Evolution Review: Practice Questions & Concepts
advertisement

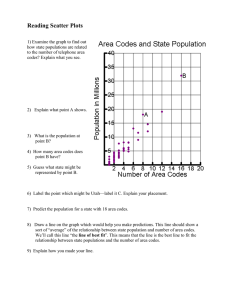
Evolution Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 20pts Name: On the Galápagos Islands, Darwin saw that the plants and animals closely resembled those found a. on islands off the coast of North America. c. on islands off the coast of Africa. b. in South America. d. in South Africa. Which of the following is a Tenet of evolution? a. Individuals of a population overproduce. c. Individuals better suited reproduce more often. b. All populations are genetically diverse. d. All of the above Which of the following is not a factor in natural selection? a. All populations have genetic variation. b. Individuals of a species cannot compete if they are to survive. c. All populations depend upon the reproduction of individuals. d. Individuals tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. When a population of a species is split in two and the two groups separate for a long period of time, the two groups may become a. different families. c. different species. b. the same species. d. unrelated. The fossil record provides evidence that a. older species from the past gave rise to more-recent species. b. all species were formed during Earth’s formation and have changed little since then. c. the fossilized species have no connection to today’s species. d. fossils cannot be dated. Comparing human hemoglobin (protein that carries oxygen) with the hemoglobin of gorillas, mice, chickens, and frogs reveals that humans have the fewest amino acid differences (therefore the most in common) with a. gorillas. c. chickens. b. mice. d. Frogs. Individuals that are better able to cope with the challenges of their environment tend to a. decrease in population over time b. leave more offspring than those more suited to the environment. c. leave fewer offspring than those less suited to the environment. d. leave more offspring than those less suited to the environment. Natural selection acts directly on which of the following? a. Genotypes c. both phenotypes and genotypes b. Phenotypes d. neither phenotypes nor genotypes Which factor does not play a role in natural selection? a. overproduction c. Lamarckian inheritance b. variation d. Adaptation Different populations of the same species a. always become different species over time. c. can no longer interbreed successfully. b. may change enough to become different species. d. will never diverge to become different species. Which of the following statements best reflects the evolutionary importance of the figures to the right? a. New genetic instructions have been disregarded in the evolution of vertebrates. b. In parts of development, vertebrate embryos show evidence of common ancestry. c. The evolutionary history of organisms is seen in transitional embryos. d. All adult vertebrates retain tails Which of the following statements is not true about anatomy and evolution? a. Homologous structures indicate common ancestry of organisms. b. The bone patterns making up the forelimbs of tetrapods are similar. c. Internal similarities do not indicate shared evolutionary history. d. Most vertebrates have four limbs. When the individuals of two populations can no longer interbreed, the two populations are considered to be a. different families. c. the same species. b. reproductively isolated. d. unrelated. Members of different subspecies a. are completely different species. c. can no longer interbreed successfully. b. have different adaptations than their parent species. d. will never diverge to become different species. In large, randomly mating populations, the frequencies of alleles and genotypes are likely to remain constant from generation to generation unless a. evolutionary forces are absent. c. the populations are bacterial. b. evolutionary forces act on the population. d. the populations are human. Evolution Review 20pts Name: Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase in the space provided. 16. Darwin felt that fossils of extinct armadillos (glyptodon) that resembled living armadillos were evidence of ______________________ with ______________________. 17. Evolution is the process by which ______________________ may change over time. 18. A trait in a species that results in it being better suited to survive and reproduce in its environment is called a(n)______________________. 19. Humans _______________ to high elevations by producing more red blood cells. 20. Humans _______________ cold weather by putting on jackets and gloves. 21. The most complex fossils are found in the _____________ strata and the youngest fossils are in the _____________ strata. 22. Given that the forelimbs (arms) of all vertebrates share the same basic arrangement of bones, forelimbs are said to be ______________________ structures. 23. Some whales have tiny ______________________ bones as evidence of their land-dwelling mammalian ancestors. These are called __________________ ____________________. 24. Bird wings and insect wings are considered __________________ _______________. 25. Species that shared a common ancestor in the recent past have many ______________________ ______________________ or ______________________ sequence similarities. 26. A(n) ______________________ is a group of individuals that belong to the same species, live in a defined area, and breed with others in the group. 27. Populations evolve, but ______________________ do not evolve. 28. The formation of a new species is called ______________________. 29. A type of evolution with small scale changes in genes is called ______________________. 30. Microevolution is the study of evolution at the level of __________________. 31. What was Lamarck’s incorrect hypothesis regarding inheritance called? 32. A female robin that chooses a mate based on how well he sings is demonstrating _______________ _______________. 33. Migration into or from a population results in _________________ _________________. 34. The mechanisms that is most affected by population size is ______________ ______________. 35. Over time, change within species leads to the addition of new species while some species become _________________. 36. The changing of a species that results in its being better suited to its environment is called ______________________. 37. The main way scientists prove evolution is by detecting significant changes in _______________ ___________________. 38. A condition in which two groups of a population have diverged enough so they can no longer interbreed is called ______________________ ______________________. 