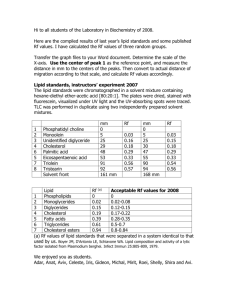
HIF DRIVES LIPID DEPOSITION AND CANCER IN CCRCC VIA REPRESSION O F FAT T Y A C I D M ETA B O L I S M B Y: O F U R E A K H I G B E D AT E : 3 0 A P R I L 2 0 2 0 INTRODUCTION Clear cell caused by lipid and glycogen rich deposit Also known as renal cell carcinoma occurs in both sporadic and heritable forms Different subtypes of renal cell carcinoma: Clear-cell INTRODUCTION Fatty acid (FA) synthesis is an anabolic process that responds to excess citrate in the cytoplasm. Metabolism of glucose under aerobic conditions produces pyruvate Citrate can also be produced from metabolism of glutamine via αketoglutarate in cancer cells either through forward flux through oxaloacetate, or through reverse cycle activity of isocitrate dehydrogenase and aconitase Enters the citric acid cycle in mitochondria by the action of pyruvate dehydrogenase to produce acetyl-CoA, and then citrate-by-citrate synthase. Produce citrate FATE OF THE EXCESS CITRATE exported to the cytosol, where it is a substrate for ATP citrate lyase to produce cytosolic acetyl-CoA. carboxylation of acetyl-CoA by acetylCoA carboxylase to form malonyl-CoA malonyl-CoA to fatty acid ROLE OF FATTY ACID To serve as substrates for membrane synthesis, Energy stores Production of signaling molecules. Abnormal cancer metabolism leads to excessive storage in the form of lipids. GOAL OF THE RESEARCH To determine the molecular mechanisms driving lipid deposition in ccRCC. MATERIAL/METHOD Mouse tumor assays Fatty acid uptake assay Materials and Methods Chromatin Immunopreci pitation(ChIP) Cell culture and reagents Oil red O staining Real time PCR Western blots RESULT Lipid droplet formation requires glucose, but not glutamine. Together, the observations suggest lipid droplet formation in ccRCC cells is highly dependent on glucose rather than glutamine RESULTS Lipid droplet formation is dependent on HIF. OVERALL CONCLUSION Metabolic adaptation in clear cell renal cell carcinoma resulting in activation of lipid storage pathways is a necessary step in the development of malignancy. Metabolic changes in ccRCC include shifts to anaerobic metabolism through the HIF-dependent activation of many genes in the glycolytic pathway, reductive carboxylation of glutamine derived α-ketoglutarate as a carbon source in place of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. FOLLOW UP EXPERIMENT Would slowing down or reducing the amount of glucose produced in ccRCC patients help in reducing lipid deposition? Follow up Experiment: I would cultivate cells from renal cancer patients with lipid deposits and monitor how the rate of glucose production affects the lipid deposition THINGS I LEARNED FROM MY INTERVIEW: I interviewed Ms Ann Cooke Ms Ann Cooke was diagnosed with breast cancer a day before her nineteenth anniversary breast cancer changes a woman both physically and emotionally Cancer does not just affect the body physically it is very important for patients to build a personal connection with their surgeon and team. REFERENCES Du, Weinan, et al. “HIF Drives Lipid Deposition and Cancer in CcRCC via Repression of Fatty Acid Metabolism.” Nature News, Nature Publishing Group, 24 Nov. 2017, www.nature.com/articles/s41467-017-01965-8.