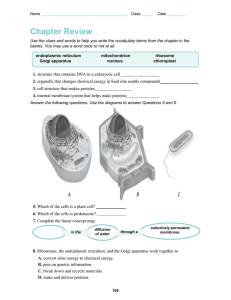
HW 4 1. 1 meter = _____ centimeters. 1,000 1,000,000 1,000,000,000 100 1,000,000,000,000 2. Which of the following choices correctly matches a tool and its proper application? View Available Hint(s) scanning electron microscopy (SEM) to study the detailed movements of living cells light microscopy to study the internal structure of cilia transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to study the movement of organelles within a living cell cell fractionation to study the function of specific organelles transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to study the surfaces of preserved cells 3. _____ are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface. Flagella Fimbriae Mitochondria Ribosomes Cell walls What is a function of a bacterium's capsule? DNA storage propulsion protein synthesis protection The DNA-containing region of this bacterial cell is indicated by the letter _____. Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found? ribosomes nucleus peroxisome nucleoid region capsule In a bacterium, where are proteins synthesized? ribosomes nucleus peroxisome nucleoid region capsule What name is given to the rigid structure, found outside the plasma membrane, that surrounds and supports the bacterial cell? capsule pili cell wall flagella nucleoid region The _____ is the bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to leave the cell. plasma membrane nucleoid region ribosome pili cell wall The structure that regulates the passage of material into and out of this bacterial cell is indicated by the letter _____. 4. Beginning within the nucleus, the first step leading to the synthesis of a polypeptide is _____. translation of an RNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids linking of nucleotides to form a polypeptide removal of introns from RNA and the stitching together of exons transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA translation of a DNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids 5. Which organelle plays a role in intracellular digestion? plasmodesma ribosome Golgi apparatus lysosome chloroplast 6. Mitochondria are found in _____. View Available Hint(s) plant cells only animal cells only plant and animal cells all cells animal cells and prokaryotic cells, but not plant cells 7. Plant cells and animal cells share many of the same structures, but each type of cell also has unique structures. In this activity, you will indicate which cell structures are found only in plant cells, only in animal cells, or in both plant and animal cells. Drag each cell structure to the appropriate bin. If a structure is found in both plant cells and animal cells, drag it to the "both" bin. Nucleus | chloroplast | mitochondrion | golgi apparatus | central vacuole | centriole | cytoskeleton | plasma membrane | cellulose cell wall | endoplasmic reticulum Plant cell only: Animal cell only: Both: Drag the correct description under each cell structure to identify the role it plays in the plant cell. Makes sugar by converting light energy into chemical energy A) B) C) D) E) Regulates cytoplasm composition, creates internal pressure, and stores cell compounds Modifies and packages proteins Strong, protective structure made from cellulose fibrils Houses the genetic information of the cell Produces chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell ___ plant cell wall ___ central vacuole ___ chloroplast ___ mitochondrion ___ golgi apparatus The structure of a chloroplast is closely tied to its function as the site of photosynthesis. Some of the following statements are true for chloroplasts; others are true for mitochondria. Which statements are true for chloroplasts? Select the three that apply. They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy from food molecules to ATP. Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae. They are the sites of reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy. Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. They have membranous sacs called thylakoids that are surrounded by a fluid called stroma. 8. Part A – diagram skip Part B – comparing eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells Lysosome | nucleoid | flagella | mitochondria | plasma membrane | ribosomes | nucleolus Prokaryotic only: Eukaryotic only: Both: Part C – diagram skip 1. In eukaryotic flagella, the fibers that slide past one another due to the activity of dynein proteins are microtubules . 2. Many cell organelles, most notably the nucleus, are anchored by intermediate filaments which are assembled from a diverse class of proteins. 3. Centrosomes are sites where protein dimers assemble into microtubules . 4. The extension of pseudopodia in amoeba is due to the regulated assembly and destruction of microfilaments . 5. The only cytoskeletal fibers not associated with intracellular movement or whole cell locomotion are the intermediate filaments . 6. During muscle contractions, myosin motor proteins move across tracks of microfilaments . 9. Structure: desmosomes | cellulose | plasmodesmata | gap junctions | collagen | tight junctions Pick one: Plant or animal 1) Membrane protein complexes that strengthen the adhesion between adjacent cells, like rivets, to protect against pulling forces 2) Small channels that form across the plasma membranes of adjacent cells; especially important in intercellular communication 3) Membrane proteins that create a watertight seal between cells 4) Small channels between cells that are otherwise surrounded by walls; enable movement of water and solutes between cells 5) A polysaccharide that is used to synthesize cell walls, which protect cells and help maintain their shape 6) Long fibers of protein found in the extracellular matrix that provide structural support for cells ANSWER KEY: 1. 100 cm 2. cell fractionation to study the function of specific organelles 3. a. a. Fimbriae b. b.protection c. c. D d. d. nucleoid region e. e. ribosomes f. f. cell wall g. g. plasma membrane h. h. C 4. transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA 5. lysosome 6. plant and animal cells 7. a. plant cell only: chloroplast, cellulose cell wall, central vacuole animal cell only: centriole both: mitochondrion, ER, cytoskeleton, golgi, nucleus, plasma membrane b. plant cell wall: strong, protective structure made from cellulose fibrils central vacuole: regulates cytoplasm composition, creates internal pressure, and stores cell compounds chloroplast: makes sugar by converting light energy into chemical energy mitochondrion: produces chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell golgi apparatus: modifies and packages proteins c. They are the sites of reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy. They contain the green pigment chlorophyll. They have membranous sacs called thylakoids that are surrounded by a fluid called stroma 8. PART A a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Synthesizes lipids Assembles ribosome Defines cell shape Produces secretory proteins Modifies and sorts proteins Digests proteins Generates ATP PART B Prokaryotic only: nucleoid Eukaryotic only: mitochondria, lysosome, nucleolus Both: ribosomes, flagella, plasma membrane PART C 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Microtubules Intermediate filaments Microtubules Microfilaments Intermediate filaments Microfilaments 9. a. b. c. d. e. f. 1. Desmosomes – animal 2. Gap junctions – animal 3. Tight junctions – animal 4. Plasmodesmata – plant 5. Cellulose – plant 6. Collagen - animal