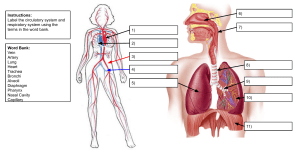
Human Anatomy & Physiology The Cardiovascular System Vocab and Questions for Review Learning Targets: 11-1: Describe the location of the heart in the body, and identify its major anatomical areas on an appropriate model or diagram. 11-2: Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. 11-3: Compare the pulmonary and systemic circuits. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Cardiovascular system Mediastinum Apex Base Pericardium Fibrous pericardium Serous pericardium Parietal layer Visceral layer (epicardium) Pericarditis Myocardium Endocardium Atria (label and Label on picture define) Ventricles (label and define) Interventricular septum Label on picture Interatrial septum Label on picture Superior venae cavae Inferior venae cavae Pulmonary trunk Label on picture Pulmonary arteries Label on picture Pulmonary veins Label on picture Pulmonary circulation Aorta (label and define) Systemic circulation Questions for Review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. What is the location of the heart in the thorax? 2. Which heart chamber has the thickest walls? 3. What is the functional significance of the heart’s structural differences in wall thickness? 4. How does the function of the systemic circulation differ from that of the pulmonary circulation? Learning Targets: 11-4: Explain the operation of the heart valves. 11-5: Name the functional blood supply of the heart. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Atrioventricular (AV) valves Label on picture Bicuspid (mitral) valve Label on picture Tricuspid valve Label on picture Chordae tendineae Label on picture Semilunar valves Label on picture Pulmonary valve Label on picture Aortic semilunar valve Label on picture Endocarditis Coronary arteries Label on picture Coronary sulcus Label on picture (atrioventricular groove) Anterior interventricular artery Label on picture Circumflex artery Label on picture Posterior interventricular artery Label on picture Marginal artery Label on picture Cardiac veins Coronary sinus Label on picture Angina pectoris Infarct Myocardial infarction Questions for Review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Why are the heart valves important? 2. Why might a thrombus in a coronary artery cause sudden death? Learning Targets: 11-6: Name the elements of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart, and describe the pathway of impulses through this system 11-7: Explain what information can be gained from an electrocardiogram. 11-8: Define: systole, diastole, stroke volume, cardiac cycle, heart sounds, and murmur. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Intrinsic conduction (nodal) system Sinoatrial (SA) node Label on picture Atrioventricular (AV) node Label on picture and define Atrioventricular (AV) bundle Label on picture and define Bundle branches Purkinje fibers Label on picture Pacemaker Heart block Ischemia Fibrillation Tachycardia Bradycardia Systole Diastole Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart murmurs Questions for Review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Look at Figure 11.8: Are the ventricular cardiac cells contracting isometrically or isotonically during the first part of phase 2? 2. What is the function of the intrinsic conduction system of the heart? 3. To which heart chambers do the terms systole and diastole usually apply? 4. What cause the lub-dup sounds heard with a stethoscope? Learning Target: 11-9: Describe the effect of each of the following on heart rate: stimulation by the vagus nerve, exercise, epinephrine, and various ions. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Cardiac output (CO) Heart rate (HR) Stroke volume (SV) Pulmonary edema Questions for review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. What does the term cardiac output mean? 2. What would you expect to happen to the heart rate of an individual with a fever? Why? 3. What is the most important factor affecting stroke volume? Learning Target: 11-10: Compare and contrast the structure and function of arteries, veins, and capillaries. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Vascular system Arteries Arterioles Capillary beds Definition Venules Veins Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa Valves (venous) Microcirculation Vascular shunt Terminal arteriole Postcapillary venule Precapillary sphincter Varicose veins Thrombophlebitis Pulmonary embolism Questions for review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Assume you are viewing a blood vessel under the microscope. It has a large, lopsided lumen, relatively thick tunica externa, and a relatively thin tunica media. Which kind of blood vessel is this? 2. Arteries lack valves, but veins have them. How is this structural difference related to blood pressure? 3. How is the structure of capillaries related to their function in the body? Learning Target: 11-11: Identify the body’s major arteries and veins, and name the body region supplied by each. