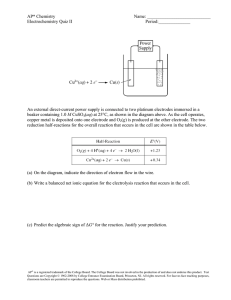
Voltammetry Group Members Amna Khalid (F2018067027) Sadia Nasreen (F2018067007) Presented to Dr. Naveen KOsar Introduction of Voltammetry • Electroanalytical Method • Information about analyte is obtained by measuring current as potential is varied[1] • Electrolysis on microscale is done • Smaller concentration i.e in micromolar can be determined Steps involved in voltammetry • Voltage ramp is applied to electrode • Measurement of current • Reduction or oxidation ions in electrodes[2] Voltammogram The resulting plot of current versus applied potential is termed as voltammogram Voltammetric Cell • It is just like an electrochemical cell • It consist of commonly three electrodes 1. Working Electrode 2. Auxiliary Electrode 3. Reference Electrode[3] Working Current-Voltage Curve Evs SCE = EVS NHE – 0.242 Decomposition Potential • Difference in the electrode potential cathode and anode in order for electrolysis to occur. • Minimum voltage produced electrolytic cell • Used in the electrolysis process from an Limiting Current • Rate of charge transfer to an electrode is increased. • The limiting current can be approached • When further increase in potential does not effect the increase in current. This is termed as limiting Current. [4] Voltammetric Curve Curves obtained in the graph between potential and applied current Types of voltammetric curve The shape of the curves depends on • The speed of potential variation • Whether the solution is stirred mass transfer[5] S-shaped Curve • Solution is stirred or electrode is rotated • Limiting current is constant • S-shaped curved is obtained Peaked Curve • Solution is unstirred • No mass transfer • Peaked wave is obtained Some Terminologies • Polarized Electrode • Depolarized Electrode • Depolarizer Two Voltammetric Waves • Depolarizer is oxidized then anodic current is recorded at potentials more positive than decomposition potential Applications Measurement of • Concentration and Activity. • pH. • Hardness • Complete voltammetric cells are referred to as sensors.[6] References 1. Kissinger, Peter; William R. Heineman (1996-01-23). Laboratory Techniques in Electroanalytical Chemistry, Second Edition, Revised and Expanded (2 ed.). CRC. ISBN 0-8247-9445-1. 2. Zoski, Cynthia G. (2007-02-07). Handbook of Electrochemistry. Elsevier Science. ISBN 0-444-51958-0 3. https://chem.libretexts.org/Under_Construction/Purgatory/Book%3A_Analytica l_Chemistry_2.0_(Harvey)/11_Electrochemical_Methods/11.4%3A_Voltammetric _Methods 4. Harris, Daniel C. (2016-01-01). Quantitative Chemical Analysis, Ninth Edition (9 ed.). W.H. Freeman and Company. ISBN 978-1-4641-3538-5 5. Bard, Allen J.; Larry R. Faulkner (2000-12-18). Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications (2 ed.). Wiley. ISBN 0-471-04372-9 6. Sanghavi, Bankim; Srivastava, Ashwini (2010). "Simultaneous voltammetric determination of acetaminophen, aspirin and caffeine using an in situ surfactant-modified multiwalled carbon nanotube paste electrode".