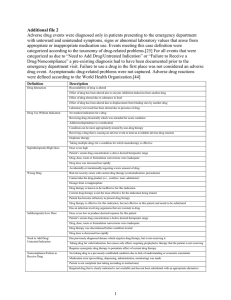
1. Generic Name: Aspirin Pharmacologic class: ANTT-THROMBOTIC AGENT Drug formulation: TABLET 80 mg Mechanism of Action: INHIBITS PROSTAGLANDIN RELEASE; inhibits more COX 1 than COX 2 Indication: For ischemic stroke, MI Dose: Adult: Ischemic stroke- 50- 325 mg initial; Angina 75-300 mg od; Secondary Prevention for 75-325 mg od Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to Aspirin, Asthma and rhinitis, avoid in children with viral infection w/ or w/o fever can cause REYE’S SYNDROME Interactions: Beta blockers ACE Acetazolamide increase concentration Diuretics diminish diuretics effect Methotrexate inhibit renal clearance Adverse reactions: Fever, hypothermia Dehydration, metabolic acidosis Nausea and Vomiting Rhabdomyolysis 2. Generic name: Bambuterol Pharmacologic class: B2-adrenoceptor agonist Drug formulation: Oral 1o mg tablet/ 1mg/ 60 ml oral solution Mechanism of Action: relaxes bronchial smooth muscle by acting to B2-receptors Indication: Persistent reversible airway obstruction Dose: Adult: 10-20 mg od Children: 2-5 yrs old 10 mg in general ; 5mg Asian children 10 mg initial dose Warning/Precautions: Can cause hypokalemia, monitor K levels; Used in precaution for lactating and pregnant women Adverse reactions: tremor, headache 3. Generic Name: Dipivefrine Pharmacologic class: prodrug for epinephrine Drug formulation: Ophthalmic solution Indication: open angle glaucoma Dose: Adult: instill 1 drop every 12 hours 4. Generic name: Valganciclovir Pharmacologic class: Antiviral ; Prodrug for ganciclovir 1 Drug formulation: Tablet 450 mg, oral solution Indication: For CMC cytomegalovirus retinitis Dose: Adult: CMC rhinitis 900 mg per day Children: 4 months to 16 yrs old = 7 x BSA x Cr Cl Warning/Precautions: Do not give to pregnant women, it is teratogenic 5. Generic name: Secnidazole Pharmacologic class: Nitro imidazole antibacterial drug Indication: Bacterial vaginosis; Trichominiasis; Candidiasis Dose: Adult: 2 g orally once a day Contraindications: Hypersensitive to secnidazole Warning/Precautions: Can cause vaginal yeast infection; Do not breastfeed Interactions: interacts with ethanol Adverse reactions: Nausea and vomiting ; headache 6. Generic name: Latanoprost Pharmacologic class: Prostaglandin analog Mechanism of Action: ester pro drug to free acid; analog to F2 alpha prostraglandins Indication: Open angle glaucoma; Ocular hypertension Dose: Adult: Lower intraocular pressure, instill 1 drop Adverse reactions: Iris pigmentation changes, Intraocular inflammation 7. Sulfasalazine Pharmacologic class: DMARDS; Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Drug formulation: Suppository Mechanism of Action: direct anti-inflammatory action in the colon Indication: IBD; Inflammatory Bowel Disease; Rheumatoid Arthritis Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to Sulfa drugs; Blood dyscrasias Warning/Precautions: Hepatic/ renal impairments; G6PD deficient ; - hemolytic anemia 8. Olsalazine Pharmacologic class: Prodrug for Mesalamine; Anti-inflammatory Drug formulation: Capsule Mechanism of Action: Derivative of salicylic acid; it is converted by the bacteria in the colon to mesalamine Indication: treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Ulcerative Colitis 2 9. Enalapril Pharmacologic class: ACE inhibitors; Converted to Enalaprilat Mechanism of Action: Pro drug for enalaprilat; inhibits angiotensin converting enzyme Indication: Management of hypertension, monotherapy or in combination Dose: Adult: IV solution; 1.25 mg every 6 hrs; Oral 5 mg od Children: 20 – 50 kg; 2.5 mg od above 50 kg; 5 mg od Contraindications: History of angioedema with ACE Inhitors; not for pregnant women Warning/Precautions: Cerebrovascular disease Interactions: Potentiate with hypotensive with other hypertensive drug Adverse reactions: Chest pain, angina pectoris, tachycardia, orthostatic hypertension 10. Chloramphenicol succinate Pharmacologic class: Anti-infectives Drug formulation: Otic and Opthalmic drops, IV solution; Eye ointment Mechanism of Action: Antibiotic, eye and ear infection, typhoid fever; Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to chloramphenicol, blood dyscrasias, Pregnancy and lactation Warning/Precautions: Avoid prolong use, not for prophylactic use Interactions: Enhances coumarin