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Aorta Ascending aorta Label on picture Aortic arch Label on picture Thoracic aorta Label on picture Abdominal aorta Label on picture Right (R) coronary artery Label on picture Left (L) coronary artery Label on picture Brachiocephalic trunk Label on picture R common carotid artery Label on picture R subclavian artery Label on picture L common carotid artery Label on picture L internal carotid Label on picture L external carotid Label on picture L subclavian artery Label on picture Vertebral artery Label on picture Axillary artery Label on picture Brachial artery Label on picture Radial artery Label on picture Ulnar artery Label on picture Celiac trunk Label on picture Superior mesenteric artery Label on picture Renal arteries Label on picture Gonadal arteries Label on picture Inferior mesenteric artery Label on picture Common iliac arteries Label on picture Internal iliac artery Label on picture External iliac artery Label on picture Femoral artery Label on picture Deep artery of the thigh Label on picture Popliteal artery Label on picture Anterior tibial Label on picture artery Posterior tibial artery Label on picture Dorsalis pedis artery Label on picture Arcuate artery Label on picture Superior vena cava Label on picture Inferior vena cava Label on picture Radial veins Label on picture Ulnar veins Label on picture Brachial veins Label on picture Axillary vein Label on picture Cephalic vein Label on picture Basilic vein Label on picture Median cubital vein Label on picture Subclavian vein Label on picture External jugular vein Label on picture Vertebral vein Label on picture Internal jugular vein Label on picture Brachiocephalic veins (R and L) Label on picture Anterior tibial vein Label on picture Posterior tibial vein Label on picture Fibular vein Label on picture Popliteal vein Label on picture Femoral vein Label on picture External iliac vein Label on picture Great saphenous veins Label on picture Dorsal venous arch Label on picture Common iliac vein (R & L) Label on picture External iliac vein Label on picture Internal iliac vein Label on picture R gonadal vein Label on picture L gonadal vein Label on picture Renal vein Label on picture Hepatic portal vein Label on picture Hepatic veins Label on picture Questions for review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Look at Figure 11.12: Assume the capillary bed depicted here is in the biceps brachii muscle of your arm. What condition would the capillary bed be in (a or b) if you were doing push-ups at the gym? 2. In what parts of the body are the femoral, popliteal, and arcuate arteries found? 3. In what part of the body are the axillary, cephalic, and basilic veins located? Learning Target: 11-12: Discuss the unique features of the arterial circulation of the brain, fetal circulation, and hepatic portal circulation. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Internal carotid artery Label on picture Anterior cerebral artery Label on picture Middle cerebral artery Label on picture Vertebral arteries Label on picture Basilar artery Label on picture Posterior cerebral artery Label on picture Cerebral arterial Label on picture circle (circle of Willis) Hepatic portal circulation Hepatic portal vein Label on picture Inferior mesenteric vein Label on picture Splenic vein Label on picture Superior mesenteric vein Label on picture L gastric vein Label on picture Umbilical vein Umbilical artery Ductus venosus Foramen ovale Ductus arteriosus Fossa ovalis Ligamentum arteriosum Questions for Review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Which vessel - the hepatic portal vein, hepatic vein, or hepatic artery - has the highest content of nutrients after a meal? 2. In what two important ways is the pulmonary circulation different from the systemic circulation? 3. What is the ductus venosus, and what is its function? Learning Target: 11-13: Define pulse, and name several pulse points. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Pulse Pressure points Question for review - Answer this question as you read. 1. Which artery is palpated at each location: Wrist Groin Neck Learning Targets: 11-14: Define blood pressure, and list factors affecting and/or determining blood pressure. 11-15: Define hypertension and atherosclerosis, and describe possible health consequences of these conditions. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Blood pressure Atherosclerosis Systolic pressure Diastolic pressure Auscultatory method Peripheral resistance Vasoconstriction Epinephrine Hypotension Orthostatic hypotension Circulatory shock Hypertension (high blood pressure) Primary (essential) hypertension Definition Questions for Review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. How does blood pressure change throughout the systemic circulatory pathway? 2. What is the effect of hemorrhage on blood pressure? Why? Learning Target: 11-16: Describe the exchanges that occur across capillary walls. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Definition Interstitial fluid (tissue fluid) Intercellular clefts Fenestrated capillaries Questions for review - Answer these questions as you read. 1. Look at Figure 11.24: Assume there is a bacterial infection in the interstitial fluid. How would this affect fluid flows across the capillary walls in the area? 2. Would you expect fluid to be entering or leaving the capillaries at the venous end of a capillary bed? Learning Targets: 11-17: Briefly describe the development of the cardiovascular system. 11-18: Name the fetal vascular modifications or “fetal shunts,” and describe their function before birth. 11-19: Describe changes in the cardiovascular system with aging and list several factors that help maintain cardiovascular health. Vocabulary - Define the following terms as you read. Term Coronary artery disease Definition