions are called ___________. Remember that the charge of an ion can be determined by its place on the Periodic Table. +1 +2 +3 Look for the Roman Numeral! +4 or -4 0 -3 -2 -1 For each elements on your notes, predict the charge of its most common ion using the periodic table. -3 + -21 0 + +2 1 + -1 2 -3 + -22 + 1 -1 + 1 -1 0 -1 0 Rules for Naming Ions When metals lose electrons they become ions, but their name does not change. Na sodium Mg magnesium + Na + e sodium electron +2 Mg 2e magnesium + 2 electrons Rules for Naming Ions When nonmetals gain electrons they become ions, and their name does change. F + fluorine e electron F fluoride S + 2e -2 S sulfur 2 electrons sulfide Rules for Naming Ions 1. The names of metals do not change. 2. Changing the name of nonmetals: root of element name + -ide = name of ion Examples: The name of chlorine’s ion: chlor- + -ide = chloride The name of nitrogen’s ion: nitr- + -ide = nitride Examples of naming ions: The name of calcium’s ion: calcium (The names of metals don’t change!) The name of oxygen’s ion: ox- + -ide = oxide The name of aluminum’s ion: aluminum (The names of metals don’t change!) There are also ions that form after elements have shared electrons. These ions are known as polyatomic ions, and each polyatomic ion already has a name. Steps for Naming Ionic Compounds CaBr2 calcium bromide Step 1: Write the name of the metal ion. Step 2: Write the name of the nonmetal ion. Step 3: YOU ARE DONE! It is that easy. 1. NaF sodium 3. MgO fluoride SrCl2 strontium 5. 4. chloride CaO calcium 2. magnesium oxide Li2S lithium 6. oxide sulfide KI potassium iodide You can also determine the formula of an ionic compound from its name. To do this, you will need to use what you already know about the Periodic Table. magnesium iodide +2 Mg I MgI2 - Step 1: Write the symbol of the metal ion. Step 2: Write the symbol of the nonmetal ion. Step 3: Determine the charges using the periodic table. Step 4: Determine the formula from the ions. This is just as easy to do with polyatomic ions. You just need to use the name of the polyatomic ion. strontium nitrate Sr +2 NO3 Sr(NO3)2 Step 1: Write the symbol of the metal ion. Step 2: Write the formula of the polyatomic ion. Step 3: Determine the charges using the periodic table and the table of polyatomic ions. Step 4: Determine the formula from the ions. Be very careful that you do not mix up the names of ions. This is very common for beginners to naming. Decide which name goes with each ion. -3 N -2 S -3 P nitrate nitride sulfide sulfite NO3 - -2 SO3 phosphate phosphide -3 PO4 Helpful Hint: If the ion ends in –ide, it is probably from the periodic table. If the ion ends in –ate or –ite, it is a polyatomic ion. Examples: sulfate sulfite sulfide -2 S SO3 -2 nitride nitrite -3 N NO2 SO4 -2 nitrate - NO3 - Naming Binary Covalent Compounds shared electrons Nonmetals Chemical reactions occur when atoms gain, lose, or share electrons. Sharing electrons creates a covalent bond share electrons to Nonmetals can _______ form a covalent bond. molecule This creates a ___________. Determining if a compound is ionic or covalent is easy. What elements do covalent compounds contain? Covalent compounds contain only nonmetals. What elements do ionic compounds contain? Ionic compounds contain a metal and a nonmetal. Decide whether the compounds on your notes are ionic or covalent. C C I C I I Important Facts: Because hydrogen only has 1 proton and 1 electron, it behaves differently than any other element on the periodic table of elements. Hydrogen can donate its 1 electron. H+ H Hydrogen can share electrons. Hydrogen can gain 1 electron. This means that hydrogen can act as either a metal or a nonmetal! H2 There are 7 elements that exist in nature as diatomic molecules. What elements exist as diatomic molecules? H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2 There are millions of covalent compounds. These can be classified into many different types of compounds. Each type of compound has a different set of rules for naming. You will be learning about the easiest type of covalent compound to name: Binary Covalent Compounds Binary means 2. Binary covalent compounds are between 2 different nonmetals. What does binary mean? Nonmetals can share electrons in many different ways. This means that two nonmetals can create multiple compounds together. carbon and oxygen CO CO2 phosphorous and chlorine PCl3 PCl5 nitrogen and oxygen N2O4 N2O3 Each of these contains a different ratio of elements. Because of this, we have to make sure that the name of the compound explains the correct ratio. To show the correct ratio of elements, we use prefixes. Steps for Naming Binary Covalent Compounds N2O4 dinitrogen tetroxide oxide Step 1: Write the name of the first nonmetal. Step 2: Write the name of the second nonmetal changing its ending to -ide. Step 3: Add prefixes to specify how many of each element are present. How would you write each of the prefixes in front of oxide? Remember: Remove the -o or -a from a prefix before adding it to oxide. Leave -i alone. monoxide mono- ____________ trioxide tri- ____________ pentoxide penta- ____________ heptoxide hepta- ____________ nonoxide nona- ____________ dioxide di- ____________ tetroxide tetra- ____________ hexoxide hexa- ____________ octoxide octa- ____________ decoxide deca- ____________ Name the binary covalent compounds that are found on your notes. carbon dioxide carbon disulfide phosphorous tribromide phosphorous pentabromide diphosphorous pentasulfide dinitrogen monosulfide silicon disulfide nitrogen tribromide dinitrogen tetrachloride Because of the prefixes, it is very easy to go from the name of a binary covalent compound to its formula. dinitrogen tetrafluoride N2 F4 Step 1: Write the symbol of the first nonmetal and the subscript that matches the prefix. Step 2: Write the symbol of the second nonmetal and the subscript that matches the prefix.