effects, antiepileptics, Adverse reactions: Ototoxicity, eye disorder, optic neuritis, N and V, stomatitis 11. Simvastatin Pharmacologic class: Statin; HMG co-reductase inhibitors; Prodrug that hydrolyzed its lactone ring into B-deta-hihyroxy acid Contraindications: Pregnancy and lactation Interactions: Increased myopathy and rhabdomyolysis with amiodarone; 12. Famciclovir Pharmacologic class: Antiviral; Pro drug to the active anti-viral compound penciclovir Drug formulation: Oral dosage dorm Indication: acute herpes zoster infections shingles Dose: Adult: herpes zoster infections shingles 500 mg tid for 7 days Adverse reactions: Headache, nausea and vomiting, constipation; dyspepsia 13. Paracetamol Pharmacologic class: Analgesic Drug formulation: Tablet, Syrup 3 Drug’s chemical structure: Interactions: Adverse reactions: Allergic reactions , flushing 14. Sulindac Pharmacologic class: NSAIDS Drug formulation: Tablet Mechanism of Action: converted to active sulfide compound by liver enzymes; inhibit prostaglandin release Interactions: nephrotoxicity with ciclosporine Adverse reactions: HA, N and V, diarrhea, rash, urine discolaration 15. IBUPROFEN Pharmacologic class: NSAIDS Drug formulation: Tablet 16. Azathioprine Pharmacologic class: Immunosuppressants; Prodrug for 6-Mercapturine Indication: Adjunct to prevent organ rejections 17. Omeprazole Pharmacologic class: Proton Pump Inhibitor Drug formulation: Tablet; IV solution Mechanism of Action: blocks final step in gastric secretion Indication: Eradication of Helicobacter pylori; Duodenal and gastric ulcer; GERD Adverse reactions: Hypomagnesimia, SLE, Clostridum difficili diarrhea 18. Allopurinol Pharmacologic class: Xanthine oxidase inhibitor Drug formulation: Tablet Mechanism of Action: A produg that is converted to oxypurinol Indication: Gout, hyperuricemia 19. Terfenadine Pharmacologic class: Metabolized into Fexofenadine ; Antihistamine Drug formulation: Tablet 4 20. Codeine Pharmacologic class: Opioid Analgesic; converted to morphine (active metabolite) Mechanism of Action: phenantherene derivative; suppress cough Indication: IM moderate pain- 30- 60 mg every hour as needed Adverse reactions: CNS depressions; blood and lymphatic system disorders 21. Disulfiram Pharmacologic class: Alcohol antagonist Drug formulation: Tablet Drug’s chemical structure: blocks alcohol oxidation Contraindications: Alcohol containing products 22. Pyridoxine Pharmacologic class: Vitamin B6 derivative; converted to pyridoxal 5-phosphate 23. Isoniazid Pharmacologic class: Anti tuberculosis Drug formulation: Tablet, Oral Solution, Solution for Injection Mechanism of Action: activated by bacterial catalase; Indication: to treat active tuberculosis; Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to the drug Warning/Precautions: History of psychosis, neuropathy, pyridoxine neuropathy Interactions: (-) hepatic metabolism of benzodiazepine; increase toxicity warfarin; Adverse reactions: optic neuritis; peripheral neuritis; 24. Tegafur Pharmacologic class: Anti-metabolites; Anti neoplastic Mechanism of Action: Prodrug of 5-fluorouracil; used for colon/bowel cancer Dose: Children: not applicable Contraindications: Pregnancy/ lactation Warning/Precautions: hepatic impairment Interactions: Increase phenytoin toxicity; Increase thrombosis for tamoxifen Adverse reactions: N & V, mucositis; alopecia; myocardial ischemia 25. Fosinopril 5 Pharmacologic class: Ace inhibitors Mechanism of Action: Prodrug for Fosinoprilat Indication: Mild to moderate hypertension, Dose: Adult: 10 mg od; risk of hypotension 5 mg od; maintenance 10-40 mg once daily Children: based on weight; Contraindications: history of angioedema with ACEis; pregnancy/ lactation Warning/Precautions: Mitral valve stenosis/ Dialysis/ renal impairment Interactions: Increase lithium toxicity; Adverse reactions: Persistent and nonproductive COUGH; URTI infection, N and V; Fatal: anaphylaxis 26. Naproxen Pharmacologic class: NSAIDS Indication: Arthritis; osteoarthritis; dysmenorrhea Dose: Adult: Children: based on weight Contraindications: Contraindicated to known hypersensitivity to naproxen Adverse reactions: cardiovascular risk; GIT discomfort; diarrhea; headache, hypersensitivity reaction 27. Levodopa Pharmacologic class: Antiparkinsons drug Drug formulation: tablet Mechanism of Action: converted into dopamine