Name
CHAPTER 12
Class
Date
Mendel and Heredity
SECTION
4 Beyond Mendelian Heredity
KEY IDEAS
As you read this section, keep these questions in mind:
• Are there exceptions to the simple Mendelian pattern of inheritance?
• How do the heredity and the environment interact to influence
phenotype?
• How do linked genes affect chromosome assortment and crossing
over during meiosis?
READING TOOLBOX
Summarize As you
read, write paragraphs to
summarize each of the
exceptions to patterns of
Mendelian inheritance. In
your paragraphs, describe
how each exception differs
from the patterns Mendel
saw in pea plants.
What Are Some Exceptions to Mendelian
Inheritance?
Mendel’s work formed the foundation of hereditary
science. However, scientists have discovered that traits
are not always inherited according to the patterns Mendel
described. In fact, the inheritance of most traits do not
follow Mendel’s rules.
MULTIPLE ALLELES
An individual can have only two alleles for a gene.
However, some genes have multiple alleles. That is, they
have more than two possible alleles. For example, three
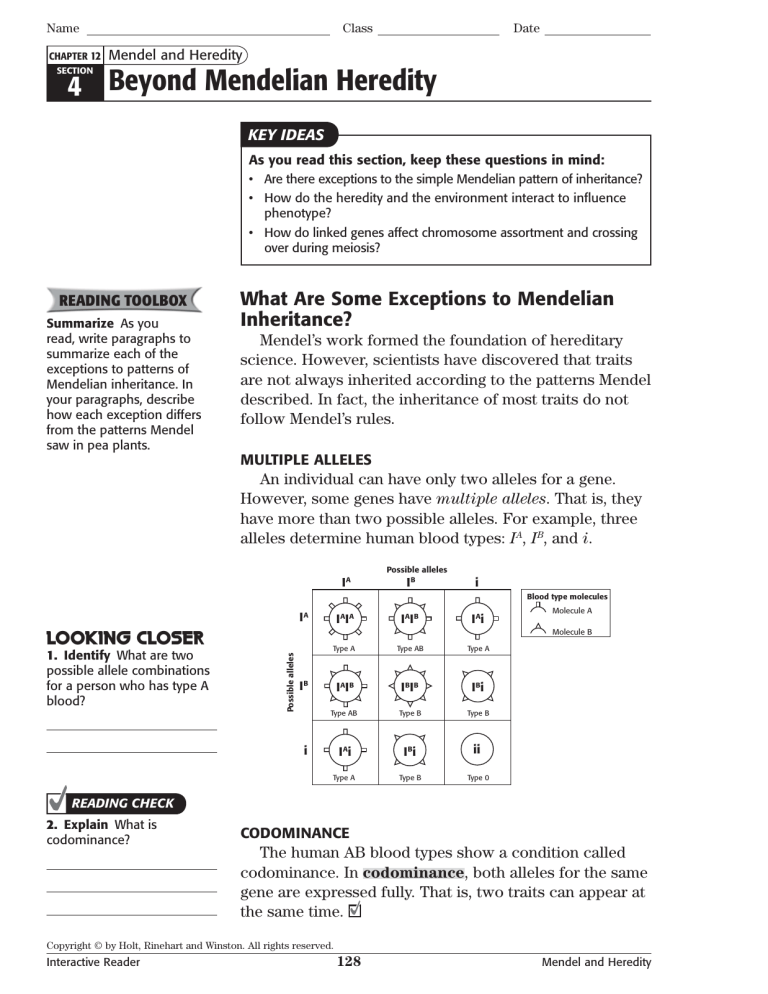
alleles determine human blood types: IA, IB, and i.
Possible alleles
IA
IB
i
Blood type molecules
I
A
I AI B
IAi
Type A
Type AB
Type A
I AI B
IBIB
IBi
Type AB
Type B
Type B
I Ai
IBi
ii
Type A
Type B
Type 0
Molecule A
Molecule B
Possible alleles
EHHDBG@<EHL>K
1. Identify What are two
possible allele combinations
for a person who has type A
blood?
I AI A
IB
i
READING CHECK
2. Explain What is
codominance?
CODOMINANCE
The human AB blood types show a condition called
codominance. In codominance, both alleles for the same
gene are expressed fully. That is, two traits can appear at
the same time.
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Interactive Reader
128
Mendel and Heredity
Name
SECTION 4
Class
Date
Beyond Mendelian Heredity continued
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE
For some characters, the offspring’s trait is
intermediate between the traits of its parents. This
pattern is called incomplete dominance. For example,
in snapdragons, neither allele for color is dominant or
recessive. If you cross a snapdragon that has red flowers
with one that has white flowers, the offspring will have
pink flowers.
POLYGENIC INHERITANCE
Some traits, such as human eye color, are determined
by more than one gene. When several genes affect a
character, it is called a polygenic character. The genes
for a polygenic trait may be on the same chromosome or
a different chromosome. Height and skin color are two
other polygenic characters in humans.
READING CHECK
3. Describe In incomplete
dominance, how does the
offspring’s trait compare to
the traits of the parents?
How Can the Environment Affect a
Character?
A character is not always determined entirely by
genes. An organism’s phenotype can be affected by its
environment. For example, temperature affects the
fur color of Arctic foxes. During summer, genes cause
production of pigments that result in dark fur. During
winter, the genes stop causing production of pigment.
What Are Linked Genes?
Recall that during meiosis, genes on different
chromosomes can be sorted independently. Some genes
are close together on the same chromosome. During
meiosis, these genes are less likely to be separated than
genes that are far apart. Genes that are close together
and the traits they determine are linked. Linked genes
tend to be inherited together.
8g^i^XVa I]^c`^c\
4. Infer How is the effect
of the environment on the
fur color of Arctic foxes an
advantage for the foxes?
READING CHECK
5. Explain Why do linked
genes tend to be inherited
together?
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Interactive Reader
129
Mendel and Heredity
Name
Class
Date
Section 4 Review
SECTION VOCABULARY
codominance a condition in which both alleles
for a gene are fully expressed
linked in genetics, describes two or more genes
that tend to be inherited together
polygenic character describes a character or
pattern of inheritance that is influenced by
more than one gene
1. List What are three exceptions to the Mendelian pattern of one character
controlled by two alleles?
2. Compare How does codominance differ from incomplete dominance?
3. Predict What are the possible genotypes and phenotypes for blood type of an indi-
vidual whose father is IAIB and whose mother is ii? Use a Punnett square to show
these possibilities.
4. Analyze In humans, height may be affected by both heredity and the environment.
If an individual has tall parents, what kind of environmental, or outside, factors
may cause the individual to be short?
5. Explain If two genes are known to be linked, what would you expect to happen to
these genes during meiosis?
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Interactive Reader
130
Mendel and Heredity




