Uploaded by
luyolo macetyana
Grade 9 EMS: Economic Systems & Circular Flow Lesson Plan
advertisement

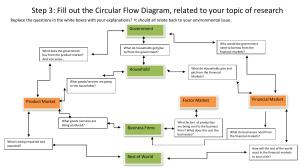
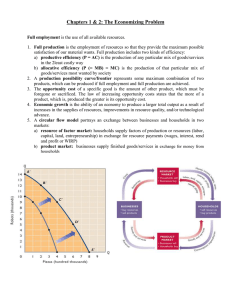
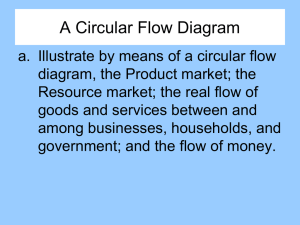
SUBJECT: GRADE: EMS AIMS OF LESSON: RESOURCES 7 9 WEEK: CAPS SECTION: Term 1: Lesson 1 Term 1: Lesson 1 The Economy Learners must be able to understand: 1. Economic systems: namely the planned economy, market economy and mixed economy 2. The characteristics of each economic system 3. The global economy 4. The circular flow: the participants in the circular flow of a closed economy; the flow of goods and services, money and factors of production in the circular flow of a closed economy; and illustrated by using a flow diagram PAPER BASED RESOURCES: • Textbooks DIGITAL RESOURCES: • https://www.thelearningtrust.org/asp-treasure-box • wcedeportal.co.za Prior content knowledge: Needs, services and factors of production Link with the next lesson: Circular flow and price theory By the end of the lesson learners will be able to: • Understand the three major economic systems and the circular flow INTRODUCTION TERMINOLOGY 8 DATE: • • • • • • • • • • • Any terms that appear in the topic that do not form part of the learner's normal vocabulary. Markets Economic systems Capitalism Socialism Traditional system Globalisation Integration Circular flow model Circulation Participants Financial institution • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Expenditure Consumers Producers Exchanged Start-up capital Households Government Businesses Interact Factors of production Goods and services Public goods and services Savings Investments Loans Goods and service market Factor market Labour market Collectively Income Wages Labour Spending Taxes Real flow Rent Profit Introduction • • An economic system is a system that a country chooses to allocate its resources and distribute its goods and resources. The economic problem is how to meet the endless wants and needs of people with limited resources Three economic systems • • • Planned economy Market economy Mixed economy Planned economy CONTENT: CONCEPTS and/or SKILLS An economic system in which government make all the decisions about the production and consumption of goods and services. Characteristics of Planned economy • • • • • • The government owns the land, natural resources, factories and the farms People are not allowed to own property The government decides what should be produced and how it should be sold for Workers don’t have a choice about what they want to do The government gives workers everything they need to live, including their food Examples of countries with planned economies are Cuba, Libya, India, China, North Korea, Iran, Saudi Arabia Market economy An unplanned economy in which land, property and business are owned by private people, not the government. Characteristics of Market economy • • • • • • • Aim of business is to make a profit Entrepreneurs decide what goods and services to produce Businesses and people borrow money from banks Workers can choose what work to do and who they want to work for Consumers, government and businesses spend money on goods and services Workers and businesses make money from producing goods and services The government makes money from taxes Mixed economy A mixture of private and government control of the economy. The government, as well as people and businesses, own the land and natural resources. Characteristics of Mixed economy • • • • Capital comes from banks, shareholders and the government through the spending of taxes Entrepreneurs decide what to produce The government spends taxes on education, housing and clean water South Africa is a mixed economy The global economy: ➢ The term ‘global economy’ refers to how the economies of most of the countries in the world have become interconnected. ➢ The world has virtually become one big marketplace where all countries trade. ➢ This has given rise to the term ‘globalisation’ which means the integration of production and consumption in all markets across the world. ➢ Transport and communication are continually making trade between countries increasingly easier. ➢ In addition to goods and services, labour and capital are now also more mobile and respond to the market forces of demand and supply. ➢ This has affected the prices of products, which have become more equal around the world. ➢ Some people are critical of these new developments. ➢ They believe that they are a means of strengthening capitalism. ➢ They feel that the economies of those countries that prefer to have more state control of production will be affected negatively because capitalist countries will not trade with them. ➢ Some critics say that globalisation takes jobs away from well-paid workers in the wealthy nations and creates sweatshops (large factories where workers work long hours in poor conditions and earn low wages producing goods for international markets) in the poor countries. ➢ Another criticism is that globalisation has impacted on the cultures of many peoples and countries. ➢ International marketing has led to international brands, so people all over the world end up wearing the same clothes, eating the same foods and buying many of the same consumer goods. ➢ Supporters of the global economy say that the free movement of capital stimulates investment in poor nations and creates jobs in them. ➢ It also gives domestic consumers a large number of imported goods to choose from. EXPLANATION OF THE CIRCULAR FLOW The circular flow of money, good and services, and factors of production. Business Government • The business buys goods and services from the government. This