Indication: symptoms of Parkinsonisms; Dose: Adult: 250 mg 2 to 4 times a day, not more 8 g a day Children: Contraindications: Psychotic patients exacerbation to mental disturbance, may activate malignant melanoma Warning/Precautions: open-angle glaucoma; high blood pressure, asthma, COPD; ulcers, depression, psychosis Interactions: Pyridoxine, MAOi inhibitors Adverse reactions: Anxiety, confusions, delusions, anorexia,, N and V ; 28. Ramipril Pharmacologic class: ACEis; active metabolite Ramiprilat Drug formulation: Capsule/ Tablet 6 Mechanism of Action: (-) ACE ; result to blood pressure decreases Indication: - hypertension, prevention heart failure, MI Dose: Adult: 2.5mg once a day; preventing heart attack 2.5 mg once a day; Children: not applicable Contraindications: Renal artery stenosis, low blood pressure Warning/Precautions: Can cause to serious harm to the baby; do not use in pregnancy Adverse reactions: Can cause dizziness, tiredness, causes dry cough 29. Pentazocine Pharmacologic class: Analgesics 30. Fludarabine Pharmacologic class: Antimetabolites; purine nucleoside Mechanism of Action: A prodrug that is converted to the free nucleoside 9-beta-D-arabinosyl-2fluroadenine Indication: leukemia and lymphoma Dose: Adult: leukemia; Children: Contraindications: Hemolytic anemia; lactation Warning/Precautions: Sever impairment of bone marrow; hepatic impairment; pregnancy Adverse reactions: Skin cancer exacerbations, seizure, peripheral neuropathy; GI: N and V, diarrhea; GI bleeding, constipation Respiratory: cough, bronchitis, hypoxia 31. Benzhydrocodone Mechanism of Action: Prodrug for hydrocodone; Contraindications: Bronchial asthma; GI obstruction Warning/Precautions: can cause drowsiness and breathing problems when taken with alcohol Adverse reactions: N and V, headache, drowsiness 32. Bacaillin Pharmacologic class: Penicilllins Drug formulation: Oral tablets/ capsule Mechanism of Action: prodrug of ampicillin; Indication: pneumonia; typhoid fever, UTI Dose: Adult:400 mg Children: 7 Contraindications: hypersensitivity to Penicillins Interactions: Probenecid stays longer Adverse reactions: hypersensitivity reactions urticaria, angioedema, serum sickness, thromcytopenia 33. Temozolomide Mechanism of Action: hydrolyzed to 3-methyl-imidazole-4 carboxamide active metabolite to dacarbazine Indication: treatment recurrent or progressive gliomas, melanoma Dose: Adult: 200 mg/m2 ; 150mg/ m2 Children: Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to dacarbazine; Warning/Precautions: Sever hepatic/ renal impairment; avoid becoming pregnant; irreversible infertility Interactions: reduce effectiveness of vaccines; Adverse reactions: N and V; diarrhea; stomatitis; tremors, speech disorder; 34. Capecitabine Pharmacologic class: Antineoplastic, Drug formulation: Tablet Mechanism of Action: Active metabolite fluorouracil; Indication: first line treatment for colorectal carcicnoma; Contraindications: altered Interactions: increase plasma concentration of phenytoin; Adverse reactions: N and vomiting, palmar plantar; fatigue 35. Fosphenytoin Pharmacologic class: Anti-seizure drug Drug formulation: IV solution Mechanism of Action: converted to phenytoin; Contraindications: Hypersensitivity to phenytoin; Warning/Precautions: hypotension, sever myocardial insufficiency, hyperbilirubinemia; phosphate restrictions; poor and intermediate metabolizers Interactions: increase plasma levels amiodarone, azole antifungals; 8 36. Prednisone Pharmacologic class: Corticosteroids Drug formulation: Oral solution Mechanism of Action: converted into prednisolone Indication: Inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; Warning/Precautions: hypertension, osteoporosis, Interactions: antiplatelet drug such as clopidogrel, Adverse reactions: acne, heart burn, irregular menstrual period 37. Pivampicillin Pharmacologic class: Antibacterial Mechanism of Action: Prodrug of ampicillin Contraindications: Porphyria; Warning/Precautions: Neurotoxicity Adverse reactions: fever, rashes, angioedema; 38. Selexipag Pharmacologic class: Selective prostacyclin receptor agonist Mechanism of Action: Prodrug of ACT-333679 (the free carboxylic acid) Indication: treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension Contraindications: Severe hepatic impairment; Adverse reactions: headache, diarrhea, 9