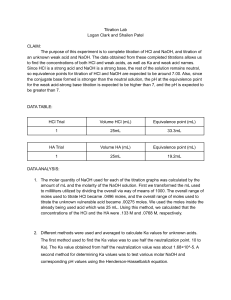
AP Chemistry: Mrs. Robinson Acid/Base/Buffer Worksheet Name: _____________________________ Date: ___________________ Block: _____ 1. Determine the pH at the equivalence point of the following titrations. It’s the pH of the salt made by combining the acid and base. From dilution, the molarity of the salt is half the original acid or base. Look up Ka or Kb values, when necessary. a. 0.200 M NaOH with 0.200 M HCl (7) b. 0.100 M HClO with 0.100 M NaOH (10.11) c. 0.200 M hydroxylamine with 0.200 M HCl (3.52) d. 0.150 M ammonia with 0.150 M HBr (5.19) e. 0.300 M HBrO with 0.300 M KOH (10.89) 2. A 20.0 mL sample of 0.200 M HCl solution is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH solution. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of base have been added. Don’t forget that the solutions are getting diluted as the titration takes place! a. Initial pH (0.70) b. 15.0 mL (1.54) c. 19.9 mL (3.30) d. 20.0 mL (7.0) e. 20.1 mL (10.7) f. 25.0 mL (12.35) 3. A 20.0 mL sample of 0.200 M acetic acid is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH. Calculate the pH of the solution after the following volumes of base have been added. a. Initial pH (original weak acid) (2.72) Before the equivalence point, use the Hendersen-Hasselbalch equation: b. 9.0 mL (4.65) c. 10.0 mL (4.74) d. 11.0 mL (4.83) e. 19.0 mL (6.02) f. 19.9 mL (7.04) At the equivalence point, moles of acid = moles of base. The produced salt determines the pH. g. 20.0 mL (8.87) After the equivalence point, the excess base determines the pH. h. 20.1 mL (10.70) i. 21.0 mL (11.69) j. 25.0 mL (12.35) 4. A hypothetical weak acid, HA, was combined with NaOH in the following proportions: 0.20 mol HA, 0.08 mol NaOH. The mixture was diluted to a total volume of 1.0 L and the pH was found to be 4.80. a. What is the pKa of the acid? (4.98) b. Challenge Problem: How many additional moles of NaOH would need to be added to the solution to increase the pH to 5.00? (ask me!) 5. Calculate the pKa and Ka for the following indicators: a. Bromocresol green: yellow at pH 4, green at pH 4.6, blue at pH 5.2 b. Methyl orange: red at pH 2.8, orange at pH 3.8 (and higher pH’s) (2.5 x 10-5) (5 x 10-4) c. Alizarin yellow R (acidic form yellow, basic form red) has a Ka of 6 x 10-12. At what pH does this indicator change color? (11.2) 6. Calculate the Kb for this unknown base that was titrated with 0.100 M HCl.