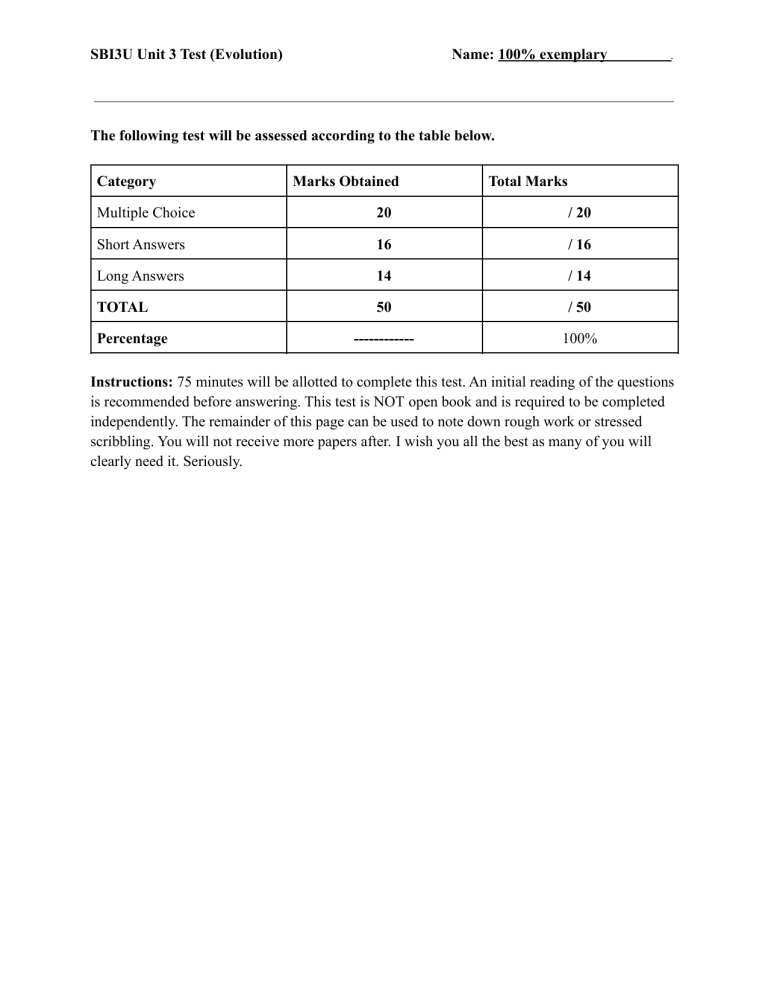
SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary . The following test will be assessed according to the table below. Category Marks Obtained Total Marks Multiple Choice 20 / 20 Short Answers 16 / 16 Long Answers 14 / 14 TOTAL 50 / 50 ------------ 100% Percentage Instructions: 75 minutes will be allotted to complete this test. An initial reading of the questions is recommended before answering. This test is NOT open book and is required to be completed independently. The remainder of this page can be used to note down rough work or stressed scribbling. You will not receive more papers after. I wish you all the best as many of you will clearly need it. Seriously. SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary Section I: Multiple Choice (20 points) 1. The evolutionary theory of Uniformitarianism was advocated extensively by English geologist Sir Charles Lyell. This theory states that: (1) a. Earth has developed by same processes in the past as can be seen happening today b. Geological change is slow & occurs gradually c. Natural laws and processes are constant and eternal d. All of the above 2. The following diagram shows the theory of evolution by the Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics. Which of the following scientists had proposed this? (1) a. Charles Robert Darwin b. Alfred Russell Wallace c. Jean-Baptiste Lamarck d. James Hutton 3. Behavioural Isolation can be defined as: (1) a. When reproductive organs can function only when in the presence of the same species b. Preventing fertilization on the molecular level. c. Different rituals or actions used to recognize a suitable mate. 4. The reproductive isolating mechanism in question 3 is an example of which category? (1) a. Prezygotic mechanism b. Post-zygotic mechanism c. Behavioural Isolation is not an example of reproductive isolation mechanisms. 5. The name of the book which Darwin published introduced the Theory of Natural Selection. (1) a. Darwin and the Origin of Species b. Theory of Natural Selection by Darwin c. On the Origin of Species d. Natural Selection: The Theory . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary 6. Match the following terms with a definition or an appropriate example. (5) 7. Which of the following is not an example of mimicry? (1) a. An octopus distorts its body and adapts its colour to resemble a poisonous sea snake. b. A harmless garden snake closely mirrors the deadly coral snake. c. A garden bug looks like the average wasp. d. An emu resembles an ostrich. 8. A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance is called (1) a. Gene flow b. Natural selection c. Genetic drift d. Sexual selection 9. Organisms on islands are different, however closely related to similar ones found on the nearest continent. This is evidence that (1) a. They have descended from common ancestors b. Similar environments are inhabited by the same organisms c. The islands were originally part of the continent before geological changes d. The island forms and mainland forms are a coincidence 10. Which of the following are reasons for intrasexual competition: (1) a. Territorial fights b. Courtship rituals c. Battles d. All of the above . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary 11. The following graph represents: (1) 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. a. Stabilizing selection b. Disruptive selection c. Directional selection Homo sapiens are a part of which evolutionary group: (1) a. Ardipithecus b. Australopithecus c. Homo group d. Paranthropus 2 sibling rats have mated. This causes frequencies of genotypes to change in the population but it does not change the allele frequencies. This is an example of: (1) a. Inbreeding b. Founder effect c. The wolverine effect Structures that are similar in structure, but not origin are: (1) a. Homologous b. Analogous c. Fossil records d. Embryology This was NOT a piece of evidence that Darwin used to back up his theory of natural selection. (1) a. fossil records b. DNA c. Embryology d. Vestigial structures Which of the following best describes the role of beneficial mutations? (1) a. They improve the appearance of the individuals. b. They provide individuals with a better chance of survival. c. They expand the size of the individuals. . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary Section II: Short Answers (16 points) 1. How do adaptions develop? (1) Adaptions are changes that are the result of random, heritable mutations in DNA that develop over generations. 2. Which mechanism of evolution are the two figures showing? Describe what is happening in figure (a) VS. figure (b). (2) These graphs are documenting genetic drift. In figure (a), it is proven that smaller populations have dramatic changes in allele frequencies. While in figure (b), it is shown that in larger populations, genetic drift is not significant. 