39. Darwin knew about heredity, but he did not know about _________________. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. Write a line matching the description that best matches each term. a. the visible expression of various genotypes population genetics b. a population that has diverged noticeably from other populations normal distribution c. a state in which allele frequencies of a population remain the same phenotypic variation d. the study of the changes in numbers and types of alleles in populations genotype e. a pattern of distribution in which trait values cluster around an average genetic equilibrium f. a set of alleles that determine an individual’s phenotype reproductive isolation g. a state in which a population is no longer interbreeding with other populations subspecies Evolution Review 20pts Name: Evolution Vocabulary Practice In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement. There are “distractors” in the list so check your answers against resources! 1. ____Darwin published a book outlining the a. adaptation. process of “descent with modification” called… b. Allele frequencies 2. ____The process of change by which new c. analogous. d. artificial selection. species can develop over time from preexisting e. biological change. species with traits well suited to an environment f. camouflage. is called… g. divergence 3. ____A trait that improves an organism’s ability to h. evolution. survive and reproduce is a(n)… i. fossils. j. genotypes 4. The characteristic of evolution that chooses the k. homologous. best suited trait for an environment is called… l. industrialization. 5. ____When species produce more offspring than m. lower can be supported in an environment, this is the n. natural selection. Tenet called… o. not an advantage. p. observational selection. 6. Within natural populations there exists _____ that q. origin of species. natural selection can act on. r. overproduction 7. ____Similar structures in two or more species s. phenotypes that have been inherited from a common t. radioactive carbon dating. ancestor are… u. sexual selection. v. simpler 8. ____Traces of organisms that lived in the past w. speciation. are… x. trait mechanisms. 9. ____Selection for desired traits that is done by y. upper humans is called… z. variation 10. ____The process by which new species form is called… 11. ____Microevolution is the slow change in… 12. ____Natural selection selects the best (genotype/phenotype) for the environment. 13. ____Age of fossils is made possible by… 14. Older fossils are found in ____ strata and are _____ than those found in ____ strata. 15. Bird wings and bat wings are considered ____ structures. 16. ____Creating multiple species from a single common ancestor is made possible through… 17. ____Reproductive isolation is also called… 18. ____Mates are choosy. This aspect of microevolution is called… Evolution Review 20pts Name: adaptive radiation analogous structure polygenic genetic equilibrium reproductive isolation extinction gene flow nonrandom mating normal distribution Use the word bank above to complete the sentences below. 19. 20. convergent evolution population genetics microevolution gene pool genetic drift divergence speciation subspecies A trait that is influenced by several genes is called ________________. The evolutionary forces include the mutation of genes and ______________________ ____________________, which is the movement of alleles into or out of a population. 21. In small populations, the frequency of an allele can be greatly changed by a chance event, such as a fire or landslide. This change in allele frequency is called _______________ __________________. 22. If you were to plot the height of everyone in your class on a graph, the values would probably form a hill-shaped curve called a(n) ____________________ ______________________. 23. Sometimes, individuals prefer to mate with others that live nearby or are of their own phenotype, a situation called ______________________ ______________________. 24. Similar habitats and selective pressures will cause organisms not closely related to develop similarities that are built very differently from each other called ______________ ____________. 25. Evolution at the level of genetic change is called ________________. 26. When a species fails to produce any more descendants, ____________ occurs. 27. A population in which no genetic change is occurring is in a state of ______________________ ______________________. 28. The type of evolution that explains the development of wings in birds, bats, and butterflies is called _______________ __________________. 29. The divergence of multiple lineages into many new species in a specific area and time is called _________________ __________________. 30. The particular combination of alleles in a population at any one point in time makes up a(n) ________________ _________________. 31. The study of changes in the numbers and types of alleles in populations is called __________________ ___________________. 32. A state in which two populations can no longer interbreed to produce future offspring is ___________________ ______________________. 33. The accumulation of differences between populations is called ______________________. 34. A population that differs from, but can interbreed with, other populations of the same species is called a(n) ______________________. 35. The process of forming new species by evolution from preexisting species is called ______________________. Evolution Review 20pts Evolution Review Answers 1. B 2. D 3. B 4. C 5. A 6. A 7. D 8. B 9. C 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. B 14. B 15. B 16. Descent (with) modification 17. Species 18. Adaptation 19. Acclimate 20. Accommodate 21. Upper/upper 22. Homologous 23. Hip/vestigial structures 24. Analogous structures 25. Amino acid/DNA 26. Population 27. Individuals 28. Speciation 29. Microevolution 30. Genetics 31. Gradualism 32. Sexual selection 33. Gene flow 34. Genetic drift 35. Extinct 36. Evolution 37. Allele frequency 38. Reproductive isolation 39. Genetics/genes 40. D 41. E 42. A 43. F 44. C 45. G 46. B Name: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Evolution Vocabulary Practice Answers Q H A N R Z K I D W B S T M–V–Y C G (or W) G U Polygenic Gene flow Genetic drift Normal distribution Nonrandom mating Analogous structures Microevolution Extinction Genetic equilibrium Convergent evolution Adaptive radiation Gene pool Population genetics Reproductive isolation Divergence Subspecies Speciation