is done through the purchase of goods by state-owned businesses, where the business would then pay the government an agreed price. • Businesses pay taxes to the government for the provision of services and infrastructure in the country. Government Businesses • Government buys the goods and services produced by businesses and pays them the agreed price. • The government also collects taxes from businesses which they use to make improvements to the country and supply businesses with services and other infrastructure needed by them and the country. • The government makes investments into businesses which allow them to flourish. The government also offers guidance and legislation to support and help businesses in the country to be ethical and profitable. Households Government • Households own factors of production and sell them to the government. For example, households supply government with labour to work for the government and municipalities in the country, for which the government pays the wages. • Households pay tax to the government for the services and infrastructure they supply. Government Households • The government provides households with goods and services such as infrastructure, education, healthcare, and so on. • Government supplies households with employment and capital in return for factors of production. Households Businesses • Households sell the factors of production they own to businesses who can then convert them into goods and services. • Households buy goods and services from businesses to satisfy their wants and needs and allow businesses to make a profit. • Households supply businesses with labour, i.e. people in the households are the workers in a business. Businesses Households • Businesses sell goods and services to households. • Businesses employ people from households and pay them salaries and wages. Activity 1 Compare the 3 main economic systems by completing the following table: Write in the answer that answers the question to the characteristics. Characteristic Planned economy Market economy Mixed economy Government control Profit Motive Ownership of factors of production Choice of occupation CONSOLIDATION ACTIVITIES Allocation of resource Distribution of output Prices Economic growth Privatization Bureaucracy Interest Decisions Private Enterprise Activity 2 Study the following diagram and answer the questions that follow. A. ______________ C. ___________ HOUSEHOLDS SUBSIDIES GOVERNMENT PUBLIC SERVICES B.__________ TAXES MARKET FOR FACTORS OF PRODUCTION 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Complete the diagram above by writing the letters A to E and the correct answers. (5) Give any two examples of public services provided by the government to households. (2) Write the correct participant for each of the activities below: 1.3.1 ...sells goods and services to other participants. 1.3.2 ...provides labour to the government and businesses. 1.3.3 ...buys factors of production to produce goods and services. 1.3.4 ...receives taxes from the other participants. 1.3.5 ...earns wages from the other participants. (5) Discuss four (4) roles of the government to the businesses in the circular flow in the closed economy. (8) [20] MEMORANDUM OF ACTIVITIES Memorandum: Activity 1 Characteristic Planned economy Government control Central Profit Motive No Ownership of factors of Government production Choice of occupation People are trained and educated according to the needs identified by the government Allocation of resource The government decides what the production targets are and allocates resources accordingly Distribution of output The government distributes not only capital goods but also consumer goods Prices Economic growth Privatization Bureaucracy Market economy No control Yes-the driving force Private Mixed economy Semi-control Yes – the driving force Private People can choose their field of study and level of education People may usually choose their occupation Consumers determine how resources are allocated Government has key industries for the whole economy. Provincial incentive schemes. Market free to operate according to supply and demand. Government has certain license requirements Competition determine prices Consumer and government play a role Privately and publicly owned. Increases scope of the market Very little In a marketplace where goods are exchanged for money Fixed – set by the government Determined by government None Competition checks price Very important because of central planning and centralization Not much because the government’s officials do not play a fundamental role Consumer Privately owned Interest Society Personal Personal, society Decisions Central government Individuals - decentralized Private Enterprise Government is responsible for the production Can produce, buy and sell as much as they like Individual Government The government provided certain services. Others by private individuals Activity 2 1.1 A. Market for goods and services B. Businesses C. Households pay taxes to the government D. Households supply factors of production E. Households buy goods and services 1.2 Water, Electricity, medical, educational, safety and security, soial welfare, etc Any correct two (5) (2) 1.3 1.3.1 Business 1.3.2 Household 1.3.3 Business 1.3.4 Government 1.3.5 Household (5) 1.4 a) Government buy goods and services produced by businesses? b) Government collects taxes from businesses which they use to make improvements in the country and supply businesses with services and infrastructure c) Government makes investments into businesses which allow them to grow d) Government also offers guidance and legislation to support and help businesses (8) [20]