3. Define artificial selection. What does the “artificial” in artificial selection refer to? (2) Artificial selection is conducted breeding where individuals that exhibit a particular allele are chosen as parents of the next generation. It is termed to be “artificial” because it occurs in captivity rather than in a natural setting, and humans choose which specific animals or plants are bred. 4. An athlete badly injures her leg. Years later, she has a child. When the child starts walking, there is an evident limp. Is this an example of evolution? Explain your answer briefly. (2) This is not an example of evolution as an injured leg is temporary and has no genetic influence on an offspring. . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary 5. Some animals have evolved protective coloration. Observe. (3) a. What is this an example of? (1) This is an example of mimicry. b. What does this pattern represent? (1) This pattern represents the eyes of a much larger animal. c. According to natural selection, why is this animal favoured in survival? (1) Since the eyes scare of predators thinking this is a larger animal, it increases the survival rate of this organism. 6. Sticklebacks are well suited for evolutionary biology as well as molecular biology. What are the important characteristics sticklebacks possess that result in this coincidence? (2) The stickleback is small enough, has a short enough generation time and can be bred in labs. They are found all across the northern hemisphere as well. 7. At least one gene responsible for the development of the stickleback pelvis and spines has homology to a gene involved in hind-limb formation in mice and other vertebrates. What is this suggesting? (1) This suggests that pelvic formation occurs through a genetic mechanism shared throughout the common ancestry. . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary 8. Name the two types of sexual selections found in birds and briefly discuss their differences. (3) Intrasexual selection - when male individuals compete with each other for the mate. Also, intersexual when the female chooses the mate. . SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary . Section III: Long Answers (14 points) 1. Like all other mammals, humans possess 3 bones in our ears. Reptiles only have one. How did humans evolve to possess 2 extra bones? Use Opposusms as an example for your answer. (4) Opposum embryos have reptilian-style ears, with only one bone. The two extra ear bones are part of their jaws. Then, after they’re born and while growing up, those extra bones decrease in size and develop into mammalian ears, apart from the jaw and onto their upper skull. Similarly, more recent fossil records show that mammals had formed a completely new jaw joint - with the bone that holds teeth increasing in size enough to touch the skull. Over time, bones that held the old jaw shrank and became redundant. Instead of diminishing, however, these fossil records show that humans now hear with the bones that our reptilian ancestors once ate with. 2. According to the graphs above, what has occurred in these 3 situations? (3) In graph A, there’s a shift in the average bird beak size with the size decreasing. In graph B, stabilizing selection has occurred in the bird body mass average. In graph C, disruptive selection has occurred in the bird beak size average. a. Name one possible scenario that could explain the changes in Graph A. (2) Multiple possible answers. Example: Recently, precipitation of the area may have decreased, resulting in decreasing food availability and vegetation. Trees and nuts will have harder shells as well. This will result in direct favour of birds with larger beaks to crack them open and find the food in the first place. SBI3U Unit 3 Test (Evolution) Name: 100% exemplary . 3. Evidence for evolution includes fossil records. Fish were found to be in the deepest sedimentary layers. Amphibians, reptiles and mammals, seemed to have appeared later. a. Using your knowledge of fossil records, describe the timeline of this evolution. (3) The information provided shows that the fossils of amphibians, reptiles and mammals are most similar to species alive today, while fish are older. Fossils appear in chronological order within the sedimentary layers, and the deeper the layers, the older the fossils. Therefore, this evidence suggests gradual structural changes of a species occurred over time. b. Identify and define the term used to describe fragments of fossils in records. Provide one example. (2) Vestigial structures - these are reduced forms of structures that were functional in an organism’s ancestors. An example of vestigial structures would be wisdom teeth. (Multiple possible answers for example)