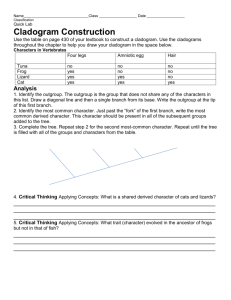
[Type text] Name:_______________________________________ Score:_______ Make a Cladogram On Your Own! Imagine you are a scientist trying to determine the evolutionary relationship between a group of organisms. Using the information given and your prior knowledge, you will create a cladogram that represents how these animals are related. You will create a cladogram similar to the one that is shown below. Please note that your cladogram must have 8 vertical lines to represent each of the 8 different animals you will place on the cladogram. You must also leave enough room between each line to paste the picture of the animal at the top of the line. In the space between each vertical line, you should write the shared, derived trait that separates the group(s) below and the group(s) above. You will select the images of the animals you will use from a Google search. All images must be IN COLOR for full credit. You may wish to choose organisms from a popular show, a book, or that follow a theme. For example, you may use images of animals that come from a Disney movie, or a Pixer film—use your creativity and make it look nice!. Animal List: Lizard, Bird, Beetle, Octopus, Butterfly, Gorilla, Elephant, Frog Consider the following shared, derived traits when designing your cladogram. The terms in bold should be written in the space separating each group from the groups above it. 1.Determine which 3 animals are invertebrates (no backbone). 2.Of these, determine which have a rigid skeleton and which has a hydroskeleton. 3.Place the animal with the hydroskeleton at the far left on the cladogram, this is the outgroup. All of the other animals have a rigid skeleton. 4.Draw a V shaped line extending out from the main line of the cladogram. With the two remaining invertebrates place the one that does not have wings on the lower line of the V and the one that does have wings in the upper line of the V as shown below: Etc! wings Etc! Rigid skeleton 5.All the remaining animals are vertebrates. One of the remaining animals shows external fertilization and does not have an amniotic egg. Place this animal next in the cladogram. 6.All of the remaining organisms have an amniotic egg which contains its own fluid inside a shell and can be laid on land or kept within the body. 7.Of the four remaining organisms, only one is ectothermic, the other three are endothermic. Place the ectothermic organism next. 8.All of the remaining organisms are endothermic or warm blooded. 9.Of the three remaining animals, only two have mammary glands to feed milk to the young. Place the one that does not have mammary glands next on the diagram. 10.Of the two remaining animals, only one has an opposable thumb that can be used to grasp. 11.Place the organism that does not have an opposable thumb next on the cladogram. 12.Place the animal with the opposable thumb at the top right position of the cladogram. When finished, your cladogram should have all of the organisms placed along the top in the proper order, and the bold faced words should be placed along the diagonal line to show the characteristics that separate each group from those above it. The image of the cladogram above is only a starting point for you! [Type text] Name:_______________________________________ Score:_______ Analysis 1. Complete the following character table to illustrate which characteristics are present and which are absent in each group. A 0 indicates absent; a 1 indicates that the character is present. Octopus (outgroup) Beetle Butterfly Frog Lizard Bird Elephant Chimp Rigid skeleton Vertebrate Amniotic egg Endothermic Mammary Glands Opposable thumb 2.Describe what is meant by “systematics” and discuss what tools are used in modern systematics. 3.Define the term “outgroup” and explain why the animal on the left of your cladogram is an outgroup. 4.Discuss why the evolution of the amniotic egg was a major step in the evolution of animals. 5. Write a paragraph in which you describe at least three of the most significant evolutionary adaptations that facilitated life on land for the animals.