Psychrometry: Properties of Moist Air & Psychrometric Chart
advertisement

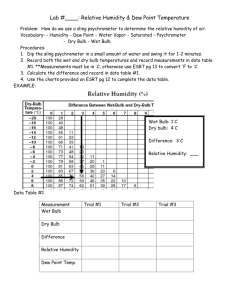
Chapter 3: PSYCHROMETRY Eng. Miral Al-Shraideh Department of Renewable Energy Al al-Bayt University What is Psychrometry Psychrometry is the study of the properties of mixtures of dry air and water vapor. Why study Psychrometry? To be able to analyze various processes involving moist air. Example: if the air is warm and wet, what will be the air-conditioning design required Basic Definitions Dry air The dry air is a complex mixture of several gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases such as argon , carbon monoxide and neon. It does not contain water vaper Moist air The moist air is mechanical mixture of dry air and water vaper. Thus, when the air is cooled, it looses moisture due to condensation of the water vapor in the air Dry Bulb Temperature Dry bulb temperature is the temperature of the moist air as measured by a standard thermometer or other temperature measuring instruments. Wet Bulb Temperature Air temperature measured using a wetted thermometer bulb is known as wet bulb temperate. Relative Humidity The amount of moisture that air holds relative to the maximum amount of moisture the air can hold at the same temperature. Relative humidity is normally expressed as a percentage. When Φ is 100 percent, the air is saturated Humidity Ratio (w) Is the mass of water vapor associated with each kilogram of dry air. the humidity ratio is given by: mv – Mass of vapor ma – Mass of dry air Units – g / kg Dew-Point Temperature he temperature of saturated moist air at the same pressure and humidity ratio of a given air mixture. This is the temperature at which condensation begins when the air is cooled at constant pressure Specific Volume The specific volume is defined as the number of cubic meters of moist air per kilogram of dry air. Unit – m³ /kg of dry air Enthalpy Is equal to the sum of the total enthalpy of dry air and that of the water vapor. Psychrometry Chart A Psychrometric chart is graphical representation thermodynamic properties of moist air. Need two quantities for a state point – Can get all other quantities from a state point of the Example 1 Using the Carrier’s psychrometric chart, Find the wet bulb temperature, humidity ratio, dew point temperature and specific volume of dry air at 24˚C dry bulb temperature and 50% relative humidity. Example 2 The inside design condition of a room is 24 C dry bulb temperature and 60 % relative humidity. Find the following by using Carrier’s Chart 1. Humidity ratio 2. Specific enthalpy 3. Dew point temperature 4. Specific volume of the dry air