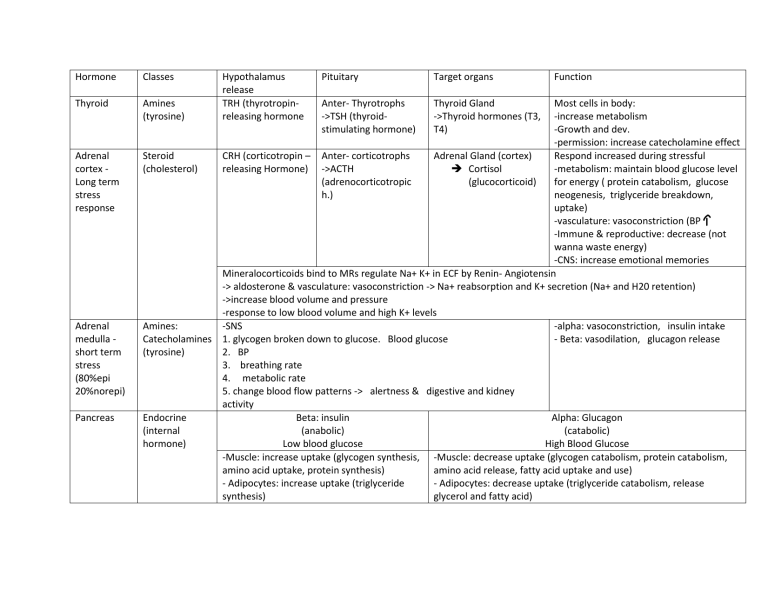
Hormone Classes Thyroid Amines (tyrosine) Adrenal cortex Long term stress response Adrenal medulla short term stress (80%epi 20%norepi) Pancreas Hypothalamus release TRH (thyrotropinreleasing hormone Pituitary Target organs Anter- Thyrotrophs ->TSH (thyroidstimulating hormone) Thyroid Gland ->Thyroid hormones (T3, T4) Function Most cells in body: -increase metabolism -Growth and dev. -permission: increase catecholamine effect Steroid CRH (corticotropin – Anter- corticotrophs Adrenal Gland (cortex) Respond increased during stressful (cholesterol) releasing Hormone) ->ACTH Cortisol -metabolism: maintain blood glucose level (adrenocorticotropic (glucocorticoid) for energy ( protein catabolism, glucose h.) neogenesis, triglyceride breakdown, uptake) -vasculature: vasoconstriction (BP -Immune & reproductive: decrease (not wanna waste energy) -CNS: increase emotional memories Mineralocorticoids bind to MRs regulate Na+ K+ in ECF by Renin- Angiotensin -> aldosterone & vasculature: vasoconstriction -> Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion (Na+ and H20 retention) ->increase blood volume and pressure -response to low blood volume and high K+ levels Amines: -SNS -alpha: vasoconstriction, insulin intake Catecholamines 1. glycogen broken down to glucose. Blood glucose - Beta: vasodilation, glucagon release (tyrosine) 2. BP 3. breathing rate 4. metabolic rate 5. change blood flow patterns -> alertness & digestive and kidney activity Endocrine Beta: insulin Alpha: Glucagon (internal (anabolic) (catabolic) hormone) Low blood glucose High Blood Glucose -Muscle: increase uptake (glycogen synthesis, -Muscle: decrease uptake (glycogen catabolism, protein catabolism, amino acid uptake, protein synthesis) amino acid release, fatty acid uptake and use) - Adipocytes: increase uptake (triglyceride - Adipocytes: decrease uptake (triglyceride catabolism, release synthesis) glycerol and fatty acid) Growth hormone Parathyroid Exocrine (external digestive) peptide -Liver: decrease gluconeogenesis (glycogen synthesis, triglyceride synthesis, NO KETONE synthesis) **control: plasma glucose, plasma a.a, incretins, PNS, SNS -Liver: Increase gluconeogenesis, glycogen catabolism, KETONE synthesis and release GHRH (growth hormone- releasing hormone) Liver IGF-1 Ante- somatotroph GH SNS: extreme stress -> release epi from adrenal medulla (ex: fasting over 24h). -growth (IGF-1) -Protein synthesis -increase glucose and lipid, but preserve muscles ( gluconeogenesis, lipolysis, uptake) Opposite insulin, main anabolic, some catabolic (BUILD proteins but break down fat and carbs) Bone growth: (L34)GH and main Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), thyroid h. (T3), insulin, sex h. (Estrogen and testosterone). Cortisol (-) -increase Ca2+ reabsorption in kidneys -increase osteoclast -increase formation of vitamin D -> increase uptake of Ca2+ in GI tract -decrease Ca2+ by inhibit osteoclast - secretion ONLY HIGH Ca2+ level Calcitonin (from parafollicular of thyroid) Prolactin Inhibit by dopamine unless new mother needs it (breastfeed or sucking)- milk production Oxytocin Milk delivery and uterine constraction Vasopressin Low Water (high blood plasma osmolarity) -release ADH, increase thirst –AQPR 2-> Na+ and H2O retention AVP/ADH Steroids and thyroid: protein bound and intracellular receptor -> gene transcription -> slow Peptides and catecholamines: free (unbound), plasma protein receptors (GPCR)-> second message -> fast
