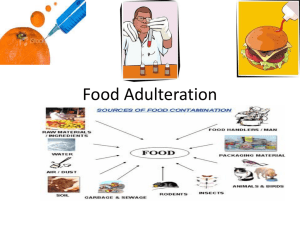
ADULTERATION OF CRUDE DRUGS DEFINATION Adulteration is a practice of substituting original crude drug partially or whole with other similar looking substances but the latter is either free from or inferior in chemical and therapeutic properties. OR Adulteration in simple words is the debasement of an article. OR Adulteration is broadly defined as admixture or substitution of original or genuine article/ drug with inferior, defective uselessor harmful substances. or otherwise ADULTRANT : The adulterant must be some material which in both cheap and available in fairly large amounts. Substitution is the addition of an entirely different article in place of that which is required e.g. Supply of cheap cottonseed oil in place of olive oil (Sweet oil). TYPES OF ADULTERATION 1.Deliberate ( Intentional ) adulteration 2. Accidental ( In-deliberate) adulteration 1. DELIBERATE ADULTERATION ( INTENTIONAL ) Deliberate adulteration – Are normally commercial mainly with the intention of enhancement of profits . 2. IN-DELIBERATE ( ACCIDENTAL) ADULTERATION In - Deliberate adulteration – Are normally naturally occurring, accidental, careless or by ignorance and non harmful. REASONS FOR ADULTERATION 1.Scarcity of the drug. 2.The high price of the drug in the market, eg: Clove, Cinnamon, Cardamom 3.It is very common with the contraband drugs e.g. Opium CONDITIONS OR STAGES OF ADULTERATION The term 'adulteration' or debasement of an article covers a number of conditions, which may be deliberate or In- deliberate. Inferiority, Spoilage, Deterioration, Admixture, Sophistication Substitution , Inferiority Is a natural substandard condition (e.g. where a crop is taken whose natural constituent is below the minimum standard particular drug) for that Spoilage Is a substandard condition produced by microbial or other pest infestation, which makes a product unfit for consumption. Deterioration Is the loss in the quality or value of an article due to destruction valuable constituents by bad treatment or aging or to the deliberate extraction of the constituents. Admixture Is the addition of one article to another through accident, ignorance or carelessness e.g. Inclusion of soil on an underground organ or the co-collection of two similar species. Sophistication Is the deliberate addition of inferior material with intent to defraud ( cheat to get money ) ; such materials are carefully produced and may appear at first sight to be genuine. E.g. Powder ginger may be diluted with starch with addition of little coloring material to give the correct shade of yellow colour. Substitution Is the addition of an entirely different article in place of that which isrequired. E.g. Supply of cheap cottonseed oil in place of olive oil (Sweet oil). METHODS OF DRUG ADULTERATION 1.Substitution with Inferior/Sub- standard Commercial Varieties 2. Adulteration by Artificially Manufactured Substitutes 3. Substitution by Exhausted Drugs 4. Adulteration by Addition of Worthless Heavy Materials ( Harmful Adulteration) 5. Addition of Synthetic Principles 6. Usage of Vegetative Matter from the Same Plant 7. Adulteration of Powders 1.Substitution with Inferior/Sub-standard Commercial Varieties Due to morphological resemblance to the authentic drugs, different inferior commercial varieties are used as adulterant which may or may not have any chemical or therapeutic potential asthat original natural drug This is the most common type of adulteration Eg. Arabian Senna and Dog Senna have been used to adulterate Indian Senna (Cassia senna) Eg. Medicinal Ginger ( Zingiber officinale) is replaced by Japanese ginger (Zingiber mioga ) 2. Adulteration by Artificially Manufactured Substitutes Here the substances artificially prepared to resemble the original drug ( provide the general form and appearance i.e colour, shape, size) and are used as substitute of the original one. Generally , this practice is followed for much costlier drugs Eg. Artificial invert sugar for Honey Eg. Paraffin wax made yellow coloration and substituted for Bees wax. Eg. Compressed chicory in place of Coffee 3. Substitution by Exhausted Drugs In this type the same plant drug is admixed but it is devoid of any medicinally active constituents as they extracted out. components as extracted out). (no are active already medicinal they have already been This practice is most common in case of volatile oil containing materials like clove, fennel , cardamom, cinnamon etc., Eg. Exhausted Clove to Clove Eg. Exhausted Ginger to Ginger 24 5. Adulteration by Addition of Worthless Heavy Materials ( Harmful Adulteration) Here, the wastes from market are collected and admixed with original drug. This is particularly noticed for liquids and unorganized drugs. Eg. Limestone in Asafoetida Eg. Pieces of amber colored glass in Colophony Eg. Addition of rodent is a waste matter to cardamom seed adulteration very harmful Eg. White stones in rice 6. Addition of Synthetic Principles Sometimes to fortify inferior natural products, synthetic principles are added Eg. Adding Citral to Oil of Lemon Eg. Benzyl benzoate to Balsam of Peru etc. 7. Usage of Vegetative Matter from the Same Plant Some times, the other plants growing along with medicinal plant are mixed due to their resembling colour, odour and in some cases constituents. Eg. The lower plants like Moss,Liver warts and epiphytes growing on plant (bark) portion are mixed with Cinchona or Cinnamon Eg : Stems portions are mixed along with leaf drugs like Lobelia, Senna, Datura etc 8. ADULTERATION OF POWDERS Besides the entire drugs, the powdered forms are frequently , found to be adulterated. Eg. Red Sanders wood in Capsicum Eg. Exhausted Ginger powder in powdered Ginger Eg. The powdered bark is frequently adulterated with Brick powder QUESTION BANK Long Essays: 10 Marks 1.Explain in detail the various methods of adulteration of crude drugs with examples. 2. Explain the five different methods used for adulteration of crude drugs and discuss. 4. Define adulteration. Explain the various methods of adulteration with examples. 5.What do you mean by deliberate and indeliberate adulteration give examples Short Essays: 5 Marks 1. Define adulteration and explain the various methods of adulteration. 2. Define adulteration and give the reasons for adulteration with examples. 3. What do you mean by deliberate and indeliberate adulteration with examples? 4. Discuss with examples on adulteration of powder and liquid drugs. 5. Explain in detail the methods of adulteration of crude drugs with examples. 6. Name five different methods used for adulteration of crude drugs and explain with examples. 7.What is adulteration? Explain in-deliberate adulteration of crude drugs with examples 8. Name five different methods used for adulteration of crude drugs and explain with examples. 9. What is adulteration? Explain in-deliberate adulteration of crude drugs with examples 10.What is adulteration? Explain the deliberate adulteration of crude drugs with examples. Short Answers: 2 Marks 1.Define Adulteration and Substitution. 2. What do you mean by deliberate and indeliberate adulteration? 3. Give the various reasons of adulteration 4. Artificial adulteration with examples. 5. Name the different methods of adulteration of crude drugs. 6. Define adulteration and sophistication. 7.What are exhausted drugs? Give examples. 8.What is harmful adulteration? Giveexamples. 9. Give the difference between substitute and official drug with example. 10.What is substitution? Giveexamples. 11.What is deterioration? Giveexample. 12.Adulteration of crude drugs with artificial adulterants