Changes of State Worksheet: Melting, Freezing, Evaporation
advertisement

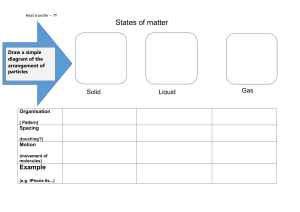
Changes of State Worksheets Starter: Retrieval Practice * Solids Liquids Gases Particle model Particle arrangement Forces between particles Very strong forces between bonds. Weak forces between bonds. Particles are far apart in a random arrangement. Quite strong forces between bonds Particles are very close together in an ordered arrangement. Particles are quite close together but can move round each other. Starter: Retrieval Practice ** Solids Liquids Gases Particle model Particle arrangement Forces between particles Very strong forces between bonds. Weak forces between bonds. Particles are far apart in a random arrangement. Quite strong forces between bonds. Particles are very close together in an ordered arrangement. Particles are quite close together but can move round each other. * Objective: To Identify State Changes Look at the above diagram and use the appropriate changes of state to fill in the gaps where you think the processes go. Keywords: Freezing Melting Evaporating Condensing ** Objective: To Identify State Changes Look at the above diagram and use the appropriate changes of state to fill in the gaps where you think the processes go. Objective: To Identify State Changes * Answer the following questions: 1. In which change of state does a liquid turn into a gas? 2. In which change of state does a liquid turn into a solid? 3. In which change of state does a solid turn into a liquid? 4. In which change of state does a gas turn into a liquid? 5. Which 2 changes of state are linked with heating? 6. Which 2 changes of state are linked with cooling? Keywords: Freezing Melting Evaporating Condensing ** Objective: To Identify State Changes Answer the following questions: 1. In which change of state does a liquid turn into a gas? 2. In which change of state does a liquid turn into a solid? 3. In which change of state does a solid turn into a liquid? 4. In which change of state does a gas turn into a liquid? 5. Which 2 changes of state are linked with heating? 6. Which 2 changes of state are linked with cooling? Objective: To describe what happens to the energy at each change of state * Melting Solid Evaporating Liquid Liquid Fill in the blanks: _____ energy _____ forces of attraction between particles Particles move ______ apart Keywords: gain breaks further Gas ** Objective: To describe what happens to the energy at each change of state Solid Liquid Liquid Label the change od state occurring and then fill in the blanks: _____ energy _____ forces of attraction between particles Particles move ______ apart Gas * Objective: To describe what happens to the energy at each change of state Condensing Freezing Liquid Solid Gas Fill in the blanks: Energy is _____ Forces of attraction between particles ______ Particles move ______ apart Keywords: closer lost reform Liquid ** Objective: To describe what happens to the energy at each change of state Liquid Solid Gas Label the change od state occurring and then fill in the blanks: Energy is _____ Forces of attraction between particles ______ Particles move ______ apart Liquid Objective: To represent changes of state in a graph form (heating and cooling curves) * 2. What is the state of matter at: P: Q: R: 3. What change of state is happening at: A: B: Temperature 1. Does the graph show heating or cooling? B A Q P Time Keywords: Liquid gas evaporating solid melting R Objective: To represent changes of state in a graph form (heating and cooling curves) 1. Does the graph show heating or cooling? 2. What is the state of matter at: P: Q: R: 3. What change of state is happening at: A: B: Temperature ** B A Q P Time R * Objective: To represent changes of state in a graph form (heating and cooling curves) 1. Does the graph show heating or cooling? 3. What change of state is happening at: C: D: Temperature 2. What is the state of matter at: X: Y: Z: X liquid freezing solid D Time Keywords: gas C condensing Z ** Objective: To represent changes of state in a graph form (heating and cooling curves) 1. Does the graph show heating or cooling? 3. What change of state is happening at: C: D: Temperature 2. What is the state of matter at: X: Y: Z: X C D Time Z Plenary * The table summarises what happens to the particles in a substance when it gains energy, and it melts or evaporates (i.e. changes state) so fill in the blanks: Melting Description (change of state) Closeness of particles Motion of particles Description (change of state) Stay random Arrangement of particles Motion of particles Freezing Gas to liquid Closeness of particles Stay close together Start to move around each other Condensing Evaporating Liquid to gas Arrangement of particles The table summarises what happens to the particles in a substance when it looses energy, and it freezes or condenses (i.e. changes state) so fill in the blanks: Stay close together Stay random Stop moving around each other, and only vibrate on the spot Plenary ** The table summarises what happens to the particles in a substance when it gains energy, and it melts or evaporates (i.e. changes state) so fill in the blanks: Melting The table summarises what happens to the particles in a substance when it looses energy, and it freezes or condenses (i.e. changes state) so fill in the blanks: Condensing Evaporating Description (change of state) Description (change of state) Closeness of particles Closeness of particles Arrangement of particles Arrangement of particles Motion of particles Motion of particles Freezing